Definition: Financial leverage refers to the utilization of borrowed funds to acquire new assets which are assumed to generate a higher capital gain or income as compared to the cost of borrowing. It is a liability for the borrowing business organization whereas, makes a source of income for the lender.
The three ways in which the company can obtain funds are as follows:
- Debt: Debts are the funds borrowed in the form of bonds, commercial papers and debentures to be paid back to the lender with interest.
- Equity: Equity is the issuing of shares to the public for gathering funds by giving ownership.
- Leases: Lease refers to a legal agreement abiding to which the lessor provides a property to be used by the lessee for the defined period in exchange for money.
Content: Financial Leverage
- Factors
- Measures
- Debt-Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Interest Coverage Ratio
- Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL)
- Example
- Solution
- Benefits
- Limitations
- Conclusion
Factors Affecting Financial Leverage
Financial leverage is more about the borrowings from external sources and needs to be repaid sooner or later. To understand more about financial leverage, let us go through the following factors: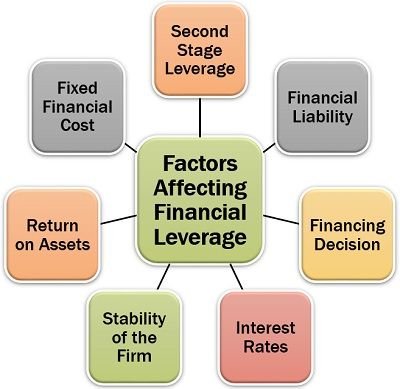
- Second Stage Leverage: The financial leverage is considered as second stage leverage because it is dependant upon the degree of operating leverage. If the operating risk is high, the company will plan for low financial leverage and vice-versa.
- Financial Liability: The borrowings in the form of debts create financial liability on the company.
- Financing Decision: The financial leverage decision is a part of the company’s financing strategy planned by the directors.
- Interest Rates: These borrowings are usually payable with interest which is quite high.
- Stability of the Firm: The most important factor considered by the management while taking the financing decision is the firm’s position and balance, to bear the risk.
- Return on Assets: The returns which the additional capital needs to be estimated to find out whether the company will be able to generate higher profits on the capital employed or not.
- Fixed Financial Cost: The debts create a fixed financial burden in the form of interest over the company.
Measures of Financial Leverage
After employing additional capital into the business, the management uses various financial ratios to the performance of the company. The four most crucial financial leverage ratios or measures are given below:
Debt-Equity Ratio
The debt-equity ratio is the proportion of the funds which the company has borrowed to the fund raised from shareholders. In short, it is the ratio of the borrowings to the owner’s fund.![]()
Analysis: The higher the debt-equity ratio is, the weaker is the financial position of the company. Therefore, this ratio should always be less to avoid the risk of bankruptcy and insolvency.
Debt Ratio
The debt ratio determines the company’s asset position or strength to meet its liabilities.![]()
Analysis: Lower is the debt ratio of the company; the sounder is its financial position, indicating that the company has sufficient assets to pay of the liabilities at the time of downfall.
Interest Coverage Ratio
The interest coverage ratio emphasizes the company’s ability to pay off the interest with the profits earned.![]()
Analysis: If the ratio is high, it signifies that the company can make enough profit to pay the interest due and vice-versa.
Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL)
The degree of financial leverage (DFL) signifies the level of volatility in the earning per share (EPS) with the change in operating income as a result of the capital restructuring, i.e., acquisition of debts, issuing of shares and debentures and leasing out assets.![]()
Where,
Percentage Change in EPS = [(New EPS – Old EPS)/Old EPS]
EPS stands for earning per share
Percentage Change in EBIT = [(New EBIT – Old EBIT)/Old EBIT]
EBIT stands for earnings before interests and taxes
Analysis: A higher DFL indicates that the company is more sensitive to the change in operating income, ultimately showing its unstable earnings per share.
Example
ABC Ltd. expanded its business unit by investing $200000 out of which $50000 was acquired through debts. The company issued 1500 equity shares of $100 each for the remaining amount. The company generates a profit before interests and taxes of $20000 annually. The total assets amounted to $145000, and the liabilities were $75000. The interest payment is $5000.
The previous year’s earning per share (EPS) was $3.5, and in the current financial year, the EPS is $4.8, if the last year’s EBIT is $8000. Find out the related financial leverage ratios.
Solution
Debt Equity Ratio = Total Debt/Shareholder’s Equity
Debt Equity Ratio = 50000/150000
Debt Equity Ratio = 0.33
Debt Ratio = Liabilities / Assets
Debt Ratio = 145000/75000
Debt Ratio = 1.93
Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expenses
Interest Coverage Ratio = 20000/5000
Interest Coverage Ratio = 4
Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL) = Percentage Change in EPS/Percentage Change in EBIT
Percentage Change in EPS = [(New EPS – Old EPS)/Old EPS] ⨯ 100
Percentage Change in EPS = [(4.8 – 3.5)/3.5] ⨯ 100
Percentage Change in EPS = 37%
Percentage Change in EBIT = [(New EBIT – Old EBIT)/Old EBIT] ⨯ 100
Percentage Change in EBIT = [(20000 – 8000)/8000] ⨯ 100
Percentage Change in EBIT = 150%
Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL) = 37/150
Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL) = 0.25
Benefits of Financial Leverage
The financial leverage has various advantages to the company, management, investors and financial companies. The following are some such benefits: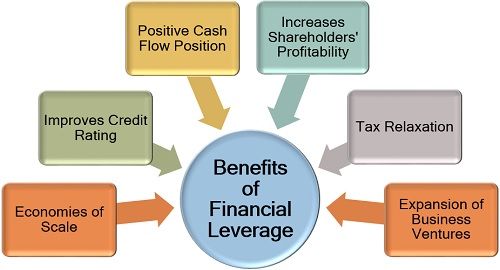
- Economies of Scale: The financial leverage helps the organizations to expand its production unit and manufacture goods on a large scale, reducing the fixed cost drastically.
- Improves Credit Rating: If the company take debts and can pay off these debts on time by generating a good profit from the funds availed, it secures a high credit rating and considered reliable by the lenders.
- Favourable Cash Flow Position: This additional capital provides an opportunity to increase the earning power of the company and hence to improve the cash flow position of the company.
- Increases Shareholders’ Profitability: As the company expands its business through financial leverage, the scope for profitability also increases.
- Tax Relaxation: When the debts and liabilities burden the company, the government allows tax exemptions and benefits to it.
- Expansion of Business Ventures: The need for financial leverage arises when the company plans for growth and development, which is a positive step.
Limitations of Financial Leverage
There are certain drawbacks of the financial leverage which are mainly related to borrowings through debts. These are as follows: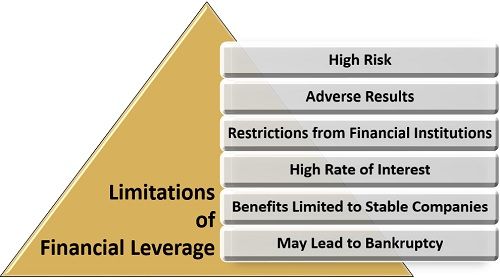
- High Risk: There is always a risk of loss or failure in generating the expected returns along with the burden of paying interest on debts.
- Adverse Results: The outcome of such borrowings may be harmful at times if the business plan goes wrong.
- Restrictions from Financial Institutions: The lending financial institution usually restricts and controls the business operations to some extent.
- High Rate of Interest: The interest rates on the borrowed sum is generally high, which creates a burden on the company.
- Benefits Limited to Stable Companies: The financial leverage is a suitable option for only those companies which are stable and possess a sound financial position.
- May Lead to Bankruptcy: In case of unexpected loss or poor returns and huge debts or liabilities, the company may face the situation of bankruptcy.
Conclusion
A company must be careful while analyzing its financial leverage position because high leverage means high debts. Also, giving ownership may prove to be hazardous for the organization and even result in huge loss and business failure.
Leave a Reply