Definition: Mezzanine Financing is a non-traditional, alternate source of finance that inherits the characteristics of both Debt and Equity.
Besides, it is a subordinated debt that is unsecured in nature. In addition, it is not backed by any collateral security. It belongs to private equity and is prominent among venture capitalists.
However, it yields higher returns than senior debts. The reason is that it charges a higher rate of interest considering the risk factor.
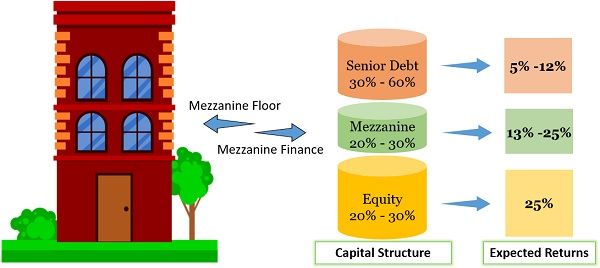
The inspiration behind its name is taken from the mezzanine floor of a building. And the word ‘Mezzanine‘ means in the middle.
Note: A mezzanine floor is a small story lying between two floors, usually the Ground and First.
Therefore, in the firm’s capital structure, the layer of mezzanine debt surfaces between Senior Debt and Equity. In short, we can say that floor symbolizes equity, whereas the ceiling stands for debt.
Mezzanine financing has filled the void existing between conventional financing sources. Thereby, creating an option for the companies to acquire additional capital.
With mezzanine debts, borrowers can generate sufficient capital without liquidating ownership. However, they opt for this option after exceeding their debt capacity.
Usually, the borrower repays this debt as a bullet payment rather than Amortization. But, they have to pay a comparatively higher cost of capital.
The instruments are offered along with Warrants to secure the investors’ interest. These warrants empower the lender to convert to equity in case of default.
Generally, the borrowers utilize this fund mainly for Growth and Expansion.
The lender performs little or no due diligence during mezzanine Financing. On the other hand, the borrower does not have to put collaterals as security.
Content: Mezzanine Financing
- Borrower Perspective
- Investors Perspective
- Forms of Mezzanine Investment
- Warrants in Mezzanine Finance
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Mezzanine Financing in Real Estates
- Example
- Final Words
Borrower Perspective
The Mezzanine Borrower is the one who seeks the Mezzanine Capital. And the fund generated through this medium is known as Mezzanine Debt/Loan.
Owners prefer this financial source when they are unwilling to hand over business control to the lender.
Reasons to Acquire Mezzanine Capital
Following are the reasons to choose mezzanine finance over other capital sources:
- Shortage of Collaterals
- Higher Balance Sheet Leverage
- Shorter Operating History
- Other Transactional Reasons
Uses of Mezzanine Finance
The mezzanine borrower may use the generated capital for the following purposes:
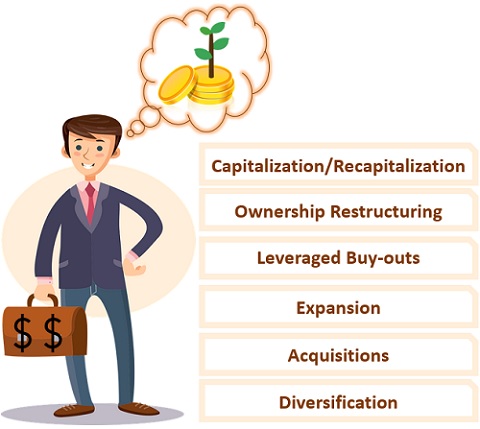
- Capitalization and Recapitalization
- Ownership Restructuring
- Leveraged Buy-outs
- Expansion
- Acquisitions
- Diversification
Costs Associated with Mezzanine Debt
The borrower has to bear the following costs in acquiring this debt:
- Arranging or Underwriting fee (0.5 to 2%).
- Commitment fee (1 to 3%).
- Up-front fee.
- A periodic fee that depends upon the periodic gross revenues.
- Also, some costs for premature exits.
Note: These fees are chargeable on the transactional value.
How to acquire Mezzanine Debt?
The borrower can acquire this debt from the following platforms:
- Public Market
- Insurance Companies
Investors Perspective
A mezzanine lender is the one who provides subordinated debt to the borrowers. They avail funds to the companies with positive cash flow seeking capital for growth.
You might be thinking, why the investors invest in such unsecured instruments?
The reason for the same is that they can generate a higher rate of return in comparison to other instruments. However, the lenders prepare a contract carrying Covenants & Warrants to protect their interests.
These warrants transfer a portion of the equity shares to the lender if the borrower defaults. Consequently, the lender can settle his loss by selling his stake in equity shares.
Perks of becoming a Mezzanine Investor
Given below are the benefits a lender enjoys through mezzanine investments:
- Cash Coupon (4 – 6% per annum)
- Payments in Kind (4 – 6% per annum)
- Stake in the Equity Share Capital (after exercising warrants)
Rate of Return generated from Mezzanine Debt
The lenders can generate a return between 15 to 30% out of mezzanine investments. However, we can disintegrate it as:
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR) – 13 to 18% per annum
- Targeted Return – 15 to 20% per annum
Considerations
Before making such capital investments, the lenders review the following constraints:
- Companies’ capabilities to settle the debt in 3 to 5 years.
- Quality of the personnel managing investments.
- Management abilities and operating efficiency.
- Track record in analyzing future efficiencies.
- Sufficient and positive cash flow.
Prominent Mezzanine Investors
Given below is the list of some prominent players in the field of mezzanine financing:
- Dedicated Mezzanine Funds
- Insurance Companies
- Business Development Companies
- Hedge Funds, etc
Forms of Mezzanine Investment
Any instrument that allows loan conversion into equity will come under Mezzanine Investment. Some common forms of such instruments are listed below:
- Preferred Stock
- Debt Instrument
- Privately Negotiated Subordinated Debt
- Subordinated Notes
Besides these, Preferred Stock and Subordinated Debt are extensively used.
In addition, the investors can generate a decent return by inculcating the following components in the warrants:
- Cash Interest
- Payable in Kind (PIK’s) interest
- Equity Ownership
- Agreement fees
Documentation
The documentation in mezzanine investments is similar to other instruments. Like –
- Loan Agreement in case of Mezzanine Debt
- Certificate of Designations in case of Preferred Stock
Warrants in Mezzanine Finance
The mezzanine finances are offered with Warrants. It is an important part of mezzanine finances that protects investors’ interests. It is a set of conditions specified with the contract.
However, the investors may also opt for a Warrantless Mezzanine Capital. In simple words, lending without any warrants, options & conversion rights.
In this case, the investors prefer PIK components over Cash Interests.
Advantages of Mezzanine Financing
The benefits of mezzanine finance for Investors and Borrowers are as follows:
For Investors:
- It has a scope to generate equity-like returns.
- Opportunity to get holding in the equity shares.
For Borrowers:
- It is the saviour when you have exceeded asset-based loan and bank credit limits.
- Tax benefits to the borrower.
- Helps in the expansion and acquisitions.
- Doesn’t necessitate immediate loan repayment.
- It does not involve a transfer of ownership.
- It has the scope of negotiation and is flexible in nature.
Disadvantages of Mezzanine Financing
Following are the disadvantages of mezzanine financing:
- Unsecured and risky investment.
- Expensive than senior debt.
- It may lead to equity dilution as a consequence of the warrant.
- It involves a high cost of capital.
- Repaid post repayment to the senior debtors.
Mezzanine Financing in Real Estates
It is quite popular in the field of real estate as well. The borrower experiences less burden in their ongoing cash flows than other sources.
The real-estate operators and developers majorly use it. And, in real-estate projects, it can provide around 10 to 40% of capital.
Unlike other sources, the real-estate mezzanine lenders expect equity holding in the property.
Example of Mezzanine Financing
Suppose, Alice owns a Café and plans to shift it to a bigger place. But, she cannot apply for a loan as she has already exceeded her credit limit.
Therefore, she decided to acquire mezzanine debt from a mezzanine lender. However, the lender agreed to certain conditions mentioned in the warrants.

Consequently, she raised a loan of 60 k Dollars from mezzanine debt with a warrant. The warrants specify the following conditions:
- 5% Cash Interest
- 11% Payment in Kind (PIK)
- 5% fully diluted ownership in the Restaurant
Final Words
By far, Mezzanine financing has grabbed a niche in the financing field. It is an alternative financing option that falls under the private equity category.
As discussed in the post, companies need capital for growth and expansion. In contrast, the investors can earn a decent return between 15 to 30%.
Leave a Reply