Do you know the majority misinterprets logistics with transportation?
Besides being the backbone of logistics, transportation is just a part of it. Logistics has a significantly wide scope. In this post, we will discuss various types of logistics available at our disposal.
Logistics is the integration of several activities. These activities are not universal but situational. As, the numbers of activities vary according to user requirements.
Therefore, we require the type of logistics best suited for specific situations. Additionally, the selection must be cost-effective and consider the 7Rs of Logistics.
The types of logistics also differ according to the various fields of logistics. Some common fields include:
- Sales Logistics
- Production Logistics
- Recycling Logistics
- Global Logistics
- Reverse Logistics
The logistics are a two-way process. Besides delivery, goods are also sourced back to the supplier for various reasons.
For Instance, presently e-commerce industry is quite trending. They give flexibility to the customers to try products at home.
In addition, customers can also return or exchange products at their wish. Thus, logistics is significant in the entire process, i.e. from product delivery to return.
Content: Types of Logistics
What is Logistics?
It is the mobilization of goods from the source (Manufacturer) to the destination (Final Consumer). Moreover, the flow of goods is directed towards the end user’s requirements.
The manufacturers desire to achieve a smooth flow of goods and accuracy in delivery.
In contrast, unplanned or fallible logistics may lead to an increase in cost. Also, it may reduce the customer’s post-purchase experience. Consequently, it reduces sales and resists future purchases.
Types of Logistics
Now, let’s understand the various types of logistics in length. Here, we have covered the major ones and grouped them as under:
- Direction of Goods Flow
- Inbound Logistics
- Outbound Logistics
- Reverse Logistics
- 3rd Party Logistics
- 4th Party Logistics
- Nature
- Business Logistics
- Military Logistics
- Event Logistics
- Service Logistics
- Level of Activity
- After-sale Logistics
- Distribution Logistics
- Disposal Logistics
- Domestic Logistics
- Global Logistics
Based on the Direction of Goods Flow
Inbound/Upstream Logistics
It involves the deployment of semi-finished goods and raw materials from suppliers to manufacturers. Generally, the transportation of raw materials takes place towards the plant or facility. Also, it includes any movement of resources within the firm.

For smooth functioning and delivery, continuous supplier coordination is necessary. As the raw materials are demanded at specific destinations and times.
Manufacturers aspects cost-effective transportation of raw materials within the facility. The major activities involved in inbound logistics are:
- Sourcing of Raw Materials
- Acquiring Raw Materials
- Storage of Raw Materials
- Delivery to production units
Example: An automobile manufacturer procures different parts of a motorcycle from external suppliers. The movement of parts from suppliers towards the production plant comes under inbound logistics.
Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics is significant for post-production activities. Here, the goods move from the manufacturer to the end user. It depicts the outflow of merchandise from the plant or facility.

For smooth functioning and delivery, coordination with distributors and transporters is essential.
The primary activities involved in outbound logistics are:
- Collection of the finished goods
- Packaging of Goods
- Storage of Goods
- Dispatching of Lots
- Distribution of Goods
Example: In the forgoing example, the delivery of the motorcycle to the buyer will come under outbound logistics.
Reverse Logistics
It is the reverse of inbound and outbound logistics. Here, the goods, raw materials or wastes move back to the source (plant or facility). It depicts the backward movement of goods, i.e. from destination to source.
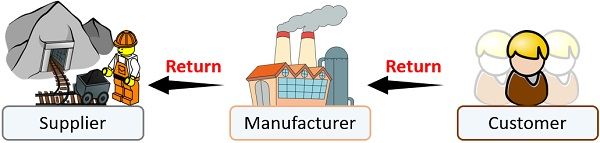
The need for reverse logistics arises during:
- Reuse or Recycle
- Return of the product
- Repair
- Processing
Example: As per our example, reverse logistics will initiate when the manufacturers return the defective parts to the suppliers. Also, when the customers apply for servicing of a specific part of the motorcycle.
Third-party Logistics
The manufacturers get engrossed in numerous complex tasks within their facilities. To achieve accuracy and efficiency, manufacturers outsource their logistical activities to external parties.
These parties are no one but firms offering logistical services to clients.
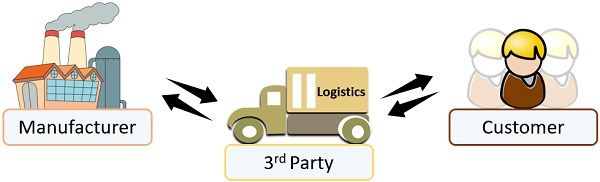
Parties involved in 3rd party logistics are:
- Manufacturer
- Logistics Company
- Consumer
Example: E-commerce companies like Amazon and Flipkart hire courier companies for product delivery.
Fourth-Party Logistics
Here the manufacturers outsource the complete logistical activities and their management. More precisely, the manufacturers hire external parties to look after the entire logistic process from beginning to end.
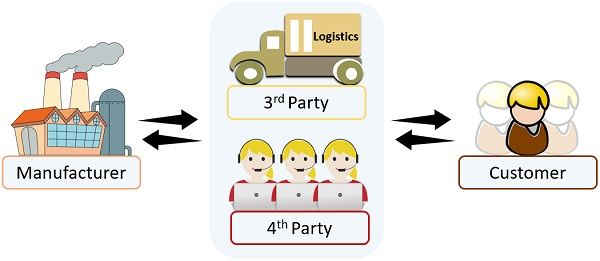
Parties involved in 4th party Logistics are:
- Manufacturer
- Logistic company (Distribution Team)
- Logistic company (Co-ordinating Team)
- Consumers
Example: Recall when you contact the delivery person for queries regarding your order from Nykaa. Your call connects to the courier service provider rather than Nykaa customer care.
The reason is, Nykaa has outsourced its entire logistical management to the logistics company.
Business Logistics
It is the most common type of logistics and is widely used by all firms, irrespective of size. It is the main ingredient of supply chain management that is concerned with the efficient delivery and storage of goods.

Example: Home delivery of Domino’s Pizza is an excellent example of business logistics.
Military Logistics
Military Forces require various resources to bring optimization to their core work. The major ones include the transfer of Men, Materials and Equipment.

Example: You might have seen the trucks passing by carrying the soldiers in them. Those trucks are a part of the military logistics. Besides this, the arms and ammunition are also transported to the battlefield.
Event Logistics
Organizing an event integrates many big and small activities. These activities require various inputs and resources like Catering, Tent, etc. The transportation of necessary resources at the venue comes under Event Logistics.

Example: Suppose you are organizing your birthday party and the invited guests are 100 in number. You will have to arrange the food and accommodation for 100 people. The deployment of such resources to and from the venue depicts event logistics.
Service Logistics
For services, logistics is relevant to facilitate the effective delivery of the service. Therefore, logistical activities involve mobilizing components or elements that support services.
Example: The bank representative coming to your doorstep to open a new account. He also brings all the required documents and tabs to complete the process.
Based on the Level of Activity
After-sale Logistics
It is similar to reverse logistics discussed in the previous sections. Here, we can observe the backward movement of the products (point of origin).
Example: Return or exchange of the old mobile phones to the company.
Distribution Logistics
This type of logistics is specifically used for the distribution of finished goods. It is a vital part of supply chain management. The typical flow of goods is directed towards retailers and wholesalers.
The activities that distribution logistics cover is as follows:
- Order Processing
- Warehousing
- Transportation
Example: Distribution of the FMCG goods to the local vendors.
Disposal Logistics
It deals with the settlement of the waste materials left after production. The waste can be accumulated either through the production of defective products or returned by the customer.
The waste generated needs to be treated and disposed of. For this purpose, the manufacturers need disposable logistics.

Example: The discarded tyres of trucks are transported for treatment. It is transformed into steel wires and fuel oil post-treatment.
Domestic Logistics
It refers to the movement of products within the country’s geographical boundaries. In other words, the flow of goods can occur anywhere within the country.
Example: Distribution of packed milk in the City, State or Country.
Global Logistics
Here, the transfer of goods happens across countries. Presently, most companies set up their production plants in one country. After that, transport the products to other countries for consumption.
Example: UAE is the largest producer of crude oil. They export oil to the rest of the world.
Logistics Management
Logistics management is the systematic management of logistical activities from beginning to end. It aims to meet the customer’s demand with the economic mobilization of goods.
With effective management firms can optimize their logistical activities. Some activities that are involved in logistics management are furnished below:
- Packaging
- Regular Security
- Warehousing
- Transporting
Final Words
The manufacturers must select a suitable logistic alternative considering costs and feasibility. Every activity involved in production to product delivery bears some cost. Consequently, it adds up to the price and makes the product costly.
Leave a Reply