Definition: Corporate spinoff refers to the dissolution of a subsidiary business entity from its parent company to form a new though smaller independent organization. The subsidiary company’s shares are majorly allotted to the existing shareholders’, as per their holding (pro-rata basis) in the parent company.
The new entity so formed has an individual identity and acquires assets, employees and other resources from its parent company. It is also separately listed under stock exchange for trading.
Content: Corporate Spinoff
Reasons for Corporate Spinoff
Why do companies need to spinoff? Is it their business strategy?
Some of the prominent ventures go for spinoffs to resolve the following related problems: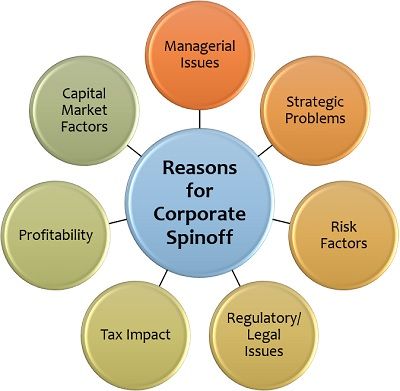
- Managing of a diversified business becomes troublesome because of varying objectives and strategies.
- Due to the changing economic environment, there emerges a need for structural reforms. Also, the individual entity’s potential remains unexplored as a single business unit.
- As a part of a single entity, the business risk of one subsidiary may affect the performance of the other.
- Separating the unregulated companies from the regulated ones is essential to refrain such entities from the burden of legal regulations.
- The parent company have fewer tax benefits from keeping subsidiaries as a consolidated organization.
- As a single business unit, the parent company experiences a lack of profitability or even incurs a loss in the business.
- It is necessary to create better shareholders’ value in the capital market, which usually becomes stagnant due to the company’s stability.
Process of Corporate Spinoff
A company opts for spinoff due to any of the reasons mentioned above. Let us now discuss the steps it takes to separate its subsidiary or division: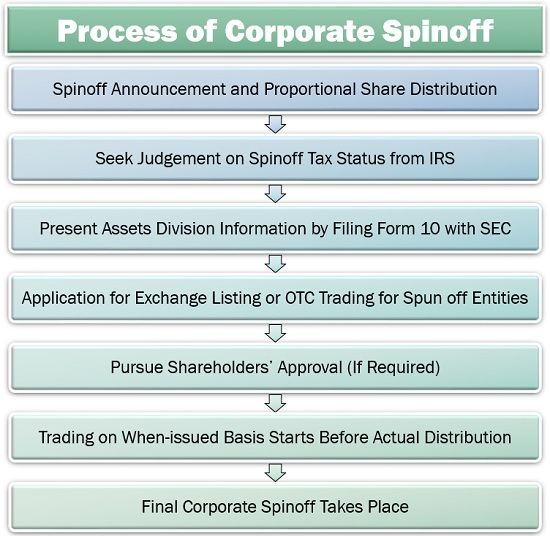
In the initial stage of the process, the company needs to declare its intention of the corporate spinoff. It should specify the proportion in which the distribution of new company’s shares among the existing shareholders, would take place.
Next, the company looks forward to the Internal Revenue Service to get a legal opinion on the spinoff entity’s taxability. It is followed by the filing of SEC’s Form C, containing information like financial statements, spun-off units, company’s value percentage, etc.
The company then decides whether to get the subsidiary listed for stock exchange or plan for Over The Counter (OTC) trading. If required, the parent company may even take the approval of its existing stockholders before spinning off the business.
After getting listed, the company can initiate the ‘when-issued’ basis of trading for the shares of the new subsidiary company. It facilitates the shares exchange, even before they are distributed.
Thus, the market is set for the subsidiary’s shares. The existing shareholders are now allocated the spinoff share units, which they can trade or hold.
Types of Spinoff
The corporate spinoff, as we know, is a strategic activity. Given below are the four ways in which a company can choose to spinoff its division or subsidiary: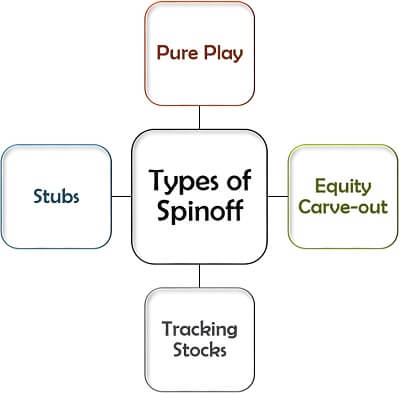
Pure Play
Being one of the purest forms of the corporate spinoff, in pure play, the parent company gives out the shares of the new entity to its existing stockholders as a special dividend.
Equity Carve-out
It is a partial spinoff where the parent company divides the total value of the subsidiary into parts, i.e., 20% and 80%. The 20% shares are issued as an initial public offering to generate capital. Whereas, 80% of the shares are allotted to the existing shareholders as a special dividend.
Tracking Stocks
The primary strategy behind tracking stock is to benefit from the parent company’s enhanced share price. Here, the company separates its subsidiary physically but not legally in terms of assets and liabilities.
Though the financial analysis and reporting of a subsidiary company are done individually, the management lies with the parent company itself (i.e., the same Board of Directors).
Stubs
The stub is the valuation of the parent company remaining after the corporate spinoff. On deducting the subsidiary’s share value from the company’s total share value, we get stub.
Advantages of Corporate Spinoff
It has been observed that many companies have saved themselves from loss, and some have even increased their profits remarkably; only through a spinoff. Let us understand the various benefits of the spinoff in detail below: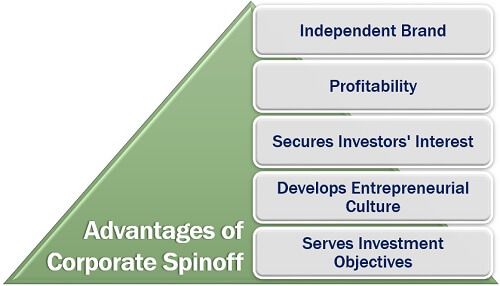
- Independent Brand: Spinoff helps the company to develop the subsidiary under a separate corporate identity.
- Profitability: As identified, the spun-off company grows impeccably, since it focuses on the core business model along with attracting new shareholders.
- Secures Investors’ Interest: Seeing the growth opportunity and potential, institutional investors show high interest in the spun-off stock.
- Develops Entrepreneurial Culture: The employees, when moved to a new entity, seek opportunities to explore their creativity and innovation, for empowerment.
- Serves Investment Objectives: The existing and prospective investors see great potential as they can view the subsidiary’s business independent from that of the parent company.
Disadvantages of Corporate Spinoff
A company creates a new entity by utilizing its resources such as finance, personnel, assets, etc. Thus, it may prove to be unfavourable, to the company as well as its employees in the following ways: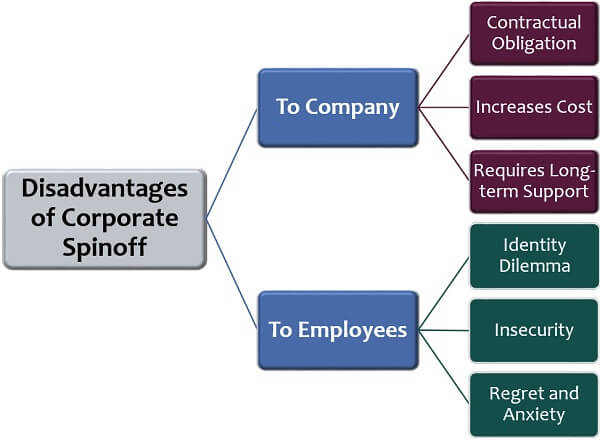
To the Company
A corporate spinoff is a beneficial approach for well-established companies. However, it has the following limitations for the organizations:
- Contractual Obligation: A company is abided to various contracts such as vendor contract, partnership deed, loan agreement, support agreement, etc. Thus, it has to get all these contracts revised to mention the spinoff.
- Increases Cost: Spinoff also adversely affect the cost structure of the company by escalating the fixed costs such as insurance, rent, maintenance and property tax.
- Requires Long-term Support: A SpinCo has been flourished under the facility of the parent company, before the spinoff. But as an independent entity, it requires much more managerial, operational, marketing and accounting backup.
To the Employees
The employees who have been working for the parent company for years are moved to the subsidiary now. They may take spinoff negatively due to the following reasons:
- Identity Dilemma: The employees see SpinCo as a small company and may consider it as their demotion. Such thoughts lead to the unmotivated and underperforming workforce.
- Insecurity: They usually view the new entity to be highly insecure as everything starts with a scratch, doubting the future a SpinCo.
- Regret and Anxiety: They feel dissatisfied and concerned about their role and responsibilities in the new environment.
Example of Spinoff
One of the prominent companies in the sector of C2C and B2C e-commerce is eBay Inc. The company had spun off its money transfer business entity, Paypal in the year 2014.
The reason behind this corporate spinoff was that Paypal had higher growth potential and the competitors like Apple Pay were ready to acquire its market. Thus, eBay sensed this competitiveness and separated the subsidiary to enhance its value and scope.
Mohsen says
Hi, I need to know more about spinoff. Especially how I can evaluate a sub for spinoff and how can I evaluate my spinoff effectiveness?
Thanks