Businesses need to make many strategic decisions to survive in the ever-changing environment. Strategic management helps businesses create a stronghold in the competitive market. One of the tools of strategic management is Business-level Strategy.

In other words, these are the specific yet integrated set of actions businesses choose as a strategy to secure competitive advantage.
Customers are the centre of business-level strategies. All the actions are directed towards creating value and satisfying the target customers.
Organizations secure competitive advantage by using their core competencies in product markets. These competencies align with target customers’ needs and want to achieve business goals.
They concentrate on specific elements that can increase market share along with profitability. For example, organizations can decide between creating a unique product or batch production.
It is an effective strategy for small-scale businesses having a single product line. Moreover, organizations with multiple businesses or product lines need a separate strategy for each business unit. It helps identify and understand customer needs and pitch them better than competitors.
Economist Michael Porter has given some strategies to position business in the industry. These strategies are discussed in the upcoming sections of this post.
Content: Business-level Strategy
Examples of Business-level Strategy
Starbucks
It is the world’s largest coffee house chain and a leader in its industry. It formed a value-based business strategy, specialising in marketing and retailing fronts.
Starbucks differentiated itself by offering premium-quality coffee and freshly made food items. They provide an exclusive experience and a unique atmosphere to the customers. Also, they provide personalized services to each of its customers.
Tesla
It is a great example of a business-level strategy. They identified a niche market of expensive high-end electric cars. They have adopted a focused differentiation strategy from the generic business-level strategies.
Types of Business-level Strategy
Porter suggested some models and strategies to build a dependable position against competitors. The most popular and effective ones are as follows:
- Potter Five Forces Model
- Generic Business Strategies
Potter Five Forces Model
The competitive environment has a strong influence on the business strategies. As per Michael Porter, competitive analysis can be performed based on five areas or forces of the overall market. Each force creates significant pressure in the market or industry.
It clarifies the actual state of competition, industry structure and opportunities. After analysis, a company get clarity about its strengths, weaknesses and industry attractiveness.
The five forces that influence the industry are as follows:
- Threat of New Entrants
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Rivalry Among Existing Firms
- Threats of Substitutes
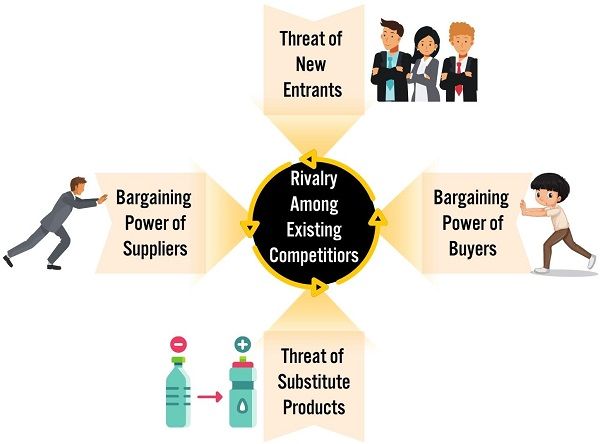
1. Threat of New Entrants
They increase competition by increasing the product supply. Also, they may launch products at reduced prices with more features. As a result, it affects the business’s profitability and market share.
2. Bargaining Power of Buyers
This force affects business when the buyers form groups or cartels. They put pressure on producers to reduce the cost or provide better services. It is mostly seen in the case of industrial products.
Usually, this situation arises when a buyer has:
- In-depth knowledge about the product and its substitutes.
- Buy products in lots and spend significantly on industrial products.
- They can easily switch between the available substitutes.
3. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Like buyers, suppliers can pressure businesses by using their bargaining power. The suppliers limited in number can have greater control. The pressure from suppliers can impact the costs of inputs like raw materials and profitability.
4. Rivalry Among Existing Firms
When multiple players exist in an industry, rivalry between them is natural. It greatly impacts the strategic decisions of each player within the industry. Moreover, it affects more at the functional level.
During the analysis, the businesses focus on the intensity of the existing rivalry. It influences factors like suppliers’ cost, distribution, customers’ attractiveness and profitability.
5. Threats of Substitutes
Another force that puts competitive pressure on the industry is the substitute products. Substitute products increase competition with price advantage or product advancement.
Customers easily switch to substitutes available in the market. Thus, businesses must keenly analyze existing substitutes to ascertain profitability.
Generic Business-level Strategies
Michael Porter has given some generic strategies that suit all kinds of businesses. These strategies are applied to business operations aiming to develop a dependable long-term position and remain competitive.
Businesses can outperform their competitors by gaining a competitive advantage using three strategies:
- Cost Leadership
- Differentiation
- Focus
The matrix below depicts the strategies and their interdependence on each other regarding competitive scope and advantage.
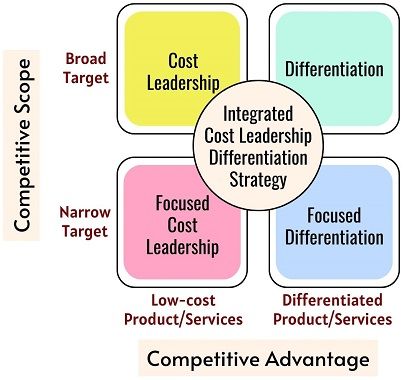
1. Cost Leadership Strategy
It is a strategy that aims to become the industry’s lowest-cost producer. Cost leaders can control costs and offer products or services at low prices while maintaining quality. Consequently, businesses can enjoy operational efficiency and economies of scale at competitive prices.
Suitability: It is effective in the case of price-sensitive customers. Also, when there is less possibility for creating a significantly differentiated product. And, the industry has many buyers with bargaining power.
Characteristics:
- Emphasis on cost reduction and efficiency.
- Large-scale production to benefit from economies of scale.
- Competing on price while maintaining an acceptable level of quality.
- Broad target market to attract price-sensitive consumers.
- Sensitive towards technological changes.
Examples: Walmart, D-mart and Zudio.
2. Differentiation Strategy
It targets the mass market and focuses on creating a unique, differentiated product. Businesses can create differentiation in product features, designs or branding. Through differentiation, companies can charge premium prices from the customers and become profitable.
Suitability: It is suitable when a company has the resources to create superior products. In addition, the product must be such that it can’t be imitated quickly at affordable prices.
Characteristics:
- Focus on product innovation, design, or brand image.
- Charging premium prices based on perceived value.
- Building strong customer loyalty and brand recognition.
- Investment in research and development.
Examples: iPhone, MacBook, Tesla and Starbucks.
3. Focus Strategy
The business identifies and concentrates on a specific market segment or Niche in a focus strategy. They serve the unique needs of specific customer groups by offering them a unique product.
Focus strategy can either be cost-focused or differentiation-focused. It is named as follows:
- Focused Cost Leadership Strategy
- Focused Differentiation Strategy
Suitability: It is beneficial when a business can master their chosen Niche. Also, when the competitors are trying to enter that particular segment.
Characteristics:
- Narrow target market focus.
- Customized products or services to meet niche requirements.
- Deep understanding of the niche market.
- Competing through specialization.
Example: Rolex, Zapper and Lefty’s.
4. Integrated Cost Leadership/Differentiation Strategy
It inherits the qualities of both cost leadership and differentiation strategies. Here, businesses aim to provide value at competitive prices with unique features.
Suitability: It is effective when a company can save costs without compromising the product’s quality.
Characteristics:
- Balancing cost efficiencies with product differentiation.
- Offering a unique value proposition.
- Appealing to a broad customer base.
- Striking a balance between quality and affordability.
Example: Toyota provides high-quality vehicles at competitive prices.
Importance of Business-level Strategy
An effective business-level strategy can be proved important for an organization in the following ways:
- Customer Satisfaction: The strategic efforts focus completely on customers and their needs. Thus, the customer’s satisfaction level is high.
- Roadmap: Strategies state the future course of action. It serves as a roadmap for the organizations in the short and long term.
- Product Differentiation: It inspires organizations to create unique products that differentiate them in the market.
- Competitive Advantage: Generic Business strategies and the five forces model help achieve an advantage over competitors.
- Long-term Planning: Strategies are formed considering the business’s long-term goals. Consequently, it facilitates long-term growth and development.
- Effective Resource Allocation: It helps in the organization’s thoughtful and optimum resource allocation.
Final Words
Business-level Strategies are strategically planned and coordinated set of actions taken to employ the target market. Companies must stress selecting the appropriate business-level strategy.
They must effectively align resources and capabilities to sustain changing business dynamics. Consequently, they can create value, enhance their position and achieve sustainable success.
Leave a Reply