Definition: Offshoring is the process of relocating the business operations unit (production or services) to a different country (usually in developing nations) where cheap labour or resources are available. Here the company do not seek global retailing; instead, it looks forward to minimizing the cost of manufacturing and other supporting services.
Setting up this new business unit for other activities is quite beneficial for the company since it can now pay more attention to its core business operations. Even the tax rate policies and other incentives benefit the organization to a great extent.
Content: Offshoring
Benefits of Offshoring
An organization plans for offshoring owing to various reasons, out of which, minimizing the cost of specific business operation is always prioritized.
Let us now learn about the different advantages below: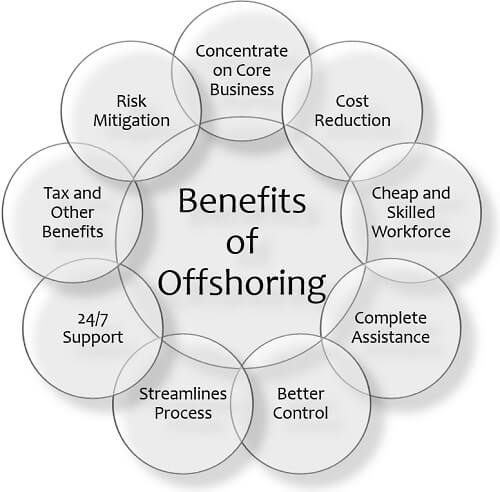
- Concentrate on Core Business: When the company offshore its other services, it can lay more focus on its core functions.
- Cost Reduction: The most crucial reason or benefit of offshoring is to cut down labour cost and other operating expenses.
- Cheap and Skilled Workforce: It is an opportunity to get competent and cost-efficient labour available in a developing nation.
- Complete Assistance: The offshore team holds expertise in its field, providing a relevant solution to every problem related to the production or services offshored.
- Better Control: The company can ensure proper management and regulation of all its operations if it opts for offshoring.
- Streamlines Process: It assures that a dedicated team is working on the offshored production or services to complete the assignment efficiently and effectively.
- 24/7 Operations: Its another advantage is that the company can continue a 24/7 service (such as customer support) which is otherwise not possible in the domestic business unit.
- Tax and Other Benefits: Many developing countries provide various types of incentives like tax holidays, to attract companies for foreign direct investment.
- Risk Mitigation: When the business operations are offshored to multiple countries, the company has a lower risk of failure or bankruptcy.
Types of Offshoring
The companies can plan for either production or services offshoring, depending upon their business activities, needs, capital budgeting strategy, etc.
To understand both of these in detail, read below: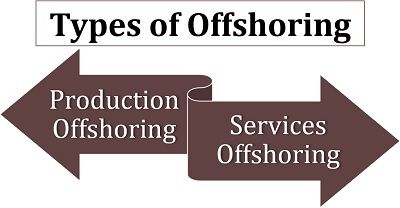
Production Offshoring
When a company establishes its manufacturing unit in a different country, to import the finished goods for selling it in the domestic market, it is termed as production offshoring.
For instance; a company manufacturing heavy machinery would set up its production unit in a country where it has an optimum supply of iron, and the local labour is cheap and skilled in such a task.
Services Offshoring
A company performs service offshoring by setting up the units in other countries to carry out service-related operations such as customer care, information technology, marketing, human resource, accounting, sales and many more.
For instance; a software company relocates its research and development unit in a country where the technical human resources are highly competent and comparatively cheaper than the domestic personnel.
Offshoring Disadvantages
Offshoring seems to be quite challenging; indeed, it is. While relocating a part or whole business operations to a different country, the management should not overlook the following drawbacks or hurdles it may face: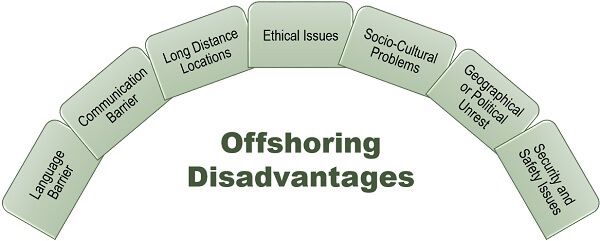
Language Barrier: When the company enters into a developing country for relocating its business operations; it finds a huge gap between the local language of the area and its native language.
Communication Barrier: Due to the difference in language and understanding, the organization fails to establish effective communication with the offshoring team.
Long Distance Locations: Usually the offshoring units are located in geographically distant locations which make it difficult for the management to visit these subsidiaries often.
Ethical Issues: If the organization pays dissatisfactory remuneration to the offshoring team or in any case if they feel that the facilities are improper, it leads to ethical problems and spreading of negative brand image.
Socio-Cultural Problems: When the company operates in a different country, it needs to acquaint with the cultural and social environment of that place; otherwise, it may face specific socio-cultural issues.
Geographical or Political Unrest: The geographical or political problems like riots, protest, shutdowns, political instability, etc. may prevail in the country where the company relocates its unit; ultimately affecting the business.
Security and Safety Issues: The company’s offshoring unit mostly faces a threat to lockout and closure if the natives find it to be unethical or harmful for their nation.
Example
You will be amused to know that the globally recognized i-phone company ‘Apple’ have relocated its manufacturing units from the U.S to some of the Asian countries.
China is top on the list of Apple’s offshoring countries because it has been known as the most cost-effective electronics manufacturing hub worldwide.
Future of Offshoring
Offshoring is a more effective means of acquiring the right talent at a minimal labour cost when compared to outsourcing, where the company has no control over the people who work on its projects.
Therefore, the companies are becoming more inclined towards this strategy (especially in the sector of information technology) to hire people with prominent skills, residing overseas.
The Asian countries like India, Philippines and China are most preferred offshoring destinations for the companies located in the United States.
Leave a Reply