Definition: Commercial Bank is the banking platform for the general public and is described as an institution whose primary business is to act as an intermediary for the purpose of settlement, i.e., receiving deposits and giving loans. These banks in India are formed as joint-stock firms and recognized as banking firms.
Content: Commercial Bank
Classification of Commercial Bank
These banks are mainly classified into scheduled banks and non-scheduled banks. Let us understand them in brief:
Scheduled Banks
The second schedule of RBI Act incorporates a record of the bank which are specified as “scheduled banks”. A bank to be nominated as a scheduled bank must have a paid-up capital and reserves as recommended by the Act. According to section 42(6) of RBI Act, 1934, the obligatory amount is only 5,00,000. Yet, in a short while to start a commercial bank, The Reserve Bank of India recommended the least capital of 100 crores and its business should be handled apparently, which in the assessment of Reserve Bank of India, is not damaging to the interests of its depositors.
The scheduled banks are also needed to manage with the RBI a deposit in the form of CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) established on its demand and time liabilities at the recommended rate. Scheduled banks involve nationalized banks, thus it is necessary to understand the concept of a Nationalized bank.
- Nationalized Banks
Nationalized banks are also scheduled banks which include 20 nationalized banks amongst them 14 banks are nationalized on 19 July 1969, and 6 banks are nationalized on 15 April 1980. After the nationalization, these banks contribute distinct classes of functions by imperative social responsibilities. By way of these banks, the government attempts to achieve its fiscal policies and distinctive attempts to achieve its fiscal policies and distinctive welfare schemes. These banks are also called as public sector banks. SBI (State Bank of India) and its branches are commercial banks producing services identical to that of nationalized banks.
Non- Scheduled Banks
Non-Scheduled banks are those banks which are not the part of the 2nd scheduled of the RBI Act. These banks are not well-known by the general public in comparison to scheduled banks, as they are less popular. Many facilities are also not available in these banks such as refinancing, discounting of bills, etc. In a matter of security also, these banks are much less secure than commercial banks as they do not have to follow guidelines given by the RBI.
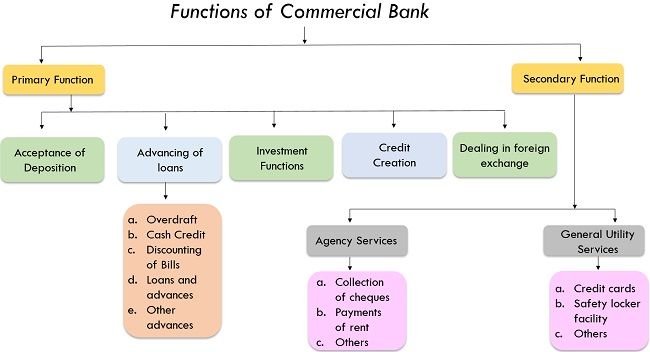
Functions of Commercial Bank
The functions of the Commercial Banks are basically divided into two parts, i.e., primary and secondary function. They are as follows:
Primary Functions
The primary functions of such banks are as follows:
1. Acceptance of Deposits
- Time Deposits
Time deposits get matured after a certain period and cannot be withdrawn by draft, cheques or by other means. These deposits include:
-
- Fixed Deposits: The deposits that may be withdrawn after completion of a fixed period for which it has been made such as 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, etc.
- Recurring Deposits: In this, the client opens an account and deposit a fixed amount every month and after a certain period, i.e., 1 year, or 2 years, the collected sum along with interest is paid to the client.
- Cash Certificates: They are circulated to the public for the expanded time period. It fascinates people as its maturity value is in multiples of the amount invested.
- Demand Deposits
Demand deposits are those deposits which can be withdrawn by the client any time without giving any earlier notice. It can be withdrawn by any mode, i.e., draft/ cheque etc. These deposits involve the following:
-
- Saving Deposits: These deposits develop prudence amidst people and can only be detained by a person and non-profit organizations (NPOs), but the interest rate of saving accounts is lower than the time deposits.
- Current Account Deposits: Normally, current accounts are maintained by the businessmen’s who require liquid balance. This account proposes high liquidity. No interest is paid on this account, and there is no limit on the withdrawals.
2. Advancing of Loans
Commercial banks grants loans and advances in distinct forms. They are as follows:
- Overdraft: The bank provides the facility of overdraft to the current account holders of the bank only. It is an understanding of the bankers with the client, which allow withdrawing money more than the balance in their account.
- Cash Credit: It is a form of working capital credit provided to the business organization. In this settlement, the client opens an account, and the permitted sum is credited in his account. The client can use that account within the permitted extent.
- Discounting of Bills: It can be another form of bank credit. The bank can buy up-country and foreign bills earlier than these are overdue for disbursement by the drawer, borrower at a lower value.
- Loans and Advances: Demand loans and term loans are the types of loans covered under this section. These are the loans and advances given to clients such as investors and people in business against some personal securities or movable or immovable goods.
3. Credit Creation
It is one of the most important primary function of commercial banks. When a bank approves a loan to the client, the bank won’t give cash. However, a deposit account is opened in a bank with the client’s name, and the sum is credited to this account. He can withdraw the amount as and when required by him/her. In such a way, the bank raises the money supply of the economy and such function is termed as “Credit Creation”.
Secondary Functions
The secondary functions of the banks involve agency functions and general utility functions. Here, we see the overview of these functions:
1. Agency Functions
These functions consist of the following:
- Collection of cheques, dividends, etc.
- Payment of insurance premium, rent.
- Buying and selling of securities.
- Trading in foreign exchange.
- Act as executor, agent, counsellor.
- Act as a contributor.
- Formation of income-tax returns.
- Others.
2. General Utility Functions
These services consist of the following:
- Security locker facility.
- Money transfer.
- Traveller’s cheque.
- Circular letter of credit.
- Issue of traveller cheques.
- Letters of credit.
- Acting as referrers.
- Provides trade information.
- ATM facilities.
- Credit cards.
- Gift cheques.
- Accepting bills.
- Merchant banking.
- Advice on financial matters.
- Factoring service.
- Others.
Conclusion
A commercial bank is outlined as one whose primary business is financial intervening such as taking deposits and providing loans. Clients of these banks involve small companies, person, or large companies.
Leave a Reply