Definition: A Production System implies the set-up consisting of assets such as facilities, machines and equipment that transform resources into valuable output using processes and technology.
In other words, we can understand it as a system that converts factor inputs into outputs which is capable of satisfying the market demand.
Majorly, it focuses on the system aspect of the production/operations function. It is a combination of three significant components given below:
- Input (Capital, Machines, Equipment & Tools, Labour)
- Conversion Process
- Output (Goods and Services)
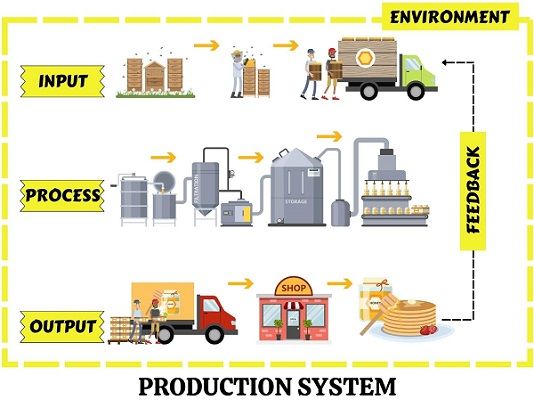
Production implies the transformation of several Inputs into Outputs, i.e., the Product.
A system is a mechanism consisting of a set of things working together.
Companies use production systems to cater for the demand of their target market. However, the requirements of the customers keep varying with time. Therefore, the requirement of the production also changes accordingly.
The production system depends on the type of products offered by the company. In addition, it is also affected by the strategies adopted to meet distinct customer needs.
The companies need to take some crucial decisions in this regard:
- Choice of the technology to be used for production.
- The capacity of the production systems.
- Production volume as per market demand.
The entire system operates in an environment. Some factors from the internal and external environment affect the production process. Thus, companies consistently take feedback and make suitable adjustments in the production system.
The system may even fail if the production processes do not generate the desired output.
Content: Production System
Production System Types
The type of production system depends upon the type and volume of output. Besides, it differs across industries and target consumer markets.
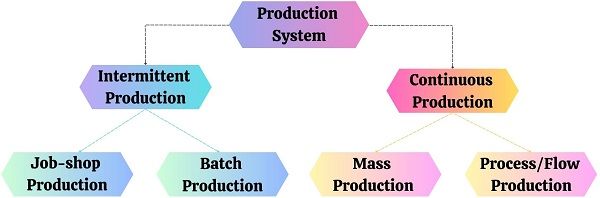
The major determinants that aid the selection of a production system are:
- Volume: It indicates the average quantity of goods for production.
- Variety: It is the product variants, alternatives and range for production.
- Flow: It indicates the nature and intensity of the production process.
Broadly, the production system is classified into two categories as follows:
- Intermittent Production
- Job-shop Production
- Batch Production
- Continuous Production
- Mass Production
- Process/Flow Production
1. Intermittent Production
It is a type of production system where the production flow is intermittent or irregular. It means the production process begins and stops at irregular intervals.
Here the production is carried out based on the customer orders, i.e. Make-to-order. Consequently, the producer can customize their products as per the orders received.
Each time the jobs and route are changed depending on the order received. Therefore, the producer needs to install general-purpose production equipment.
Features of Intermittent Production
- Order-based production of goods.
- Production on a smaller scale.
- Flexibility in production.
- Production of a greater variety of products.
a. Job-shop Production
Job-shop production or Unit Production facilitates the manufacturing of customized products. Here, the production of one or a few products takes place. Moreover, it is completely based on the user specifications and within a stipulated period and cost.
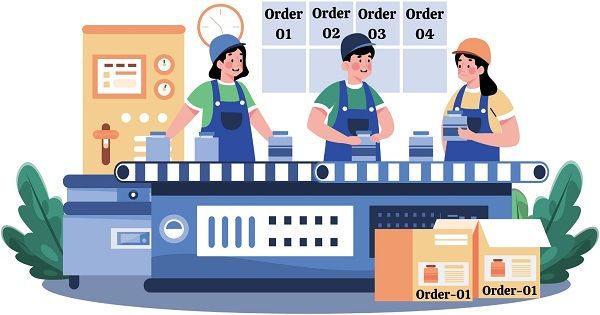
Each task has a different set of technical requirements because of personalization. For this reason, the jobs and demand are both unpredictable.
Also Read: Job Costing
Advantages
- A wide variety of products can be offered to customers.
- The workers are more skilled in comparison to other systems.
- Ease in management due to limited resources and workers.
- Flexibility in process and creative methods to generate unique output.
Disadvantages
The cost of production is high due to small-scale production.
- The higher lead time of the system.
- Under-utilization of equipment.
- Requirement of highly skilled labours.
b. Batch production
This production system is more than a unit production but less than mass production. Here, the production happens in lots and batches at regular intervals.

The batch contains a limited number of similar products manufactured simultaneously.
The product is disintegrated in the form of Jobs. Further, the whole batch passes through these jobs one at a time. The production of the next batch begins post-completion of the ongoing batch.
Also Read: Batch Costing
Advantages
- Usage general-purpose machines.
- Risk can be substituted among Batches.
- Better resource utilization.
- Per-unit cost is lesser in comparison to unit production.
Disadvantages
- It requires specific fixtures.
- High cost in sourcing materials.
- High work-in-progress inventory.
- More lead time due to changes in set-up.
2. Continuous Production
Here, the production occurs continuously with a consistent supply of materials. In other words, the products are constantly in motion.
Unlike intermittent production, there are no frequent halts. The production is carried out on a large scale. The companies maintain the inventory as per demand forecasts.
Identical goods are produced due to product standardization and bulk production.
Features of Continuous Production
- Complete utilization of equipment and raw materials.
- Production at large scale.
- Per-unit cost is less due to bulk production.
- Less lead time as the set-up is required only at the beginning.
- Highly automated and capital-intensive system.
a. Mass Production
Companies use it for carrying out production in very large quantities. It involves the manufacturing of discrete parts, popularly known as Assemblies. Here, the companies adopt a Make-to-stock business strategy.

The flow of this production system is constant and continuous. And, the facility arrangement is in line or per product layout.
Advantages
- The cycle time is comparatively less.
- Automation of material handling.
- Low work in progress.
- The cost of production is low.
Disadvantages
- Default at one place may stop the entire production.
- Line layout needs changes with the change in product design.
- High capital investments.
b. Flow Production
As the name suggests, the flow of production is uniform and standardized. All the processes are arranged sequentially, and all the products pass through them.
This production system is rigid. Companies stock the products and use them to fulfil the quick demand of the market.
Advantages
- Less amount of wastage.
- Semi-skilled can also be employed.
- Higher profit margins.
- The process flow is constant.
Disadvantages
- Less flexible to increase or decrease the number of processes.
- Restrictions on product differentiation.
- Incapable of fulfilling individual demand.
Characteristics of Production System
The varied characteristics and importance of production systems are as follows:
- Organized Activity: The production system is an organized activity. As all the activities or processes within the system are defined and run for a specific purpose.
- Transformation: This system’s main work is converting Inputs into Outputs.
- Coordination: Here, every part of the system is well coordinated. The absence of coordination may lead to system failure and losses.
- Control: It is a crucial function of this system. This is because, review and maintenance of the system are required for its healthy functioning and productivity.
- Value Addition: Through this process, manufacturers add value to the inputs. Consequently, the output generated serves the needs of the consumers.
Example of Production System
Nestle
It is a multinational food and beverages corporation having headquarters in Switzerland. Some of its bestselling products are – Nescafe, Kitkat and Maggi.
It uses Batch Production as its type of production system.
Ford Motor
It is an America-based multinational automobile manufacturer. Ford’s SUV is one of its best-selling cars, making it America’s best SUV brand.
It uses Moving Assembly Line as its production system.
Difference between Intermittent and Continuous Production
The table below clearly differentiates between Intermittent and Continuous production systems:
| Basis | Intermittent Production System | Continuous Production System |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | More Flexible | Less Flexible |
| Lead Time | The lead time is more as it requires a frequent change in set-up | Here, lead time is less; once set, it doesn't require changes |
| Wastage | More amount of waste is generated | Less amount of waste is generated |
| Product | Variety of products in less quantity | Identical product in large quantity |
| Cost per unit of Product | The price is high due to the customization | Cost is low due to standardization and bulk production |
FAQ
Q. What are Production Management Systems?
Ans: It is basically a computerized system designed specially to ensure the efficiency and control of the production systems. It is a data-driven system that sources information from departments like Production and Sales.
Q. What are the two main production systems?
Ans: The production system is classified into two primary types as follows:
- Continuous Production System
- Intermittent Production System
Q. Which production system is flexible?
Ans: The intermittent production system is flexible in nature. This is because, the product type, size and design can be altered as required.
Leave a Reply