Definition: Production Planning and Control or PPC is a managerial function that integrates and coordinates the production processes to accomplish predetermined objectives. It establishes schedules to plan the entire production and assure efficiency in processes and resources.
Basically, it determines:
- The requirement of the production facilities.
- Accommodation of the facilities in the available space.
- Production of desired product at the expected cost.

PPC integrates all the activities participating in the manufacturing process. Concurrently, the managers focus on four core elements, i.e. Quality, Quantity, Cost and Time.
Besides, it helps in achieving an uninterrupted materials flow. It ensures the availability of the materials at the Right – Time, Place and Quantity. For this purpose, it establishes Master Production Schedules and Routes.
Thus, it is said to be the Brain and Nervous System of the production system.
PPC primarily focuses on efficient and economical production. Also, it assists each activity involved in converting the raw materials into a finished product.
So, the managers strive to implement the production plan religiously. In addition, the managers also exercise control for its successful implementation.
During the planning phase of PPC, the managers must answer the following questions:
- What to Produce?
- How to Produce?
- Where to Produce?
- When to Produce?
- Who will Produce?
- How much to Produce?
Note: The complexity of PPC increases with the increment in the number of products or product mix.
Content: Production Planning and Control
- Objectives
- Functions
- Elements
- Importance
- Phases of PPC
- Steps
- PPC and Production Processes
- Primary Documents Required in PPC
- Jobs in PPC
- Difference between Production Planning and Production Control
- Final Words
Objectives
The objectives of production planning and control are furnished below:
- Optimum Resource Utilization: Production planning ensures the best use of the Materials, Men and Machinery.
- Consistent Production Flow: PPC aims to achieve consistency in the production flow. This is because, it helps in optimization and waste elimination.
- Quality and Cost: It ensures the production of quality goods at the least cost.
- Efficient Production: Through PPC, one can bring efficiency at all stages of the production system.
- Materials Management: It optimizes the use of materials and resources by creating plans and schedules.
- Fix Bottlenecks: It assists managers in identifying and fixing the bottlenecks in the process.
- Scheduling: The planning part of PPC facilitates the creation of schedules for uninterrupted production.
- Reduce Idle and Set-up Time: Routing in PPC helps avoid machine idle time and cuts setup time.
Functions of Production planning and control
Majorly it performs two functions –Planning and Controlling. However, it also serves the following functions:
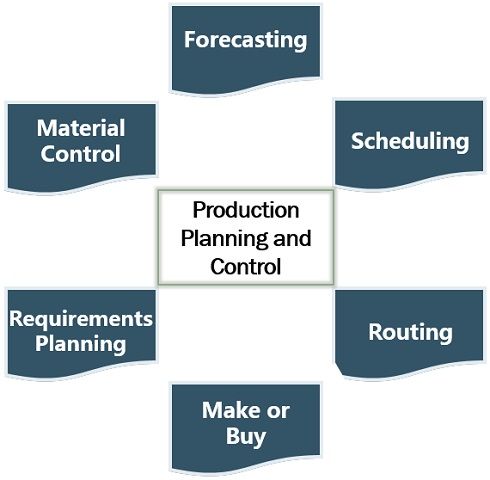
- Forecasting: The manufacturers make future projections for creating schedules.
- Scheduling: It provides the schedule or timetable for manufacturing activities. Therefore, meeting delivery commitments and completing production on time.
- Routing: PPC describes the flow of work and the sequence of production activities.
- Make or Buy Decisions: It plays an important role in taking make or buy decisions. Generally, these decisions are taken in the planning phase of PPC.
- Requirements Planning: PPC determines the exact quantity of materials required for production. Also, it assures the availability of materials whenever needed.
- Material Control: Besides availability, it also ensures the best use of resources and eliminates waste.
Elements of Production Planning and Control
The concept of PPC is made up of two elements, i.e. Production Planning and Control.

Production Planning
Production planning is the base of the PPC. It involves forecasting the requirements and making necessary arrangements for future production.
The planning process begins with data collection and ends with the development of schedules. During planning, managers consider various elements like product mix, volume, design, etc.
The nature of decisions varies at different levels of management as follows:
- Top-level management – Strategic Decisions
- Middle-level management – Tactical Decisions
- Lower-level management – Operational Decisions
Besides, the production planning consists of the following sub-elements as follows:
- Planning
- Routing
- Scheduling
- Loading
Production Control
Production control takes over from where the scope of planning ends. It inspects the operations and actual implementation of the production plan.
Because, the actual operations may deviate from the schedule. So, there is always a scope for improvement between the planned and actual application of processes.
Thus, we need to perform production control to facilitate smooth production.
Like Planning, it also includes some sub-elements as follows:
- Dispatching
- Follow up
- Inspection
- Corrective
Importance
Production planning and control benefit the manufacturing units in the following ways:
- It helps in eliminating unnecessary costs through proper estimation.
- It assists in availing better customer services that may generate re-orders.
- PPC leads to a reduction in inventory management costs.
- Employment of the right resources at the right places.
- Better coordination between various activities at the plant.
- Smooth flow of production processes.
- Avoid wastage of resources.
Phases of PPC
The overall process of PPC can be divided into three phases as follows:
- Planning Phase
- Action Phase
- Control Phase
Planning Phase
This stage of PPC is concerned with decision-making and outlining the production process. It is subdivided into Pre-Production Planning and Actual Production Planning phase.
Pre-Production Planning covers the following activities:
- Product Development
- Production Design
- Forecasting
- Aggregate Planning
- Master Scheduling
- Materials Requirements Planning
Whereas, actual production planning covers:
- Process Planning
- Routing
- Materials Planning
- Tools Planning
- Loading
- Scheduling
Action Phase
The second stage of PPC is the Action Phase. In this, the workers are instructed to begin production. And, the major activity performed in this stage is Dispatching.
Control Phase
The third and last stage in the PPC is the control phase. This phase monitors the production activities and takes corrective actions whenever necessary. It includes the following activities:
- Progress Reporting
- Data Processing
- Corrective Action
- Expediting
- Re-planning
Steps involved in PPC
One can follow the series of steps given below for Production Planning and Control:
Step 1: Planning
The first step in PPC is planning. In this, the managers prepare the production plans and schedules. During planning, the managers cover each aspect of production.
Step 2: Routing
The next step after planning is deciding the path or flow of the activities. Besides, it also determines the place and person for performing the activity.
Step 3: Scheduling
The third step is specifying the order and duration of the production activities. These schedules can be in the form of master schedules, operations schedules, etc.
Step 4: Dispatching
In this step, the production process begins as per the created routes and schedules.
Step 5: Follow-up/Expediting
And, the last step in PPC is Follow-up or Expediting. Here, the supervision of the overall production takes place. The managers identify and fix the bottlenecks of the production system.
Production Planning and Control and Production Processes
Mass Production
In this, production happens using assembly lines and workstations. However, in mass production, PPC is less complex.
This is because, the cycle time once fixed, does not change frequently. Consequently, the production rate is high and doesn’t need specialization.
Job Production
Here, the production process is based on the various jobs performed. It is like the waiting line system and sometimes even leaves machines idle. This triggers the need for Production Planning and Control.
However, PPC becomes complex due to frequent setup, sequencing, prioritizing changes, etc.
Batch Production
It includes production in lots or small quantities. The determination of batch size is based on two major factors, i.e. setup cost and carrying costs.
The manufacturers using batch production needs an elaborative PPC. As it is an expensive and time-consuming process.
Primary Documents Required in PPC
PPC considers the following reports for the functioning and coordination of different departments:
- Demand Forecasts Report
- Customer’s Order
- Estimated Sales Figure
- Long Term Production Plan
- Production Budget
- Master Production Schedule
- Work Orders
- Inventory Reports, etc
Jobs in PPC
Following are some of the job roles that one can apply for in the field of PPC:
- Production and Quality Engineer
- Manager Production Planning and Control
- Production Planner
- Production Planning Executive
Difference between Production Planning and Production Control
These two functions of PPC work parallel to each other and facilitate production. However, these differ from each other in the following ways:
| Basis | Production Planning | Production Control |
|---|---|---|
| Deals with | Planning the production process | Implementation of the plan |
| Participation in the process | Pre-production Activity | Activated during ongoing production |
| Function | Planning, Coordination, Scheduling | Monitoring, Control and Follow-up |
| Scheduling | Creation of schedules | Ensures working as per schedule |
| Focuses on | The availability of resources | Performance and corrective actions |
Final Words
All in all, the prime focus of PPC is the optimization of materials, people and facilities. Consequently, manufacturers plan, route and control the production processes.
Thus, the manufacturers can generate desired results and reduce costs through PPC.
Leave a Reply