Definition: Location Analysis Techniques are the methods that critically evaluate location alternatives to select an ideal location for the Plant or Industry. These are the tools used by the organizations for decision-making while locating a plant or facility.
Location techniques are a systematic approach for choosing the most desirable location alternative. It strives to identify a site with Geographical and Technical viability.
The goal behind using location techniques is to examine the revenue-generating potential of the alternatives. It also helps to find locations that maximize value and minimize costs.
Location techniques enable the business to accept or reject the available location alternatives. It covers both the scenarios, i.e.:
- One Facility – Multiple Candidates
- Multiple Facilities – Multiple Candidates
The location analysis is a critical process. In this, we analyze and test the capabilities of the alternative sites for selection.
Depending on the requirements, the businesses can use the following:
- Quantitative Methods
- Qualitative Methods
- Semi-Quantitive Methods
Content: Location Analysis Techniques
- What is Location Analysis?
- What is an Ideal Location for Business?
- Plant Location Techniques
- Example
- Final Words
What is Location Analysis?
Location Analysis is choosing the most suitable plant location within/outside the country. The decision-making in this regard is known as Location Decisions.
Location Decisions are crucial as they significantly affect the company’s finances and operating costs.
It is more relevant in the service industries because the service product’s production and delivery happen instantaneously.
What is an Ideal Location for Business?
The ideal location for a plant is the best location where the production and distribution cost is the lowest.
We can refer to a particular region as an ideal location when it has the following:
- Maximum Social Gain
- Least Risk
- Large Market Share
Plant Location Techniques
Following are the various quantitative and qualitative location analysis techniques. Organizations can use either one method or a combination thereof.
- The Factor-Rating Method
- Location Break-Even Analysis
- Centre-of-Gravity Method
- Load-Distance Method
- Transportation Method
- Brown Gibson Model
The Factor-Rating Method
In this location analysis technique, the analysis is based on the influential factors and the prospecting locations. It is a simple and widely used method for locating the facility.
It is the comparative analysis of alternative locations and the factors affecting business. And the site having the maximum product of factor rating and location ranks is the one to be selected.
The factors include tangible and intangible factors essential to the organization. The steps involved in the factor rating method are discussed below.
Steps in Factor Rating Method
- Identify the relevant factors affecting that business location.
- Rate various factors as per their relative importance.
- Performance rating of the alternatives as per advantage on each factor.
- Calculate the product of ratings by multiplying the factor ratings with location ratings for each factor.
- Compare the factor ratings between the available alternative.
- Select the site containing the maximum sum of the products.
Note: The higher the rank is, the more influential the factor will be.
The merits of using this method are:
- The clarity in comparison during the selection of the alternatives.
- An analysis is on the basis of multiple factors.
- Fast judgement while selecting the location.
- Can incorporate any factor that can impact the plant during analysis.
Besides all the above merits, its demerits are as follows:
- Only limited to board-level analysis
- Helpful for just initial screening
Location Break-even Analysis
Location Break-even Analysis helps in finding the most economical location alternative. This technique examines the economic aspect of the prospecting sites.
The location providing a minimum cost of production yielding maximum output is to be selected.
Therefore, we estimate the costs from various factors that significantly affect business. After that, we separate all the costs under operating and fixed costs. And then, plot the break-even analysis for each location on the graph.
Formula:
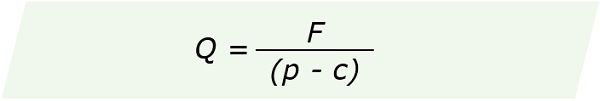
where,
Q = Break-even quantity
p = Price/unit
c = Variable cost/unit
F = Fixed cost
Centre-of-Gravity Method
Centre-of-Gravity Method is the most suitable when selecting multiple sites in an area. Generally, organizations use this technique for locating warehouses.
All the potential locations have some value. This value is the sum of transportation costs to and from that location.
The centre of gravity is where the x and y coordinates show the lowest weighted supply and demand points. For this, we plot the weights of supply and demand points on the grid.
We need to find a site where the transportation cost is minimum. In other words, the distance travelled to and from the proposed location on the grid is minimum.
Formula:
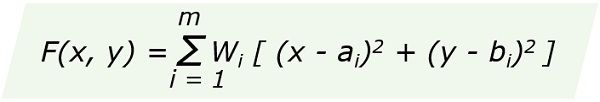
Load-Distance Method
It is a mathematical model that analyzes the Load and Distance of the sites. In this method, the choice of location depends upon the nearness of the most relevant factors.
To compare the distinct locations, we calculate the total load distance of each site. It is the product of all the essential factors of the proposed site.
Here, a load can be:
- Shipment from suppliers
- Shipments between plants/consumer
- Employees Travelling from/to the facility
The formula for calculating Load Distance is as follows:
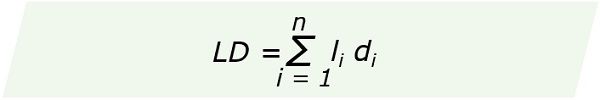
where,
LD = Load Distance
x, y = Coordinates of the new facility
xi, yi = Coordinates of the existing facility
li = the load expressed as weight, number of trips or units
di = the distance between the new and existing facility
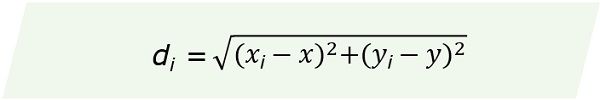
Organizations must focus on minimizing the Load Distance. Also, they must make sure that the large loads must travel short distances.
Transportation Method
The Transportation Method is a quantitative technique that uses linear programming for the analysis. It is helpful in case of multi-facility location problems. However, it does not cover all sorts of issues of multi-facility location.
It facilitates the estimation of the best possible shipping pattern for the alternative locations with given capabilities. For example: – The shipping movement amidst the plants and warehouses.
Firms must try to minimize the overall transportation cost. These costs include all the costs from multiple supply sources to various destinations.
Brown Gibson Model
This model is a composite measure of the Critical, Objective and Subjective factors for locating the plant. Basically, it is a tradeoff between the cost and the factors mentioned above.
Let us see what all things these factors cover:
- Critical Factors- Water for Refinery
- Objective Factors – Labour Cost and Raw Material
- Subjective Factors- Union Activities
The evaluation is done by putting these factors in the formula given below:

Where,
CFMi = Critical Factor Measure for the site i
(CFMi = 0 or 1)
OFMi = Objective Factor Measure for the site i
(0 ≤ OFMi ≤ 1)
SFMi = Subjective Factor Measure for the site i
(0 ≤ SFMi ≤ 1)
D = Objective Factor Decision Weight
(0 ≤ X ≤ 1)
Example
An industrialist is planning to set up a new factory. For this purpose, he shortlisted five distinct locations. All the locations possess certain merits over one another.
Therefore they opted for the Factor Rating Method to choose the best location for their factory. A senior employee of the industry collected the following data:
- The six most important factors are identified.
- The factor rating scale ranges from 1 to 100.
- Locations are also rated from 0 to 100, considering the qualitative and quantitative factors.

Rating of each location against each factor: –
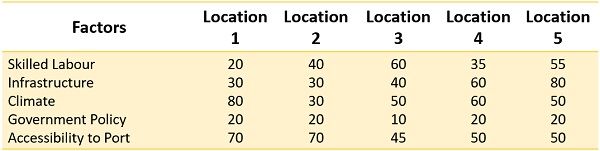
Taking this data, compute the ranking of the alternative locations.
Solution:
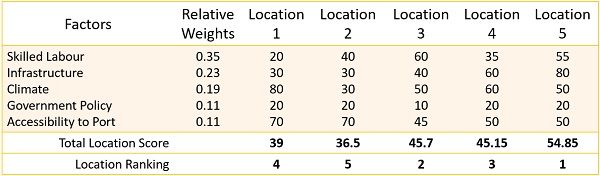
Based on the above table, location 5 is the best location for the new factory.
Final Words
In conclusion, location analysis techniques are various methods for selecting the plant location. It is the judgement to choose a feasible and cost-effective location.
Leave a Reply