Definition: Capacity Planning is a systematic approach to determine the production capacity required to satisfy current and future business requirements. In operations management, it deals with the planning and control of capacity in production units.
The production process is made up of several components that possess some kind of capacity. Thus, organizations strategically plan their production process considering their capacity.
Capacity planning is vital because the resources are finite and bear some cost. Therefore, we can also call it a Resource Management Exercise.
It ensures that the companies’ resources are capable of meeting the demands. These resources may include:
- Employees
- Materials
- Equipment
- Operations
It is the first level of planning which aims to match the level of operation with demand. It involves crucial decision-making about capital-intensive resources.
Capacity planning helps in determining:
How much capacity is needed?
When is this capacity required?
What kind of capacity is needed?
When to increase the capacity?
However, it’s hard to assess the fluctuations in demand due to economic and non-economic factors. Besides, the installed capacity cannot be altered frequently.
The excess capacity depicts the underutilization of resources. In contrast, the lower capacity may not meet the demand requirements.
Capacity planning is also significant in the fields like IT and Business Computing.
Content: Capacity Planning
- What is Capacity?
- Goal
- Formula
- Importance
- Types
- Strategies
- Decisions
- Factors Affecting
- Benefits
- Steps
- Template
- Example
- Final Words
What is Capacity?
In general, the capacity of anything is its ability to produce and deliver. In the case of facilities, it is the volume of output produced within a time frame.
The capacity within a facility may include:
- Units produced by the equipment.
- Location for the installation of the facility.
- Employee’s skills and ability to effectively perform the task.
Goal
Organization conduct capacity planning with the goal of satisfying distinct demand levels. Besides, the capacity planner optimizes operations to minimize wastage.
To satisfy this goal, the organization manages its three Ps:
- People
- Plant
- Processes
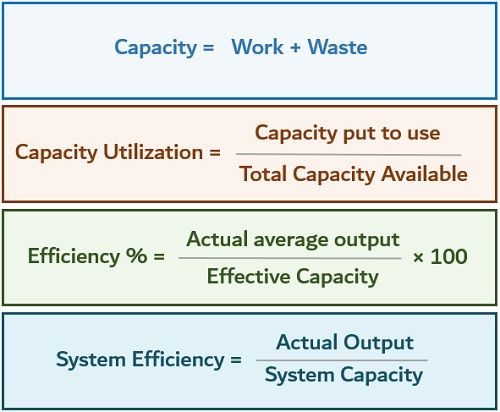
Formula
The attached image depicts formulas regarding capacity calculation.
Importance
Organizations try to achieve such capacity that can meet customers’ demands and increase profitability. The points given below explain its importance in Production and Operations Management.
- Cost Management: It affects the economic aspects of the operations. As producing more than the requirement is an unnecessary increment in cost.
- Income: There exists a direct relationship between income and capacity. As less production means fewer sales, further it results in a reduction in sale receipts.
- Quality of Operations: It plays an important part in maintaining quality in operations. So, the under and over-utilization of the capacity have adverse impacts on the processes.
- Resource Management: The organization ensures resource availability by planning and controlling the facility’s capacity. Consequently, it keeps them prepared to meet expected and unexpected demands.
- Capital Expenditures: It facilitates decision-making regarding capital expenditures. Also, it justifies these expenditures in favour of the business.
- Deployment System: It helps develop a clearly defined procurement and deployment system. This system enables resource management as per the requirement.
Types
There are different forms of capacity planning which are classified based on:
- Time Horizon
- Resources
Based on Time Horizon
- Long-term Capacity Planning: Here, the planning period ranges between 2 to 5 years. It is focused towards capital budgeting and projected growth. It does not work on the known demand but uses forecasted demand for planning.
- Medium-term capacity planning: The medium-term planning horizon ranges around one year. It mainly focuses on creating a balance between demand and supply. Thus, the major decision includes demand and supply adjustments to fulfil current requirements.
- Short-term capacity planning: In the short term, the time horizon is between one week to three months. It focuses on maximizing availability and efficient use of resources.
Based on Resources
- Product Capacity Planning: Here, the managers ensure the sufficiency of the products to satisfy the ever-changing demand. Besides, the volume of production may vary with the demand.
- Workforce Capacity Planning: The prime focus of ascertaining workforce capability to match the workload. It includes both the existing as well as future workload requirements.
- Tools Capacity Planning: Here, the manager checks the availability and requirements of the equipment needed to carry out production. Also, it considers the useful life of the equipment.
Strategies
Managers can apply the strategies discussed below to deal with dynamic demand. These are also called the methods of capacity planning.
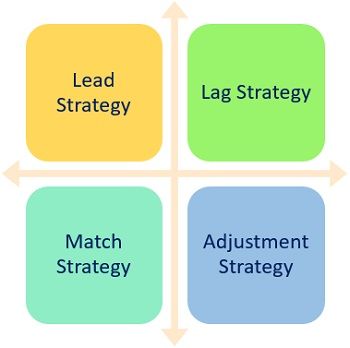
- Lead Strategy: In this strategy, the organization increases its capacity to meet the expected increase in demand. Besides, it improves its quality of services to attract customers.
- Lag Strategy: It is the complete opposite of the Lead Strategy. We will install extra capacity only when the current capacity is over-utilized.
- Match Strategy: Here, we need to match up the capacity and demand. Thus, the organization’s capacity increases with the increase in demand and vice-versa. However, it takes place in small sections.
- Adjustment Strategy: In an adjustment strategy, the addition or reduction of capacity occurs due to changes in:
- Customer Demand
- Changes in Products
- System Design
Major Capacity Planning Decisions
- Assessment: It involves the assessment of the existing facilities of the plant.
- Forecasting: Estimating the capacity requirements for the future.
- Identifying Sources: Finding the sources of capacity for future needs.
- Alternative Sources: Keep alternative sources ready considering financial, economic and technological changes.
- Strategic Selection
Selecting the alternative that is most suitable to attain the objectives.
Factors Affecting Capacity Planning
The factors that impact the planning process are as follows:
Controllable Factors
- Number of Workforces
- Equipment and Tools
- Schedules
- Productivity
- Facility layout
Less-controllable Factors
- Workers Performance
- Break-down, Failure and Faults
- Mishaps
- Natural Calamities
Benefits
It benefits organizations in the following ways:
- Waste Minimization
- Fewer Stockouts
- Better Services
- Less Ideal Time
- Optimum Resources Utilization
Steps of Capacity Planning
One can follow three simple steps while conducting capacity planning for organizations:
Step 1: Measure demand and capacity
The first step is to measure the aggregate demand against existing capacity. The capacity is to be assessed regarding labour, facility, equipment, etc.
Step 2: Alternative capacity plans
Next, figure out alternative plans to satisfy the demand. Also, find out whether to add or reduce the capacity.
Step 3: Select the suitable plan
At last, choose the most suitable plan to satisfy the demand. In addition, forecast future requirements and get prepared beforehand.
Tools
In this digital era, all business practices are taking place over software. Thus, there are many tools available to conduct capacity planning.
The managers can make use of the Project Management Software for planning. In addition, they can get Custom-made Software, especially for this purpose.
Besides software, the managers can also use analytical tools like:
- Break-even Analysis
- Decision Tree Analysis
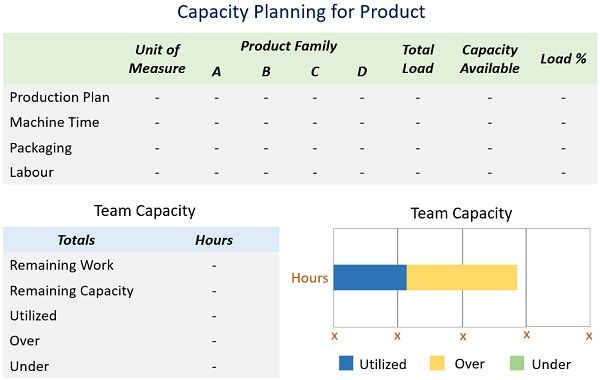
Capacity Planning Template
Example
A Bottle manufacturer is planning to increase its capacity to meet the demand in the market. Therefore, he decided to buy a new machine that could manufacture 20,000 bottles per year. The design efficiency of the product is 50%.
Find out the required Design Capacity.
Solution:
Design Capacity = Actual output per year/Design efficiency
= 20000/0.50 = 40,000
Thus, the required design capacity is 40,000 bottles per year.
Final Words
It is a systematic approach directed toward matching resources with the anticipated demand levels. This is because it is essential for the firm’s survival.
So, organizations prepare a plan to deal with demand fluctuations. To meet demand effectively, managers check the capacity of their Personnel, Products and Processes.
Leave a Reply