Definition: Demerger is a powerful strategy and a restructuring technique wherein a company split-off its existing business into separate units to form a new self-operating company.
Usually, it occurs in the case of large conglomerate businesses. Here, companies can split one or more undertakings into separate entities.
Companies use it to reposition themselves and deploy their strengths in the right direction. The division helps them to improve their operations and make the organization easily manageable.
It is alternatively known as Corporate Break-up and Split-offs.
Post-separation, the unit becomes a separate legal entity which can operate, sell or dissolve itself.
The formation of the new company occurs without any sale, purchase or sale transaction. The company that decides to demerge is known as Demerged Company. Whereas, the separate newly formed company is known as the Resulting Company.
During the entire process, the revaluation of assets is ignored. In addition, the stake of shareholders remains unchanged. Also, the existing shareholders are allotted equal shares in the resulting company.
Sometimes, it is also used as a defence against Takeover.
There are four alternatives for demerger as well listed below:
- Liquidation
- Divestitures
- Turnaround
- Retrenchment
Content: Demerger
- Example – Reliance Demerger
- Objective
- How does it work?
- Steps Involved in Demerger
- Types of Demerger
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Bottom Line
Example – Reliance Demerger
On July 2023, Reliance Industries Ltd. (RIL) demerged its financial services arm, i.e. Jio Financial Services Ltd. (JFSL).

They announced the share allocation in the ratio of 1:1. This means that the existing shareholders of Reliance Industries will get equal shares in JSFL.
The reason behind Reliance this strategic move is the significant growth in the Indian Financial Sector. Moreover, this sector still has scope for further growth and profitability. Therefore, RIL wants to tap this growth and become India’s largest NBFC.
Objective
The purpose behind corporate restructuring using demergers is to improve the business’s fit and focus. They achieve this by creating value for shareholders and separating a poor-performing unit.
Given below are several objectives behind conducting a demerger:
- Regain the parent company’s market value that might have resulted from any wrong decision.
- Business management may have lost interest in the non-performing business units.
- To use split-ups as the strategic move against the takeover.
- Ease the overall management by disintegrating some of the units managed separately.
- Restrict competitive information flow to its parents.
- Make the business flexible enough to be open to opportunities.
How does it work?
Today, companies are planning to sell out their non-core business. Some potential reasons for the same are as follows:
- Retain the focus on core competencies.
- Divest components that are not going with strategic objectives.
- Need to sell underperforming assets to generate cash.
It might seem easy, and an attractive option for stakeholders, but split-ups are complex. Therefore, it is essential to take this decision with diligence and expertise.
There is no room for mistakes, so any wrong move can deteriorate the firm’s value.
First of all, the businesses need to conduct a detailed internal analysis. After that, they need to separate components, business or product lines that are no longer part of the core business.
Next, they need to decide and announce the demerger post taking the consent of the stakeholders. The company inform all of its existing shareholders about their share in the resulting company.
The demerged company transfers the unit’s assets and liabilities into the resulting company’s balance sheet. After that, the resulting company get listed on the exchange for trading.
The main challenge in the entire process is the bifurcation of components in a justified manner.
The parent company support its subsidiary in the following ways:
- They invest equity in the freshly generated firm.
- Provide the required incubation space for Chairs, Tables etc.
- Provide services like assistance in technology, legal, finance, etc.
Steps Involved in Demerger
Given below are some generalized steps that one can follow when planning a Split off:
- The parent company recognises and lists all the resulting company’s assets.
- Like assets, they also identify the resulting company’s liabilities.
- Next, demerged company transfers the identified assets and liabilities to the subsidiary’s balance sheet.
- In rare cases, the parent company also pay a premium to subsidiaries. However, tax authorities do not promote this practice. This is because, some organizations attempt to evade tax using premiums.
Modes
There are three modes available for conducting a demerger as follows:
- By way of Agreement
- Under the Scheme of the Agreement
- Voluntary Winding-up
Types of Demerger
Split-ups are of two types, i.e., Complete Demerger and Partial Demerger.
Where the entire business is disintegrated into individual independent units is Complete Demerger. On the contrary, partial demerger is the separation of only some of the non-core units.
Besides, following are the four types of demergers takes place:
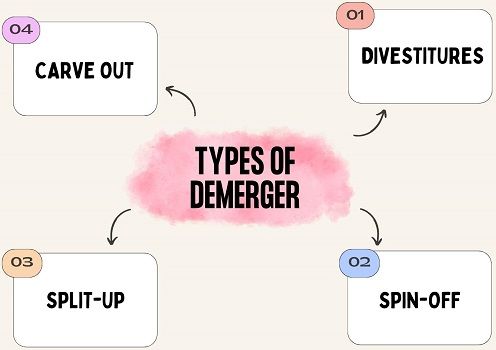
- Sell-off or Divestitures: As its name suggests, it involves divesting or selling off the non-core or non-profitable units.
- Spin-off: It is a type of partial demerger. Here, the newly formed subsidiary and demerged company become separate legal entities.
- Split-up: It comes under the complete demerger. After separating the business into units, the demerged company ceases to exist.
- Equity Carve Out: Here, the demerged company hold some stake in the subsidiary and offers a percentage of equity to the general public through IPO.
Advantages
It benefits businesses by creating value for investors. Furthermore, it helps gain a competitive advantage and makes the company more worthy.
Besides, it is also advantageous for businesses in the following ways:
- The individual parts of the conglomerate are greater than the whole.
- After separation, the businesses can raise more equity funds.
- The demerged or parent company can focus on its core business and competencies.
- It can boost a company’s valuation and provide more incentives to its employees.
- Separate financial statements help in conducting an in-depth analysis.
- It will also reduce internal competition for the allocation of funds.
Disadvantages
The ever-increasing pressure on businesses enables them to take decisions like corporate break-ups. However, there are certain demerits attached to such restructuring techniques listed below:
- Reduce the valuation of either a demerged company or the resulting company.
- Shareholders may sell off the shares of the resulting company due to excitement. As a result, the resulting company’s share price may fall.
- Business leaders face challenges in meeting the stakeholders’ expectations of new business.
- A resulting company might find difficulty in attracting institutional investors.
- Post-separation, small companies have to bear the burden of some mandatory expenses previously shared.
- A business may lose its synergy of being a conglomerate.
Bottom Line
Companies may decide to demerge for a variety of reasons. This decision greatly depends on the company’s long-term vision and strategies. However, the market needs to react in favour of the company post-demerger.
It has certain advantages as well as some major impacts. Therefore, businesses must conduct due analysis and take caution to ensure the subsidiary’s health.
Leave a Reply