Definition: A Statement of Affairs is a financial statement that summarizes the position of assets and liabilities to ascertain the profit or loss for the financial year under the Single Entry System.
It is also known as the ‘Capital Comparison‘ or ‘Net Worth Method‘.
Moreover, this statement is used to calculate the Opening and Closing Capital. For this, we prepare the summary of assets and liabilities at the beginning and at the end. However, any addition or withdrawal of capital needs adjustment.
It is similar to the Balance Sheet prepared in the Double Entry System.
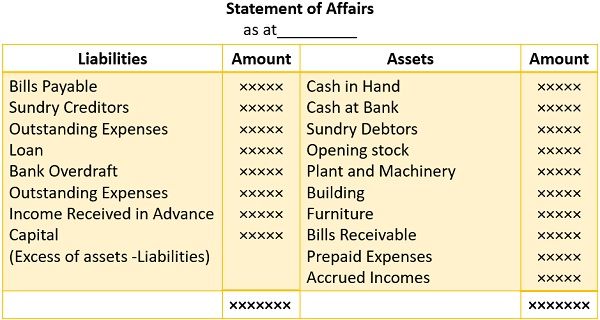
Like a balance sheet, it has two sides, i.e. Assets and Liabilities. In the statement, the assets appear on the right-hand side, whereas the liabilities appear on the left.
But, the accuracy level of the Statement of Affairs is less compared to the Balance Sheet. This is because it retrieves data from incomplete records and estimates.
Content: Statement of Affairs
- Format
- Steps for Computing Profit
- Statement of Affairs in Liquidation
- Difference between Statement of Affairs and Balance Sheet
- Example
- Final Words
Format
Steps for Computing Profit
Companies can follow the steps given below to compute profit using the Statement of Affairs:
Step 1: Determine opening capital for the year. For this, put the opening balance of assets and liabilities in the statement of affairs.
Step 2: Now, calculate the closing capital for the year. Therefore, use the closing balance of assets and liabilities in the statement.
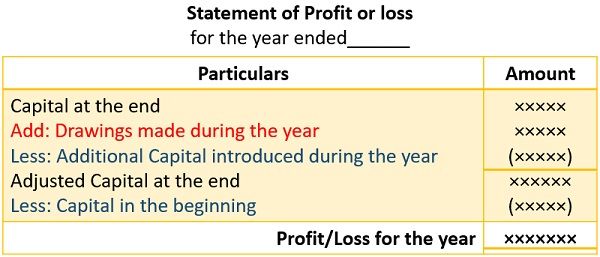
Step 3: After that, prepare a Statement of Profit and find the adjusted closing capital using the formula given below:
Step 4: Lastly, subtract the opening capital from the adjusted closing capital to calculate the profit or loss at the years end.
A company is at profit when the adjusted closing capital is more than the opening capital. Whereas, it suffers loss when opening capital exceeds adjusted closing capital.
Statement of Affairs in Liquidation
Besides the single-entry system, the statement of affairs is also prepared during insolvency. Here, the purpose of preparing this statement is to learn the company’s financial position.
During liquidation, a liquidator prepares the statement of affairs. Also, the companies can appoint a professional for this purpose during proceedings.
It consists of eight lists as follows:
List A – Assets not specifically Pledged
List B – Assets specifically Pledged/ Secured Liabilities
List C – Preferential Liabilities
List D – Debenture Holders
List E – Unsecured Creditors
List F – Preference Shareholders
List G – Equity Shareholders
List H – Deficiency/Shareholders
Points to Remember
- Individual Insolvency
Personal assets will be included in the statement of affairs to settle business liabilities. - Partnership Insolvency
The surplus left after paying off personal liabilities will be included in the statement. The firm will use this surplus to pay business liabilities.
Difference between Statement of Affairs and Balance Sheet
As discussed earlier, this statement is similar to the balance sheet prepared in the double entry system. Yet, it differs from the balance sheet as the data is taken from multiple places other than ledgers.
The chart below explains the difference between both the statements.
| Basis | Statement of Affairs | Balance Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Intent | Find out the profit or loss by calculating opening and closing capital for the accounting period | Ascertain the businesses position at the end of financial year |
| Accounting System | Single Entry System | Double Entry System |
| Accounting Information | It retrieves data from incomplete records | Whereas, it takes information from the ledger balances |
| Reliability | It is less reliable as compared to Balance Sheet because it is prepared from incomplete records | However, the Balance Sheet is reliable as it is based on the double entry system and can be verified |
| Fictitious Assets | Not recorded in the statement | Goodwill and Prepaid Expenses appear on the balance sheet |
| Assets Valuation | Depicts both book and the market value of assets | Here, the accountants only considers the book value of assets |
| Verification | Verification is difficult as it is not prepared from the trail balance | The information can be verified from the trail balance, ledgers, etc |
| Missing Items | Difficult to identify | Easily identified |
| Financial Position | Estimated financial position | Actual financial position of the business |
| Balance | The balance between the assets and liability side is capital | In this statement, assets are almost equal to liabilities; hence it doesn't show any balance |
| Profit Calculation | Profit is calculated using the statement of affairs | Profit and loss accounts compute the profit or loss for the year |
| Records | Incomplete records | Complete records |
Example
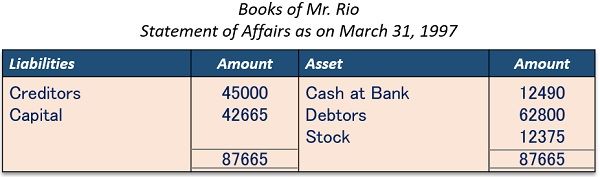
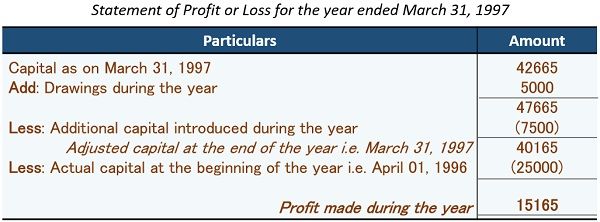
Rio commenced his shirt manufacturing business in 1996 with a capital of ₹ 25000/-. He used to maintain his accounts as per the Single-Entry System.
He introduced additional capital of ₹ 7500/- and made a drawing of ₹ 5000/- during the year.
At the year’s end, the value of his assets and liabilities were:
- Creditors – ₹ 45000/-
- Debtors – ₹ 62800/-
- Stock – ₹ 12375/-
- Cash at bank –₹ 12490/-
Estimate the amount of profit or loss he earned during the year.
Solution:
Statement of Affairs
Statement of Profit
Final Words
To sum up, a Statement of Affairs is one of the methods for finding profit or loss using incomplete records. Also, it is a summary of assets and liabilities under a single-entry system. And the difference between both columns is the capital. Thus, it analyses the amount of change in the capital during the financial year.
Felix Agbenorto says
You have made my day this afternoon. Thanks for the explanation.
John Alidu says
Thanks.