Definition: Training is a critical strategic tool usually introduced as teaching specific skills and conducts. It is a significant sub-system of human resource management and is a specific developmental function of the company. For the stability of the company, it is necessary that the individual must flourish and develop through training.
Various managers admit that regular learning in today’s market is requisite. They understand that they are in the information age. They need a competing high-performance enterprise. Training actions can revolutionize enterprises with presenting special skills to the personnel, not only to raise safety and work rate but also it leads to greater job satisfaction, which shows-up in improved corporate achievements. It serves employees the skill sets that support them to build timely, sensible decisions that they pay off both the customer and the enterprise.
Content: Training
Methods of Training
A vast range of training methods is accessible to an enterprise to guide its personnel. Based on the teaching goals and demand assessments, a suitable method may be selected. There are two alternatives available to an enterprise at the moment of deciding in a training program. It can either outline its plan or get an available outside package and make an alteration in it to satisfy the purpose and necessities of its training programs.
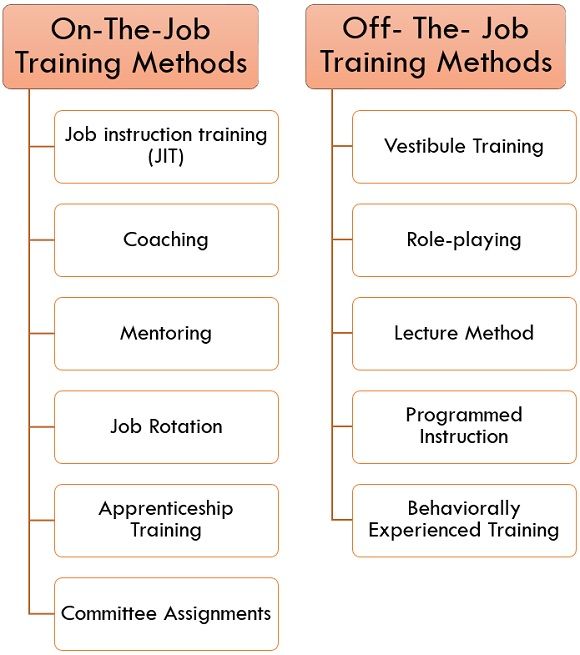
As shown in the figure below, it is divided mainly into two categories, i.e., On-the-job training and Off-the-job training. We will now explain these methods in detail.
On-The-Job Training Methods
1. Job instruction training (JIT)
The job instruction method is a four-step teaching process including formation, demonstration, operation try out and follow-up. It is used mainly to train workers on how to do their prevailing jobs. A trainer, administrator, or associate acts as a coach.
The four-steps adopted in the method are:
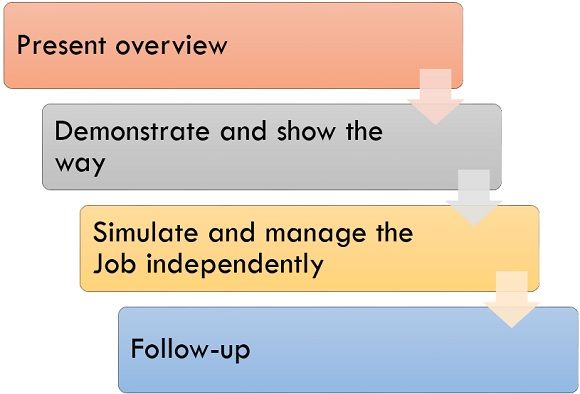
- Present Overview: The trainee meets a synopsis of a job, its aims and its desired results, with a definite focus on the purpose of training.
- Demonstrate and Show the Way: The trainee illustrates the job to give the personnel a design to copy. The trainer exhibits the correct way to manage the task.
- Simulate and Manage the Job Independently: On the side, the personnel are authorized to copy the trainer’s way. Presentations by the trainee and actions by the trainee reciprocated until the trainee directs the right way to manage the job.
- Follow-Up: In this stage, the trainer examines the trainee’s job repeatedly after the training program is ended to restrict bad work habits from improving.
2. Coaching
Coaching is a manner of routine training and responses given to the employees by recent supervisors. It includes the on-going process of learning by actions. It can be determined as an informal, random planning and development exercise administrated by supervisors and associates. In coaching, the trainee explains things and answers queries, he throws light on the reason behind kinds of stuff concluded and the manner they are done. Indeed, coaching may be a troublesome job in that the instructor may not possess essential skills to instruct the learners in an organized way. Consistently, doing a full day’s work can be more relevant than setting the trainee’s on track.
- When to manage coaching productively?
Coaching may be put to beneficial use when:
- Personnel manifests a new competence.
- Personnel conveys an interest in a distinctive job inside the company.
- Personnel solicits evaluation.
- Personnel is asserting low self-esteem, breaching company policies, or rehearsing performance complications.
- Personnel wants help accompanying a new talent following an explicit training program.
3. Mentoring
Mentoring is a connection in which a leading manager in a company acquires the accountability for educating junior personnel. Technical, social, and political skills are usually transferred in such a connection from the more knowledgeable person to their juniors. A guide is a teacher, advisor, builder of skills and abilities, manager, mentor, and most significantly follower and organizer in respect of the perspective, that the young person has almost the class of life he needs as an adult. Mentoring in India is established on the conventional guru-shishya relationship, where the guru exerts everything to flourish the personality of shishya, contributing emotional backing, and supervision.
4. Job Rotation
This class of training includes the activities of learner from one task to another. It assists him to acquire a general perspective of how the company functions. The function of job rotation is to support trainees accompanying broader administrative aspect and a higher realization of various working areas along with an improved sense of their career, goals and passion. Apart from alleviating monotony, job rotation approves trainees to form a harmony with a broad sphere of individuals inside the company, promoting future assistance amidst departments. The cross-trained employee provides a tremendous amount of adaptability for a company when promotions, relocation or restoration becomes necessary.
5. Apprenticeship Training
Most skilled employees like carpenters, electricians are trained by way of formal apprenticeship educational programs. Apprentices are learners who invest a recommended time functioning with an experienced mentor or trainer. Articleship and graduate fellowship are complementary to apprenticeship as they also need high levels of assistance from the trainee. A graduate fellowship is a type of on-the-job training that generally merges job training with lecture room guidance in schools, colleges, and various institutions.
6. Committee Assignments
In the path of the committee assignment, trainees are endorsed to handle problems which the management is facing. The company expects a relatable solution for the problem from the trainees, and by hiring the deserving candidates, the committee gives their employees an acquaint experience and gives them the information which helps them to recognize company’s governing mechanisms and issues.
Off- The- Job Training Methods
Off -The- Job Method detaches the trainees from the job status, and the company tries to attract them upon researching. However, its trainee’s job is to learn what the company is teaching and not to panic in any situation, he should learn every aspect which can help them in his role in future; however, the apprentice has hope for freedom of expression. The methods used for off-the-job training are as follows:
1. Vestibule Training
Clerical and semi-skilled employees of the company are trained in this method for a few days. The company provides the equipment’s for such training, and these kinds of training are provided in classrooms, in which trainees have to face various work situations which they really need to face while working in the company.
2. Role-playing
In this training, the company tries to build the imaginary situations on which the trainee has to work and teaches the trainee how to behave and perform their work on being on that position in a realistic situation. The trainees play various roles such as manager, clerk, supervisor, accordingly with their work profile. Role-playing is conducted to develop the quality of maintaining inter-personal relations in the company.
3. Lecture Method
This method is most common and generally used by every organization for giving training to the recruited employees. The trainee can provide vast information regarding the company’s working policies to a various number of employees altogether in this method which saves time as well as the cost of the company. However, it also has a disadvantage that some trainees may understand what the trainer has taught in his lecture, while some may not learn effectively.
4. Programmed Instruction
This approach has become famous in recent years. The topic to be learned is discussed in a sequence carefully to prepare subsequent units. These units are organized from elementary to more complicated levels of teaching. The trainee inspects these units by solving queries. Thus, this method is costly and stagnant.
5. Behaviorally Experienced Training
A few training programs aim at spontaneous and developmental learning. In this place, personnel can learn the manner of conducting oneself by role-playing in which the role participants try to act their role in that matter of a case, as they confer in real-life scenes. Sensitivity training is an example of the method used for spontaneous learning. The target of the experimental approach is accomplishing a group mechanism, an improved understanding of individuality and others.
Conclusion
Training is a programmed procedure to customize attitude, ability or proficiency by way of learning actions to obtain adequate performance in a task or sphere of talk. The training also enhances job proficiency of the employees.
Leave a Reply