Definition: Location Decision in operation management is finding an ideal geographical region to install a Facility or Plant. It is a vital component in facility planning as it greatly impacts the organization’s Profitability, Cost and Success.
In other words, the decision about the area for locating a facility is the Location Decision. It is also termed as Facility Location and Site Selection.
Here, the term Facility refers to a Plant, Industry, Factory or Manufacturing Unit.
Depending on the business and market conditions, the organizations can have all facilities under single or multiple units. It includes both the location of the plant and the facilities within the plant.
Generally, the location decision is taken to set up a new plant, relocate or expand the existing plant.
The decision depends on several factors that impact the business in the short and long run. These factors may be the industry’s size, nature and product.
The goal behind selecting a suitable location is to create accessibility to:
- Customers
- Workers
- Transportation
- Materials, etc
Installation of facilities involves massive investment and cannot be changed frequently. Due to poor location decisions, relocating to another place may lead to a heavy investment loss.
Facility location has a significant impact on different types of costs. These costs include Direct, Indirect, Fixed and Variable costs. The organization aims to deliver products at minimum cost to its customers.
Therefore, the industrialists are going for a strategic and logical approach to choose the best location. It also helps in the smooth and efficient working of the organization.
Content: Location Decision
- Objectives of Facility Location
- Criteria
- Factors Affecting Location Decision
- Location Decision Process
- Three-Tier Model for Assessing Location Competitiveness
- Location Planning Techniques
- Globalization of Operations
- Disadvantages of Poor Location Decision
- Example
- Conclusion
Objectives of Facility Location
A good site location helps in reducing costs and amplifies the profit earned. The industries invest their valuable time in search of an ideal site for the following purposes: –
- Revenue Potential from that Site
- Availability of Resources
- Tax advantages
- Reducing Cost and Production Time
- Convenient Transportation Facilities
- Suitable Environment for Employees
- Meet the Maximum Demands of Customers
- Maximum Space Utilization
Criteria
Facility location is a critical decision area and cannot depend on a single criterion. Essential criteria for selecting the location of a site are as follows: –
- Costs: The cost perspective is an essential criterion concerning the location of a facility. Any wrong decision will adversely impact the company’s finances.
- Competition: Effective location decision helps in achieving a competitive advantage in the markets. As industries can control costs and offer products at reasonable prices to consumers.
- Hidden Effects: The plant’s location affects many factors in the long run in a direct or indirect manner. To remain competitive, organizations must strategically locate their facilities.
Factors Affecting Location Decision
Numerous factors might affect the location decision. The suitable location is determined by analyzing various factors, parameters and issues. Some of the factors are listed below:

- Product and Industry: The nature of the product impacts the facility’s location. For instance, poultry farms are established on the outskirts of the city.
- Availability of Resources: The plant must be located close to the suppliers of the raw materials. This is because, it minimizes the transportation cost, time and overall cost of production.
- Proximity to Consumers: The organizations offering services may choose to locate facilities near their target customers. Thus, providing them with an advantage over similar service providers.
- Climate Conditions: Manufacturing of some products demands specific climatic conditions. For this reason, industries are set up in areas where suitable climatic condition exists.
- Proximity to Market: The companies producing customized or assembled products are located near their target market. Consequently, it reduces the time required for product assembly and delivery.
- Regulatory and Policy Issues: The political policies differ in different geographical boundaries. So, the organizations prefer locations inside open economies having favourable policies.
- Labour Supply: Before installing the plant, companies assess the availability of skilled labour. Also, they ensure the availability of basic necessities for the employee’s survival.
- Free Trade Zones: Free Trade Zones are areas in which one can conduct business free from customs duty. Thus, it is an essential factor when selecting a site location.
- Infrastructure: Before the installation, industries must assess the availability of infrastructure in that region. It may include connectivity via Rail, Roads, Air and Sea.
- Taxes: The tax rates vary within and across the regions. This factor directly impacts the organizations.
Location Decision Process
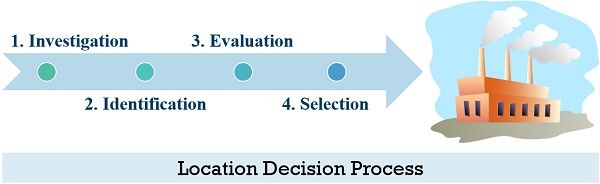
Step 1: Investigation
Firstly, the organizations investigate their requirements regarding their location. They conduct an internal SWOT analysis and decide whether to move, expand or install a new setup.
Step 2: Identification
Post investigation, they try to identify the potential locations for locating the facility. For example, installing the facility in the Domestic or Foreign regions.
Step 3: Evaluation
The next step in the location decision process is evaluating the potential locations. The evaluation process may include a detailed comparison of all the alternatives available.
step 4: Selection
Companies conduct a thorough analysis of the location and government policies in the selected region. Also, an in-depth evaluation of the merits and demerits of the chosen area. Therefore, choosing the most appropriate location of the facility for installation.
Three-Tier Model for Assessing Location Competitiveness
This model depicts the levels of competitiveness regarding the facility’s location.
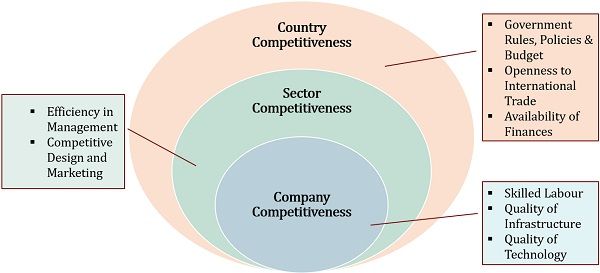
Country Competitiveness
It is the topmost level that analyses the company’s competitiveness in different countries. The main parameters for the analysis include:
- Government Rules, Policies, and Budgets pertaining to the country.
- Openness to international trade.
- Availability of finances.
Sector Competitiveness
The second layer in the model constitutes sector competitiveness. It helps in analyzing the attractiveness of the sector to operate. It includes:
- The pool of talent or availability of skilled labour.
- Analysis of the quality of infrastructure.
- Quality of the technology.
Company Competitiveness
In the last tier of this model, the companies analyze their competitors. It is the analysis of the company’s abilities to beat the competition. The parameters include:
- Efficiency in business management
- Company’s capabilities to design and market the products better than competitors.
Location Planning Techniques
Following are the location analysis techniques that help in the selection of an ideal location:
- The Factor Rating Method
- Location Break-Even Analysis
- Weighted Scoring Method
- Center of Gravity Method
- Transportation Method
- Load-distance Method
Globalization of Operations
Nowadays, companies are not restricted just to local markets. But, they are heading towards international markets to offer their products. Consequently, the globalization of operations is taking place.
The companies in the developed countries are identifying the potential markets in the developing countries. Moreover, they are looking forward to countries with open economies and free trade zones.
Hence, globalization of operations is becoming one of the crucial aspects of the business’s location decision.
Disadvantages of Poor Location Decision
Following are the disadvantages of selecting a poor location of the facility:
- The maintenance of the plant is a constant addition to the cost.
- Purchase of land and construction of infrastructure is an expensive affair.
- Difficulty in marketing and transportation of the products.
- Dissatisfaction among employees and workers.
- Abnormal wastage and delays in the processes.
Example
Sugar Mills
Companies construct Sugar mills close to the Sugarcane farms. Consequently, there is a reduction in the transportation time and carriage inwards.
Tea Factories
The tea plants need moist soil for their growth. In India, Assam, West Bengal and Karnataka are some of the major tea-producing states.
Hence, most Tea Factories are located in these states due to their climatic conditions.
Crude Oil Companies
The United Arab Emirates is the largest exporter of crude oil. Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), situated in UAE, is a leading company in this sector.
Conclusion
To conclude, facility location is the strategic and logical decision about the factory’s geographical location. There are a variety of factors that affects this decision. The organization must make efficient location decisions as it impacts the business’s finances.
Arvindakshan says
You have elaborate all the topics very neatly and in brief in four lines , all the topics of this must be covered
FRANK RAEON says
THE LOCATION FACTORS IDENTIFIED HAVE AN INDUSTRIAL FOCUS. AT LOCATION DECISION ADVISORS OUR SOLE FOCUS IS RETAIL AND RESTAURANT SITE SELECTION. THIS DIFFERENTIATION IS IMPORTANT AND NEEDS TO BE HIGHLIGHTED.