Definition: Poka-Yoke is a mechanism applied to any process to prevent human mistakes in manufacturing units. It is a part of lean manufacturing systems that helps in preventing mistakes as and when they occur.
This concept is given by an industrial engineer named ‘Shigeo Shingo‘ at Toyota Production Systems in Japan.

It was first named ‘Baka-Yoke‘, which means fool-proofing. But, due to its negative connotation, it was renamed ‘Poka-Yoke‘, meaning mistake-proofing.
We can refer to it by a variety of names like:
- Error Proofing
- Fail-safe Operation
We experience it very often in our everyday life. For example, safety features are installed in cars. Like – warnings for speed, alarms for doors left open and seat belts.
Its basic objective is to prevent mistakes at the point of origin. Also, helps in achieving Total Quality Management.
Besides, manufacturers strive to design the processes in such a way that they are error-free. Therefore, they apply an error-detection mechanism in the process wherever necessary.
Poka-Yoke performs the following activities during the defects elimination process:
- Inspection
- Prevention
- Correction
Poka-Yoke solutions are often easy to understand and apply. Besides, it is pervasive in nature and used to resolve errors of any sort in general life.
Content: Poka-Yoke
- Goal
- Functions
- Need
- Types
- Common Errors made by Humans
- Steps
- Benefits
- Limitations
- Qualities of a good Poka-Yoke
- Example
- Final Words
Goal of Poka-Yoke
The goal behind implying fail-safe operations is to eliminate errors before they become defects.
Functions
It performs three essential functions to deal with human errors:
Shutdown – It involves the complete termination of the process.
Warning – It indicates the error that may happen during the process.
Control – It consists of resolving the errors at the earliest after detection.
Need
Generally, inspection methods involve individuals in them. Therefore, these methods are less reliable. As it is human nature to commit mistakes.
Thus, companies develop mistake-proof mechanisms which identify and prevent errors. Consequently, they can reduce scrap and produce defect-free products.
Types of Poka-Yoke
It is classified into two approaches that is Prevention and Detection. These approaches consist of some methods, which are discussed in detail below:
- Prevention Based
- Detection Based
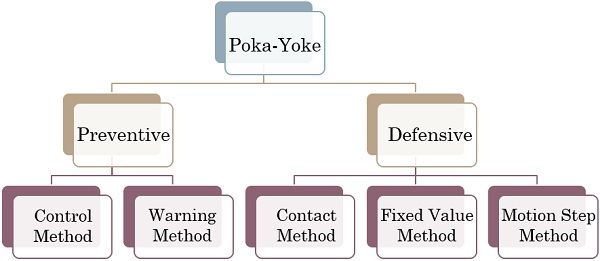
Prevention based Poka-Yoke
Here, mistake-proofing happens by eliminating errors before they originate. Therefore, manufacturers can use control and warning methods against defects.
- Control Method: In this method, the process is stopped immediately when the error is sensed. After that, implement corrective actions and avoid error iteration. It provides a high capability of achieving zero defects.
- Warning Method: This method gives indications about potential errors in an ongoing process. The warnings can be in the form of Buzzers, Lights, Sounds, Devices, etc.
Detection based Poka-Yoke
It involves spotting the defect post its occurrence. Manufacturers can use the following methods to deal with such errors.
- Contact Method: It investigates the changes in the appearance or characteristics of the product. It may include any changes in the shape, dimensions or mechanisms directly associated with the part.
- Fixed Value Method: It tracks the process’s movement using optical devices and automatic counters. It controls certain operative parameters like moves, rates and length, etc.
- Motion Step Method: This method involves the elimination of unnecessary steps from the process.
Common Errors made by Humans
Some of the common types of errors that humans may commit are furnished below:
- Forgetfulness
- Misunderstanding
- Wilful Errors
- Inadvertent Errors
- Slowness
- Lack of Standards
- Surprise Errors
- Intentional Errors
- Wrong Parts
- Missing Parts and Processes
Steps
Step 1: Define potential error-prone areas
First, you need to define the areas where the chances of defects are high. For this, you can make use of Pareto Analysis.
Step 2: Identify where the error may occur
The next step is to find out the place where the error or defect may occur.
Step 3: Find the root cause of errors
After this, find out the reasons that lead to defects. For this purpose, the 5 Whys Analysis is helpful.
Step 4: Select and implement the Poka-Yoke mechanism
Now, find the suitable method and mechanism to resolve the identified error. Post this, install the mechanism with appropriate methods.
Step 5: Perform pilot testing to check the workability
After successful installation, you need to test the workability of the mechanism.
Step 6: Train the operator
At last, provide proper training to the operator and review his performance.
Benefits
One can enjoy the following benefits by implementing Poka-Yoke mechanisms:
- Less Training: The operators need less training as the system gives alerts in case of errors.
- Quality Control: Manufacturers can have control over product quality. However, by applying it, the manufacturers can assure quality in production.
- Spot on Error Detection: The errors are detected at their origin, and necessary actions are taken thereon.
- Defect-free Production: It involves the production of defect-free products, as defect elimination takes place before they occur.
- Easy Application: These mechanisms are developed in a way that is easy to apply and cost-effective.
Limitations
Besides the above benefits, Poka-Yoke System has some limitations given below:
- Time-Consuming: The operator needs to invest more time in inspection in addition to his core work.
- Scrap Accumulation: It accumulates a large amount of scrap in the long run.
- Implementation: Practical implementation of the developed mechanism is not possible.
- Not Economical: Installation of mechanisms involves an extra cost which increases the company’s expense.
Qualities or Characteristics of a good Poka-Yoke
For successful implementation, error-free manufacturing must possess the following qualities:
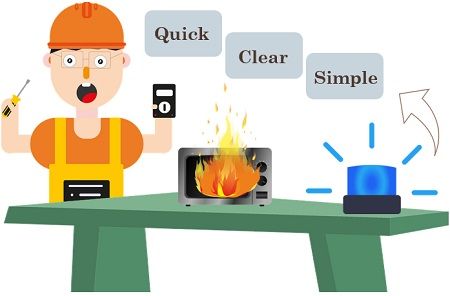
- Quick: It must provide quick feedback and assist in acknowledging mistakes at the origin.
- Clear: The system must be precise and clear to diagnose errors easily.
- Simple: Poka-Yoke must be simple and less complex. This is because it may become a time-consuming process.
Example
Following are the most common Poka-Yoke examples that we encounter in our daily life:
Lift: The lift doors have sensors that reopen them when any object comes between them.
Cables: Cables have specific symbols and colours to prevent interchangeability. It is commonly used in audio-visual cables used in Computers.
Sim Card: A diagonal cut at the edge of the sim card signifies the correct direction to insert it.
Pen Drive: The black line inside the pen drive and its respective port help plug it in quickly.
Hair Dryer: Hair Dryers have a safety feature that automatically cuts the power supply on overheating.
Final Words
To summarise, error-proofing is a preventive measure adopted to recognize and eliminate defects. Manufacturing units install it to avoid wastage and practice lean manufacturing.
It not only prevents errors but also helps in increasing operators’ productivity. Besides, it saves operators time and eases the production process.
mohan says
good data for knowledge improvement
Bhukya Veeru says
Knowledge improvement