Definition: Operations strategy is an essential part of the overall corporate strategy that specifies plans and policies to reconcile market requirements and operational resources.
It is vital for long-term strategic success and to remain competitive in the market. This is because, without a good strategy, companies may lose their market share to competitors.
It creates the best plan for the operations functions to optimize the use of the resources. Besides, it plays a crucial role in implementing pre-devised business strategies.

After setting up a business enterprise, managing it becomes a difficult task. Complexity arises due to the involvement of several dimensions, which are dynamic.
Companies create various strategies for vital aspects of the business to simplify things. Thus, they make three types of strategies listed below:
- Corporate Strategy
- Business Strategy
- Operations Strategy
Corporate strategy is nothing but the overall strategy about what the business is. Secondly, business strategy concerns the product, market, competition, etc. And, operations strategy ensures the successful implementation of a business strategy by managing operational resources.
Content: Operations Strategy
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Examples of Operational Strategy
- Operation Strategy Matrix
- Framework
- Decisions
- Components or Elements
- Relationship between Business Strategy and Operations Strategy
- Final Words
What is Operations Strategy?
It specifies the design of the deployment of resources across the company. If we break the key phrase into two, we get two solid terms, ‘Operations‘ & ‘Strategy’.
Here, Operations stand for that part of the company which involves everything from creation to delivery of products and services.
Strategy is the set of plans and policies heavily focused on achieving something. Strategies also answer two vital questions:
Where to go?
How to go?
Besides, you may get confused between operations management and strategy. There is a significant difference between both of them.
Operations management is concerned with day-to-day activities that are for the short term. And, strategies are for the long-term and effective implementation of the company’s business strategy.
Examples of Operational Strategy
It is observed that successful and competitive companies do have a robust operational strategy. We have taken the examples of some top-performing companies – IKEA and Toyota.
IKEA

It is famous for its excellent operational efficiency. They offer modern furniture, most of which is produced in-house.
IKEA made a fantastic strategy of merging retail facilities and warehouses. As a result, they registered a significant reduction in storage and distribution costs.
Toyota

Another example of a company for attaining a high degree of efficiency in operations at a global scale is Toyota. Some crucial aspects on which they have achieved expertise are:
- Toyota Production System
- Re-engineering
- Superior Technology & Quality
- Hybrid Vehicles
- Employee Welfare Costs
- Employee Satisfaction
Operation Strategy Matrix
It is a tool for assessing the significant factors affecting company operations. Also, it helps take strategic decisions and reduce risk.
This matrix intersects the company’s performance objectives with the decision area.
The strategic decisions taken based on the matrix are concerned with the following:
- Capacity
- Supply Network
- Process Technology
- Development and Organization
Furthermore, the above decisions are taken considering factors like:
- Cost
- Quality
- Speed
- Dependability
Framework
It encompasses all practices and processes working towards fulfilling its organizational objectives.
The framework consists of four views for the overall business strategy. Managers can hold all four views simultaneously or stick to a single view of strategies.
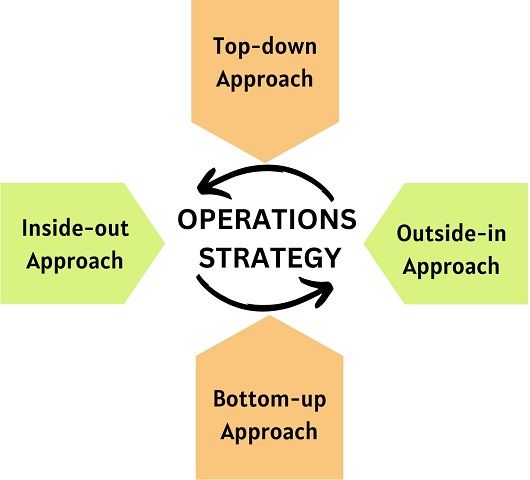
- Top-down Approach: It expresses the entire organisation or group’s desires, goals and beliefs.
- Bottom-up Approach: The strategy is based on the cumulative experience while moving upwards.
- Inside-out Approach: It disintegrates marketing decisions into operations decisions.
- Outside-in Approach: It explores the capabilities of resources in chosen markets.
Decisions
The main objective behind strategizing operations is to improve the function’s performance. It determines the optimum flow of operations by creating some decision areas explained below.
- Capacity Strategy: It determines the facility’s capacity and installed equipment configuration. Some critical decisions are as follows:
- Overall capacity level
- Facility location distribution
- Size of the facility
- Supply Network Strategy: It handles the relationship and dependency between various operations. This strategy largely depends on the type of market, customer or suppliers the company serves.
- Process Technology Strategy: These decisions involve selecting equipment types and production procedures. Majorly, it includes decisions like the latest technology to be used for production.
- Human Resource Decisions: Such decisions are related to human resource selection, organization and development. Also, the roles and mix of skills they should provide to contribute to the management of the operation.
- Inventory Strategy: This involves decisions about the storage of inventory and its location. Also, what should be the sourcing policies and the material control system to be used.
- Planning and Control Strategy: It relates to how the operations should plan its future activities. Besides, the company also decide the allocation of resources to meet its demand expectations.
- Development and Organization: Such decisions ensure optimization in day-to-day operations.
Components or Elements of Operations Strategy
The company uses this strategy to allocate resources to carry out business goals. However, they must keep the following essential elements in mind while strategizing:
- Production System: It is responsible for converting resources into finished goods. Companies must have a system with a clear workflow and top-class supply chain management.
- Facilities: To function correctly, companies must manage all the production facilities. These facilities must be equipped with safety procedures, inventory management, etc.
- Product or Services: Companies focus on creating and maintaining the quality of their products and services. They also read and analyze the product’s life cycle to formulate strategies.
- Technology: The future operational plans must also consider the latest and upcoming technology trends. For this purpose, companies make use of market forecasting tools.
- Resources: A dotting operations strategy considers all the available resources in the organization.
Relationship between Business Strategy and Operations Strategy
Business strategy is the base for operations strategy. However, both of them are interdependent. It requires the operation to work appropriately to fulfil the goals set in the business strategy. Companies can only ensure this through the successful implementation of an operational strategy.
Final Words
This strategy manages the resources and processes to outperform business activities in the long run. It includes all the activities from production to distribution.
There are many best ways to formulate a strategy. Companies often debate whether the strategy should be:
- Internal
- Resource-based
- Fully external
- Market-driven
Some companies may combine both internal and external considerations. Also, they tend to innovate by intelligently formulating strategies about technology and demand.
Leave a Reply