Definition: Maintenance Planning is a controlling function that formulates strategies to keep the Capacities and Facilities as per intended working conditions up to their useful life. It helps Minimize Costs, achieves Higher Production Efficiency, and reduces Ideal Time.
The manufacturing units produce final products using their resources and assets. These assets are the backbone of the organization, some of which include:
- Plant
- Equipment
- Buildings
- Grounds, etc

Managers focus on planning and preserving these assets to maintain efficiency. Therefore, it is important to maintain these assets on regular basis.
The purchase and maintenance of the equipment need an ample amount of time and costs. So, the machine’s downtime and ideal time are expenses for the organization.
Organizations aim to save these costs by way of maintenance planning. In addition, it provides an advantage to the organizations over their competitors.
Some activities undertaken for facilities maintenance are:
- Servicing
- Repair & Replacement
- Modification
Content: Maintenance Planning
- What is Maintenance Planning?
- Objectives
- Need
- Types of Maintenance
- Consequences of a Poor Maintenance
- Steps in Maintenance Planning
- Flowchart
- Machine Replacement
- Important Terms
- Example
- Conclusion
What is Maintenance Planning?
Strategic plans prepared to maintain capacities and facilities comes under Maintenance Planning. It assists managers in managing equipment and other assets. Also, keeping them updated to maintain productivity in the most efficient manner.
For making effective maintenance strategies, the managers need the right:
- Information
- Tools & Material
- Timing
- People
- Permission
- Scope
The scope of maintenance in organizations is not restricted to existing machinery. But, it also covers installation plus servicing of new machinery. Besides, the scope of maintenance varies depending on the type of Firm, Product and Policies.
Scope of Maintenance Planning broadly coves:
- Existing Plant, Machinery, Buildings and Grounds
- Generation and Distribution of Utilities
- Alteration of Existing Equipment and Buildings
- New Installation of Equipment and Buildings
Objectives of Maintenance Planning
By keeping the plant and machinery updated, organizations aim to retrieve maximum productivity. Thus, they plan the maintenance in advance to fulfill the following objectives:
- Lesser breakdowns in the Plants & Machinery.
- Keeping the facilities updated and in good condition.
- Ensure availability of equipment, tools, etc.
- Undisturbed production in the organizations.
- Ensure safety while working.
- Cut the maintenance and operations costs.
- Improve and deliver quality products.
- Generate Maximum productivity.
Need
Equipment is the strength of any manufacturing unit. Keeping them updated is a must as they are the resource to produce desired level of output.
Generally, the need for maintenance arises when:
- Any system or process fails to perform.
- There is a loss in production or profitability.
- Fails in completing the assigned function.
- Complete or partial damage to the machines.
Types of Maintenance
There are two types of maintenance undertaken in the organizations, i.e.
- Preventive Maintenance
- Breakdown Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance
As the name suggests, it is a type of maintenance that is preplanned. The maintenance manager anticipates breakdowns and takes corrective measures beforehand.
The goal behind taking preventive measures is to achieve an uninterrupted production process. For this maintenance managers open and inspect the equipment from time to time.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance:
- Reduced Downtime
- Lesser Major Repairs
- Reduction in Accidents
- Improved Crises Management
Breakdown Maintenance
The breakdown is the non-functioning, breakage or failure of the plant and equipment. Managers need to avoid breakdowns as it hampers the production cycle. Therefore, managers need to plan breakdown maintenance strategies in advance.
It includes the repair & replacement of the plant/equipment either entirely or partially. Besides, breakdowns and repairs include huge costs, which is also an area of concern.
Through preventive maintenance, the organizations may save breakdown costs. So, they must take extraordinary preventive measures to avoid equipment breakdowns.
Graphical Representation of Maintenance Costs:
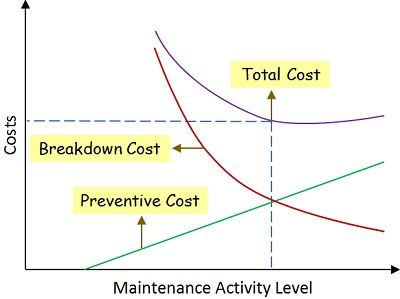
- There exists an inverse relationship between Preventive and Breakdown maintenance cost
- The maintenance manager must develop appropriate strategies to control breakdown maintenance costs.
- Preventive Maintenance follows the Pro-active approach. In contrast, Breakdown Maintenance follows a Reactive approach.
- Resource allocation must be balanced among Preventive and Breakdown maintenance.
Consequences of Poor Maintenance
From the above sections, we understood the importance of maintenance in organizations. Now, we will learn the problems faced by them due to poor maintenance.
- Backlogs: During repair, the production stops for a while, resulting in excessive backlogs.
- Incomplete Information: Today, all the information is stored and managed through Management Information System (MIS). Sometimes operators commit a mistake in uploading data providing misleading results.
- Work-order Delivery: The scheduled delivery of work orders may get delayed due to maintenance work.
- Incomplete costs: It affects the cost estimation and also excludes some costs during calculation.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPI): Maintenance results in reduced production and affects productivity. And hence, witnessing fluctuations in the KPI of the organization.
- Capacity Utilization: When the machinery is under maintenance, its full capacity may not be utilized.
- Increased Production Cost: The expenses incurred in fixing the plants and machinery are added to the products. Therefore, resulting in an increment in the overall cost of the product.
Steps in Maintenance Planning
The steps that can be followed to formulate an effective maintenance strategy are as follows:
- Inspection and Measurement
- Maintenance Modelling
- Cost Estimation
- Formation of a Suitable Maintenance Strategy
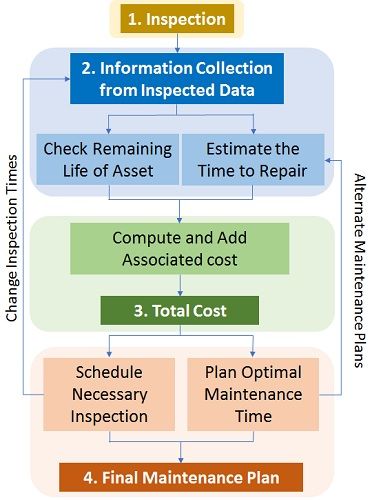
Flowchart
A detailed flowchart showing steps for making a maintenance strategy is as follows:
Machine Replacement
Replacement involves changing the whole or a part of the equipment. It is needed when the equipment becomes obsolete or damaged and can’t be repaired any further.
It is a narrower term than Maintenance. As maintenance covers all activities like Servicing, Repair, New Installation, and Replacement.
Important Terms
Crew Size determination: The maintenance managers must determine the optimum number of mechanics required. There must be a trade-off between the maintenance and labour costs.
Computerized Maintenance Management: In this era, managers use computers and software for efficient management. Thus, it is also applied in the case of maintenance management. It includes procedures like:
-
- Planning
- Documentation
- Equipment Selection, etc
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): It suggests the creation of a maintenance-free framework for facilities. In other words, organizations must have strategies that result in zero breakdowns until the asset’s life.
Wrench Time: The managers must know the exact time taken to perform actual maintenance work. In other words, the actual time spent in maintenance using tools by the mechanic.
Work Order: It is a document containing details about the guidelines for the scheduled maintenance. Generally, companies provide it to the customers along with the product. But, it may vary as per products and companies.
Example
A Tea manufacturer suffered a huge loss and a sudden fall in productivity in the past two years. The production manager investigated and presented the reasons for the loss.
Among numerous reasons, machinery failures and equipment breakdowns were the major ones. So, they decided to appoint a maintenance manager to prevent maintenance issues.
Consequently, by the end of the current year, they noticed zero breakdowns and an increase in productivity.
Conclusion
Maintenance work is carried out to keep assets in a healthy working condition. Its strategic function that maintains the equipment and assets in the production unit.
Leave a Reply