Definition: Batch costing is an extension of Job costing which calculates costs and profit for batches. The production in batches decreases the setting up costs. Whereas, it increases the carrying and holding costs. Moreover, Economic Batch Quantity (EBQ) is considered during production. It is also known as ‘Lot Costing‘.
Preparation of Batch cost sheet facilitates calculation of cost per unit of individual Batches.

The manufacturing units producing identical products in large quantities divide their total production into small groups. The size of groups may vary according to the need like- Demand and Inventory Creation.
Batch costing may apply in industries like:
- Furniture
- Small Tool Making
- Fabric Manufacturing
- Watch
- Food processing Undertaking, etc
Content: Batch Costing
- What is a Batch?
- Essentials of Batch Costing
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Procedure
- Economic Batch Quantity(EBQ)
- Solved Example
- Final Words
What is a Batch?
A batch is a collection of similar products arranged in different groups. However, a single batch contains a certain number of units. And each set is assigned a specific batch number for identification.

Essentials of Batch Costing
The points list out the essentials of batch costing:
- Preparation of a batch cost sheet is a must, where production occurs in large volumes.
- Total production is divided into batches. Therefore, there is a need for a separate cost sheet for these batches.
- Determine per unit cost and profit or loss for each batch in detail.
- The size of batches may vary in the same manufacturing unit. It is difficult to determine the overhead expenses for the batches during calculation.
Advantages
Batch costing benefits organizations in the following ways:
- Reduced Costs
The cost of production decreases due to the Economic Batch Quantity. - Saving in Job Time
The time involved during inter-job transfers is minimised. - Less Accounting Work
Here, there is a significant reduction in the accounting work. This is because we prepare separate statements for different batches. - Ease in Supervision
The idle time of supervisors and workers is utilised due to continuous production. - Economic Products
The production in batches or bulk splits the cost and results in economical products.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages associated with batch costing are as follows:
- Customisation
Customisation in the products becomes difficult. - Error Detection
In batch production, any mistake or defect persists in the entire lot. It results in an increased number of defective products, which is a loss for the company. - Difficulty in determining batches
Arrangement of jobs homogenously is challenging in big manufacturing units. One faces difficulty in the creation of batch size.
Procedure of Batch Costing
You can follow the series of steps given below while preparing the batch cost sheet:
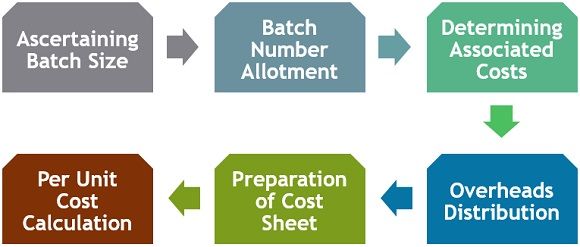
- Ascertaining Batch Size
The first step is to determine the size of the batch through production planning and control. - Batch Number Allotment
After that assign unique batch numbers for identification, management and accounting purposes. - Determining associated costs
The next step is to determine the costs and expenses associated with the production. It may include Direct Expenses, Material and Labour costs. Thereafter record these costs in the Batch Cost Card. - Overheads Distribution
Overheads are the indirect expenses incurred on production. The distribution of batches takes place among the batches considering a specific base. - Preparation of Cost Sheet
The Batch cost sheet is prepared after production to find out the cost of production. - Per Unit Cost Calculation
At last, calculate the per-unit cost of the product in the batches with the help of the formula given below:
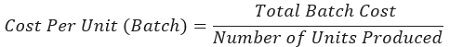
Economic Batch Quantity (EBQ)
Economic Batch Quantity is the optimum size of the batch that manufacturing units must produce. The size of the batch has a direct impact on the costs associated with it. We can categorize these costs into Setting-up costs and Carrying costs.
Economic Batch Quantity follows the approach of the Law of Increasing Returns & Economies of Scale.
By producing optimum quantities, manufacturers can decrease their production costs. As a result, it maximises the company’s profit.
You can use the given formula for calculating Economic Batch Quantity:
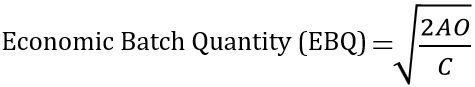
Where,
A = Annual demand for the product,
O = Setting-up cost per batch,
C = Carrying cost (cost of capital & storage)
Effect of Batch size on Setting-up Cost and Carrying Cost

Setting-up Cost: It is the cost incurred on setting up the machinery for production. The increase in batch size results in a decreased set-up cost and vice-versa.
Carrying Cost: It is the cost of carrying or storing the inventory produced. It also involves variable factors like:-
- Storage and Obsolescence of inventory
- Interest on locked-up capital
- Depreciation
The increase in batch size results in the increased carrying cost and vice-versa.
Importance of EBQ
- Production according to demand
- Reduced setting-up cost
- Less inventory accumulation
- Minimised clerical cost
Solved Example EBQ
Active ltd. has to supply 10,000 Hats per day. They can produce 12,500 Hats in a single time the production process occurs. The cost of holding Hats is 1 paise, and the setting-up cost of a production run is Rs.200 /-. How frequently should the company run the production process?
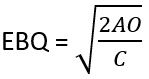
Where,
A = Annual demand for the product = 10000
O = Setting-up cost per batch = Rs.200
C = Carrying cost = Rs.0.01

Production per batch = 20000 units

Thus, Active ltd. should carry out production after every 2 days.
Solved Example of Batch Costing
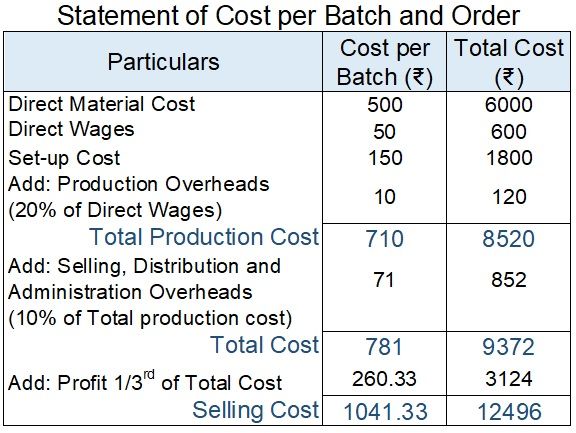
Anand ltd. is a sanitiser manufacturing company that produces 50 units of sanitiser at a time. They have received an order for 600 sanitiser bottles. The following costs are incurred to process a batch of 50 sanitisers:
Direct Materials Rs.500/-
Direct Wages Rs.50/-
Set-up cost Rs.150/-
Anand ltd. absorbs production overheads at a rate of 20% of direct wages cost. Add 10% to the total production cost of every batch for selling, distribution and administration overheads. It requires a profit margin of 25% of sales value.
Determine the selling price for 600 sanitisers.
Solution:
Number of batch = 600 units ÷ 50 units = 12 batches
Final Words
It is a form of specific order costing, in which the production happens in predetermined lots called Batches.
The cost is estimated for a batch which can be of different sizes depending on the situation and demand. The preparation of the Batch cost sheet enables us to find out the per-unit cost in a Batch.
The manufacturing units must find out the optimum size of the batches to reduce associated costs. Estimation of Economic Batch Quantity can attain this optimum quantity.
Leave a Reply