Definition: Plant Layout involves the optimum physical arrangement of the economic activity centres so that they are easily manageable. It aims at finding the quickest route for efficient material flow at minimum cost.
We can also understand it as a floor plan of the men, machines and resources used in production. It focuses on identifying the best placement for vital resources during production.
It systematically arranges the facility and makes it capable of satisfying the anticipated demand. Moreover, plant layout design must be such that it economically meets the organizational goals.
Plant layout ensures smooth production right from the material stage to the final product. It includes both formulating a new plant layout and improving an existing one.
The organization develops plans to ascertain the route and flow between the work centres. It helps in wisely using every inch of the available space and arranging everything in a planned manner.
A good layout finds the shortest route for the resource flow. Also, it increases efficiency by locating the plant facilities effectively.
Only a well-laid-out plant can achieve prompt, error-free and low-cost production.
Content: Plant Layout
- Objectives
- Types Plant Layout with Example
- Principles
- Factors Affecting
- Why is Plant layout Important?
- Parting Words
Objectives
The prime objective of the well-designed plant layout is to maximize profit by efficient, low-cost production. Besides this, the other objectives are as follows:
- Optimum use of the available floor space.
- Reduce the time lag and total production time.
- Obtaining efficiency in material management and mobilization.
- Direct the material flow within the manufacturing unit.
- Reduce the chances of any mishap or accident in the unit.
- Maintain a scope of flexibility in operations and production.
- Ensure human resource safety, comfort and convenience.
- Easy transportation of men, materials and products from one point to another.
Types Plant Layout with Example
Different types of manufacturing units and products require different plant layouts. For this reason, it is one of the vital elements of business and operations strategy.
Four basic types of plant layouts are discussed in length below with examples:
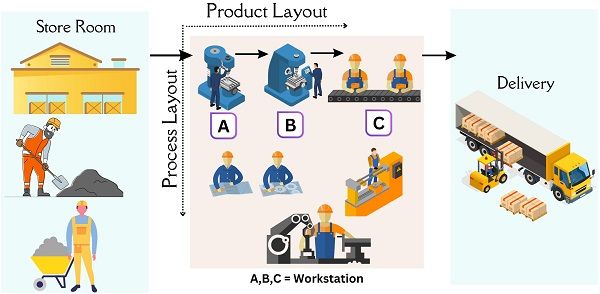
- Process Layout
- Product Layout
- Group Layout
- Fixed Position Layout
Process Layout
In Process or Functional layout, the grouping of the work centres takes place on a functional basis. It is designed by grouping similar machines and operations at one work centre.
During production, the product passes through its respective functions. Thus, the centres requiring frequent trips or movement are located shorter distances.
Suitability
It is best suited for organizations carrying out Batch Production. Moreover, it is helpful when quantity is less and standardization is not required. Like:
- Tailoring
- Jewellery
- Customized Furniture’s
- Engineering Products
Example
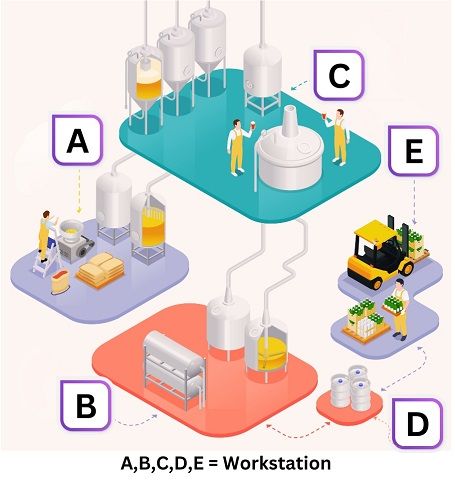
Advantages
- Manufacturers can use machines to the best of their capabilities.
- It facilitates flexibility and has sufficient scope for expansion.
- Businesses can easily maintain variety in production.
- A fault in one machine doesn’t interrupt the other, so the production process doesn’t stop.
- Manufacturers can effectively plan load distribution.
Disadvantages
- The high volume of work-in-progress inventory might require more storage.
- Management might face difficulty in Production Planning and Control.
- It requires a high degree of supervision which ultimately adds to the production cost.
- Total time to complete the production increases.
Product Layout
Product layout, also known as Line Layout, is used when the resources are located per the plant layout’s processing sequence.
Besides, it is applicable where the product variety is less, but the volume is high. Majorly, it is used for similar types of products. As a result, production planning and control is easy.
The order of the work centres depends upon the production procedure of the product. Moreover, the required resources are made available in a similar manner.
Here, manufacturers can develop fixed-path material handling systems that can save time.
Suitability
It is suitable for producing a few standardized products with stable demand. It is also adopted when the production volume is high, and the process is simple and repetitive. Some industries are as follows:
- Sugar
- Rubber
- Refineries
- Cement
- Food Processing
Example
Advantages
- Comparatively, less supervision is required.
- Sometimes even machines are not shared by different products.
- Lesser number of bottlenecks in the entire production process.
- The processing time is shorter as the product moves in a single line.
Disadvantages
- The design in this type of layout cannot adapt to changes.
- Limitation in the number of product varieties.
- The capital invested to more as compared to the process layout.
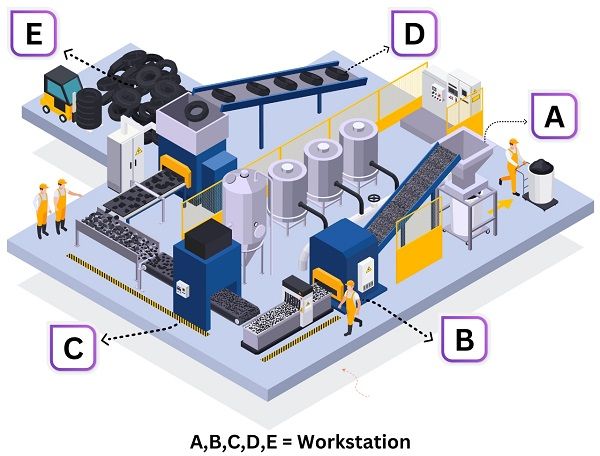
Group Layout
Group or cellular layout is a hybrid of other types of layouts. It involves the analysis and comparison of components and grouping them into families. These families require similar machines and processing at one workstation.
In general, a combination of product and process layout is widely used. It is used to get the advantage of both layouts and form the best cost-saving layout.
Suitability
It is suitable for organizations having variable batch sizes and multiple product lines. Like:
- Soap Manufacturing Plant
- Aircraft
- Forged Crankshafts
- Gear Manufacturing
Example
Advantages
- It eases the process of production planning and control.
- It helps in achieving an uninterrupted workflow.
- Supervision becomes easy.
- It occupies less floor space.
- Best utilization of men and machines.
- The total cost of production is low.
Disadvantages
- All the machines are not used to the best of their capacities.
- Higher capital investment and increase in cost.
- Organizations need to appoint skilled workforce for this work.
- To ensure production efficiency, frequent supervision is necessary.
Fixed Position Layout
Here, the product remains static and required resources are brought to this location. There is only a single work centre where the product remains fixed. Rest everything like manpower and machines are mobilized towards it.
Moving men and machines cost less than the product and process layout.
Suitability
Usually, preferred when the product is too heavy and difficult to transport. Therefore, it is often seen in industries like:
- Aviation
- Construction
- Railways
- Hospital
Example
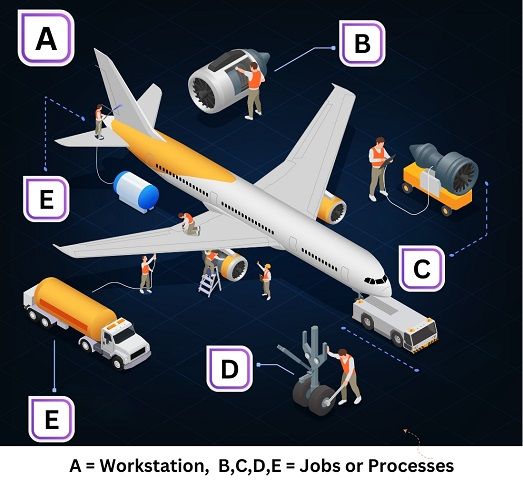
Advantages
- Effective utilization of available space.
- Less movement of mend during the production process.
- Customization of products and processes is easy.
- Material handling and mobilization are also easy.
- The total investment in this type of layout is less.
Disadvantages
- The manufacturers cannot retrieve the maximum benefit of the men and machines.
- The production process is slow, taking significant time, but the quantity produced is less.
- Supervision is complex in such cases.
- Many processes run simultaneously, which creates room for conflict and confusion.
Principles
When deciding the plant layout, one must consider the following principles.
- Minimum Movement Principle: The layout must be such that it ensures the minimum movement of men and material.
- Flow Principle: The layout flow should always be in the forward direction towards the end.
- Space Principle: The organization must use every inch of the space available, including height.
- Safety Principle: A plant layout must mandatorily make provision for the safety of the manpower.
- Flexibility Principle: It should be flexible enough to incorporate changing technology in the existing layout.
- Interdependence Principle: The level of interdependence should be less between the work centres. It helps reduce the time lag and complete the shutdown of the production process.
- Overall Integration Principle: A well-designed layout integrates all the 4Ms in an optimum way.
Factors Affecting
The major factors influencing the plant’s layout are listed below:
- Men: It is the most influential factor in the entire production process. It plays a major role in integrating all the crucial elements of the production process. In addition, men are the highly flexible element of the production system.
- Material: It is another element affecting the plant layout. Materials change form and move through various processes before converting into the final product. A good layout necessarily facilitates the effective mobilization of materials.
- Machine: Different types of machines are used for different types of products. And, the type of machine to be used for production greatly impacts the plant layout.
- Movement of Men and Materials: In the layout design, the movement of men and materials plays a vital role. This is because, the layout design directs the flow of these two.
- Building Layout: It is the major factor that houses the plant facilities and services. While designing the plant layout organization considers and refers to the building layout.
Why is Plant layout Important?
It is important because it incorporates and arranges the following vital elements:
- The flow of material and processes
- Labour efficiency
- Supervision and control
- Use of space
- Expansion possibilities
Parting Words
To sum up, it is an effective integration and utilization of 4Ms of production. The manufacturers must design the layout with expertise as it differs from one plant to another. However, the principles remain the same in all organizations.
Moreover, the layout must facilitate the manpower’s health and safety. It must be enough flexible and compatible with future expansion and diversification.
Leave a Reply