Definition: A financial market is a marketplace where trading or exchange of various financial instruments and assets takes place. The price of these assets is dependant on its demand and supply in the respective market. All the financial and economic activities in a country are dependent upon these markets
Example
The most common financial market is Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). It initiates investments from small investors who are interested in real estate investing but lack sufficient funds for the purpose. These trusts pool in the funds collected from such investors into profitable real estate projects.
Content: Financial Market
Features of Financial Markets
A financial market is as vital to the economy as blood is to the body. To know more about it, let us understand its following features:
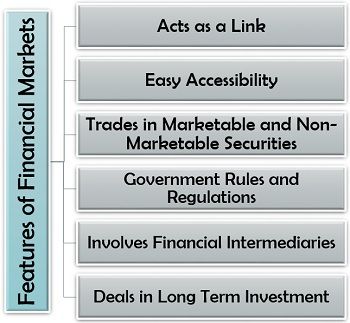
- Acts as a Link: Financial markets connect the investors to the borrowers and bridge the gap between the two for mutual benefits.
- Easy Accessibility: These markets are readily available anytime for both the investors and the borrowers.
- Trades in Marketable and Non-Marketable Securities: Financial markets initiate buying and selling of marketable commodities. Some of these are bonds, debentures and shares along with non-marketable securities like bank deposits, post office deposits and other loans and advances.
- Government Rules and Regulations: The government controls the operations of a financial market in the country by imposing different rules and regulations.
- Involves Financial Intermediaries: These markets require financial intermediaries such as a bank, non-banking financial companies, stock exchanges, mutual fund companies, insurance companies, brokers, etc. to function.
- Deals in Long and Short-Term Investment: For the investors, financial markets provide an opportunity of putting in their funds into various securities or schemes for short or long-term investing benefits.
Composition of Financial Markets
What all institutions come under financial market?
To answer this question, we must first understand that financial market consists of majorly two types of institutions. The first one is depository institutions, and the other is non- depository institutions.
Let us now classify each of them in detail below:
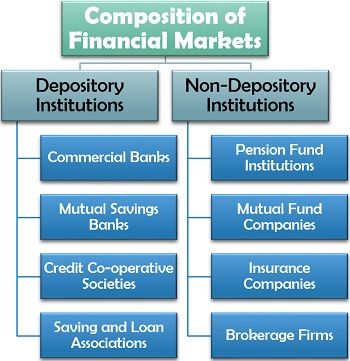
Depository Institutions
These institutions take deposits from the investors, i.e. individuals and organizations and further invest this fund into debt instruments or give out as loans in the debt market.
The four essential types of depository institutions are explained below:
Commercial Banks: The financial institutions which accept deposits from the individuals or firms (investors) and utilize this money to grant loans and advances are known as commercial banks.
Mutual Savings Banks: When the trade union members or the corporate employees of a particular institution cooperatively form a savings bank to benefit the members involved, it is called as a mutual savings bank.
Credit Co-operative Societies: It is somewhat similar to the mutual savings bank. In a credit co-operative society, the individuals from a particular locality or with the same objective come together to become members by investing and holding the shares.
These members can take loans or advances as and when required by them at a competitive price from such co-operative society.
Savings and Loan Associations: It is an association formed and managed by individuals who pool in their savings to provide the funds for mortgage loans and benefit from such advances.
Non-Depository Institutions
The institutions which function as financial intermediaries and not as banks, and hedges the risk of loss at the same time are called non-depository institutions.
Some of the well known non-depository institutions are as follows:
Pension Fund Institutions: The government and private sector companies deduct some amount yearly from the employees’ salary to deposit it into the pension schemes. These pension fund institutions further block this amount into beneficial long-term assets.
Mutual Fund Companies: These companies accept deposits from various small investors every week or month or year. Then, they invest it in a different class of assets and generate profit for such investors.
Insurance Companies: The company which provides security from several risks, by acquiring a monthly or yearly premium from the insured person or business entity is known as an insurance company.
These companies invest the premium collected from life insurance policies into long-term assets or loans and advances. Whereas, the premium from fire, theft, accident, medical and other such insurances are invested in short-term opportunities.
Brokerage Firms: The firms which deal in the equity or debt market to make commission or brokerage by facilitating transactions between the buyers and the sellers is known as a brokerage firm.
Types of Financial Markets
Any market which deals in financial assets is a financial market. The following are the different types of financial market:
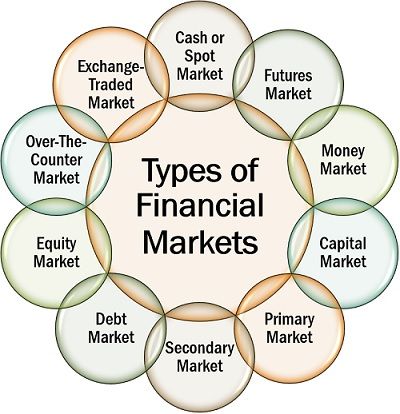
Cash or Spot Market: It is a spot or real-time market where all the trading and transactions are executed or take place immediately.
Forward or Futures Market: Unlike cash market, in future and forward markets, the execution of the transaction takes place on a future date. Here, the price of securities or transaction value is decided at present to minimize the loss to either party.
Money Market: The financial market which provides very short-term loans or advances having a maturity period within a year of issue is termed as a money market.
Capital Market: This market exists for the trading of medium and long-term financial instruments between the individuals and financial institutions.
Primary Market: In a financial market, when the listed companies issue new securities, or new companies take entry with new stocks, it is called as a primary market.
Secondary Market: It is commonly known as the stock market. It is a financial market where the individuals, brokers, companies, banks and various other parties are involved in trading of existing (already issued previously) securities.
Debt Market: The financial market which facilitates the trading of debt instruments or instrument with fixed interest such as bonds, fixed deposits, debentures are called debt market.
Equity Market: This market deals in financial instruments or securities whose value keeps on fluctuating and the claimant receives the amount which persists on the date of redemption.
Exchange-Traded Market: The market where trading of call, put, and futures options take place on an organized futures exchange in a systematic manner is called an exchange-traded market.
Over-The-Counter Market: Unlike an exchange, in this unregulated market, trading of various securities such as exotic options and derivatives, swaps, credit derivatives, forward contracts take place directly between the two parties without any involvement of the intermediaries.
Functions of Financial Markets
The financial markets play a significant role in the economy and perform some of the essential functions. Let us now discuss each of these functions one by one:
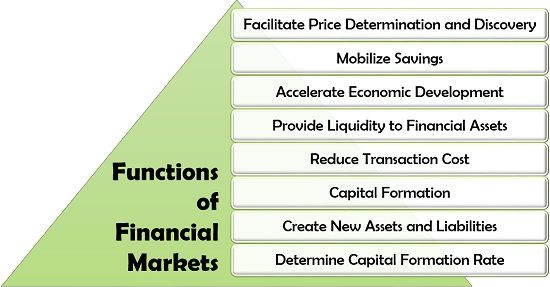
- Facilitate Price Determination and Discovery: The demand and supply of the various securities in the financial markets regulate their price.
- Mobilize Savings: The financial markets initiate the proper utilization of individual savings to generate profit by investing it in the right place.
- Accelerate Economic Development: When savings are put into use for setting up new businesses and generating revenue, the economy of the country grows parallel.
- Provide Liquidity to Financial Assets: The financial market facilitates the quick conversion of securities or commodities into cash as and when required by the investor.
- Reduce Transaction Cost: Since the information of the financial instruments or assets is available free of cost on the financial markets, it lowers the cost of acquisition and selling of the securities.
- Capital Formation: Raising capital from idle savings for the growth of business, infrastructure and economy is termed as a capital formation which is an essential function of financial markets.
- Create New Assets and Liabilities: Financial markets also encourage the creation of new assets in the form of investments and liabilities through borrowings.
- Determine Capital Formation Rate: As we know that capital formation is one of the functions of financial markets. The demand and supply of securities determine their capital formation rate to encourage people to enter the market.
Conclusion
Financial markets are the backbone of a country’s economy and are essential for the growth and development of the nation.
These markets involve a massive amount of risk. But when done wisely and strategically, they are highly beneficial for the individuals, business firms, financial institutions, brokers and various other parties involved in it.
Anonymous says
Great article with precise content indeed. Thank you for sharing.
Trade Finance Australia says
Thank you for the information; it is much better explained than on most websites. I appreciate you sharing.