Definition: National Income or (NNPfc) is a sum of factor income earned by the nation in the form of monetary value from the economic activities such as income from the production of final goods or providing services in a financial year. The level of national income can determine the level of aggregate demand for goods and services.
In the above definition, economic activities include all such human activities which generate monetary value in the economy such as manufacturing firms producing goods, farmers producing crops, lawyers providing services, etc. However, national income can be calculated in both current and constant prices, in which national income at a constant price is a real income, in contrast, national income at the current price is a national monetary income.
Content: National Income
- Formula for calculating National Income
- Measures of National Income
- Methods of Measuring National Income
- Conclusion
Formula for calculating National Income
![]()
Where,
C = Consumption
GE = Government Expenditure
IN = Investments
X = Exports
FPnr = Foreign production by national residents
M = Imports
DPnnr = Domestic production by the non-national residents
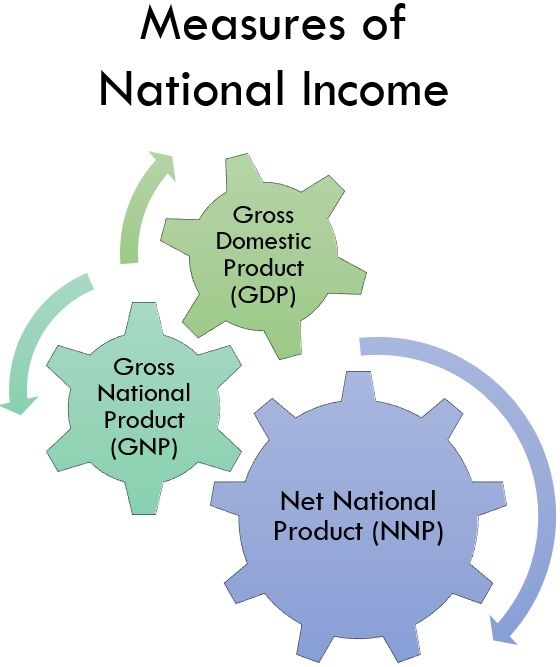
Measures of National Income
Following are some of the important measures :
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP is the fiscal value of all the final goods and services produced within the nation’s domestic territory in a financial year. The products or services produced outside the nation’s boundaries or domestic territory are not considered while computing national income even if the producer or provider is a resident of the nation. However, income earned by foreigners within the nation’s territory will be included while computing national income. Therefore, GDP can be formulated as:
2. Gross National Product (GNP)
GNP is the monetary value of the goods and services produced by the normal residents of the country in a financial year. Here, a normal resident implies an individual who usually resides in a country and has a long-term economic interest in a country. While computing GNP territory of a nation is not relevant, i.e., resident of the nation, whether producing goods or providing services in a nation or outside nation, his income will be considered while computing GNP. However, the income of a foreign company running inside a nation will not be considered while computing GNP. Thus, GNP can be formulated as:
3. Net National Product (NNP)
After reducing the amount of depreciation from the GDP, the net outcome is defined as NNP, i.e., it is the net monetary value of final goods and services produced or provided during a financial year. Here, depreciation is the reduction in the value during the production process and for calculating the NNP estimated value of depreciation gets subtracted from GDP. NNP is the real measure of income. However, it is measured at a market price, i.e., GNP at market price minus depreciation gives NNP at market price (NNPmp), then add subsidies and deduct indirect taxes in NNPmp to get the national income or NNPfc. Thus, NNP is formulated as:
- NNP at Market Price
![]()
- NNP at Factor Cost
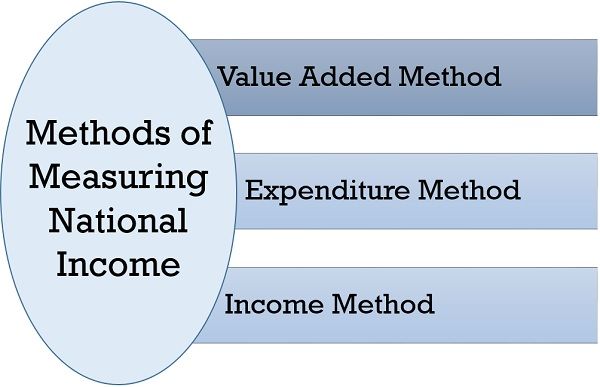
Methods of Measuring National Income
Income generated by various economic activities by the individuals is the national income of the country. For measuring it, some methods are adopted, they are explained below in detail:
-
Value Added Method
Value Added Method or the Product Method is a procedure of measuring national income based on the contribution made by all the industries within the territory of the country within a year. Here, the difference between the value of output (selling price) and the intermediate consumption (Purchase price) is the value-added (Profit) in the price of a product. Let us understand with an example:
Example: X ltd purchased a material A for 50₹ and sold it @ 80₹ to the consumer.
In the above example ₹80 will be the value of output, ₹50 is intermediate consumption, and the difference amidst them, i.e., (80-50) =30₹ is a value-added. This process of adding value starts with a manufacturer and ends up at the final consumer of the product. Every channel adds value(profit) to the product such as the manufacturer sells the product to the wholesaler after adding value. Similarly, the wholesaler sells the same product to the retailer after adding his profit, and at last, the retailer sells it to the final consumer. By summing up the value-added at all stages, we get the gross value added at a domestic product which is also known as GDPmp. After that, by reducing depreciation and net indirect tax, and adding net factor income from abroad we get national income or NNPfc. The formula for it under the value-added method can be illustrated as:
-
Income Method
In this method, national income is measured on the basis of income received by a factor of productions such as –
- Compensation to employees – It includes wages and salary in cash, wages and salary in kind and employers’ contribution.
- Operating Surplus – It includes Rent, interest, profit (Corporate tax, retained earnings and dividend).
- Mixed-Income – It includes self-employed income such as home tuition income, income from the property.
By adding the above three factors (1+2+3) we get NDPfc then we add net factor income from abroad in it to obtain NNPfc or national income. The formula for it under the income method can be illustrated as:
-
Expenditure Method
Expenditure method measures the national income by measuring the expenditures at the final consumption stage, expenditures under it are as follows:
- Private final consumption expenditure – It includes domestic final consumption expenditure plus if any final consumption expenditure by non-profit institution run by household.
- Government final consumption – It includes the expenditure made by the government in a year.
- Gross domestic capital formation – It is an expenditure in the formation of assets, i.e., on fixed assets and current assets. When expenditure is made on a fixed asset, it is known as Gross Fixed Capital Formation, and when expenditure is made on a current asset, it is known as Change in Stock.
- Net Export – Exports minus (-) Imports of a nation within the year.
To calculate NNPfc add all 4 expenditures in GDPmp then add net factor from abroad and subtract net indirect tax and depreciation. The formula for it under the expenditure method can be illustrated as:
Conclusion
National Income is the income earned by the nation in the form of money from the final goods and services (not intermediate goods) produced in a financial year.


Patrick says
Thank you so much for the wonderful article, it helped me a lot in enhancing my knowledge…