Definition: Product Decision in marketing refers to the company’s mindful decisions, major or minor regarding their product. It ranks first among the 4Ps of Marketing- Product, Price, Place and Promotion. Organizations take these decisions to attain their objectives and become profitable in the long run.
Product Decisions are vital marketing decisions to be made at various levels. These decisions broadly cover:
- New Product Development
- Modification or Elimination of existing ones
- Variants and Visual elements
- Product Mix and Line, etc.
However, Warehousing is an activity that does not come under the span of product decisions. This is because its core function is the storage of goods for selling and distribution as and when required.
The factors affecting product decisions are:
- Growth
- Market-share
- Cash flow
- Profitability
Content: Product Decision
- What is a product?
- Layers or Levels of Product
- Major Product Decisions
- Product Marketing Ethics
- Final Words
What is a product?
Anything of value that fulfils the requirement of the end-user is known as a Product. It can be goods or services, tangible or intangible, physical or psychological. The customers and competitors largely depend upon the products offered by the company.
Layers or Levels of Product
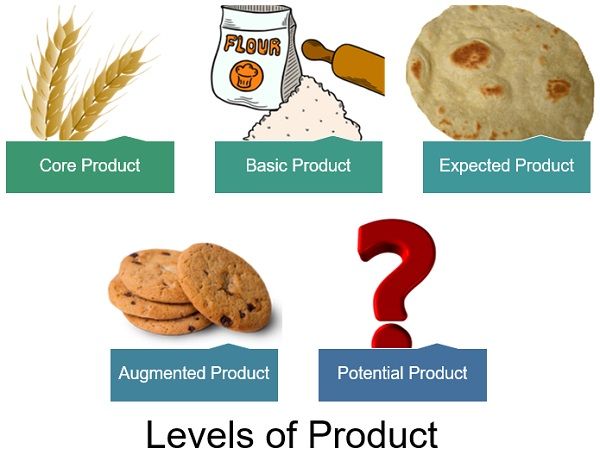
- Core or Generic Product
It is the raw product that satisfies the customer’s primary need. The core product is at its raw form, not bearing any brand name and remains undifferentiated.
For example: – Wheat is a grain that one can consume. - Basic Product
The core products differentiated from the rest become the basic product. It adds some necessary features to the products like Brand Name, Packaging and Label, etc.
For example: – Fortune Chakki Fresh Atta (wheat flour). - Expected Product
These products include the key features that customers look forward to. It also contains standard features that a product should have.
For example: – Chapati is prepared from wheat flour. - Augmented Product
To differentiate products from competitors, companies add distinctive features to them. These additions depend on the market survey conducted for the product. They try to create a Unique Selling Proposition (USP) for their products.
For example -Brown Bread and Cookies. - Potential Product
It refers to all the possible features that a product can have in the future. These features depend on the market conditions and economic changes.
Major Product Decisions
The major product decisions, which are also the types of product decisions, are discussed briefly below:

New Product Decision
A new product incorporates the elements of newness and varies from the existing ones. It may include new features, qualities or be introduced differently. Besides, adding new products can result in growth, profitability, increased market share and more.
To remain profitable and maintain sales, organizations need to launch new products. However, the products may fail, so the marketers must take new product decisions wisely.
The product decisions may include:
- Original Product
- Improved Product
- Modified Product
- Development of Product
- Launching Products, etc.
Product Mix
It refers to the aggregate range of products that a company owns. In other words, the total number of products that a company offers for sale is the product mix of the company.
Product mix decisions depend upon the following four characteristics:
- Length
- Width
- Depth
- Consistency
There are various decisions the marketers have to take regarding the product mix. It may include:-
- Expansion
- Contraction
- Product Differentiation
- Deepening and Alteration, etc.
Product line
This refers to a range of closely-related products belonging to the same class. They are sold to the same customers, having identical attributes marketed by the same distribution channel but for different segments.
The product decision relating to a product line are:
- Line Stretching
- Line Filling
Design
It indicates the appearance or personality of the product. The marketers have to decide whether to go for the standard design or the creative design.
Changing the product’s design may be effective but can be risky too. The customer may or may not like the design and face problems while using the product.
Branding
Branding is one of the vital decisions taken under product decisions. It involves the visual and symbolic elements of the product.
The marketers distinguish the product using:
- Band Name
- Trade Marks
- Logo
- Brand Marks, etc.
Packaging
Packaging is the outermost covering of the product. It enables product protection, conveys information and creates sale appeal. And is not restricted to just the safety of the product.
Packaging has evolved as the medium of marketing. Marketers use packaging to reposition or renovate their products.
Packaging decisions include:
- Size
- Design
- Innovation
- Aesthetics
- Convenience
- Material
- Environmental factors
Labelling
The label is a part of the packaging. It contains all the essential details about the product in written form. Also, it conveys information regarding performance, features, quality and price, etc.
The marketers must perform an in-depth analysis at the time of Labelling. It is a medium of communicating with customers. Vital decisions based on labelling are:
- Brand Label
- Descriptive Label
- Grade Label
- Informative Labels
Positioning
Positioning builds a unique image of the product in the target audience’s mind. Also, it differentiates products from others using benefits and attributes in the customer’s mental space.
The product decision concerning positioning are:
- Segmentation
- Differentiation
- Aggregation
Support
Support or Customer Support is the company’s added benefit for the customers. It may be offered to the end-user by after-sale services, grievances management, and so on. It assists in creating loyal customers and recurring sales.
Different customer support services possess varied cost structures. Therefore, marketers must make decisions to reduce costs and improve customer experience.
Product Marketing Ethics
Product marketing ethics is a minor term than Marketing ethics. The marketers must pay attention to the following ethical issues while marketing:
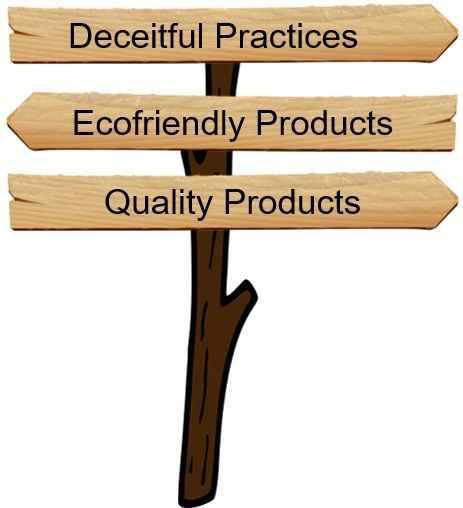
- Deceitful Practices: The marketers often put faulty or low-quality products for sale without informing customers. They also ask for additional charges in the name of customer services.
The customers acknowledge it while consuming and are left with no other option than to pay for it. - Ecofriendly Products: The companies must carry out production considering the statutory guidelines for pollution control. The product must not harm the environment at any stage, from production to post-consumption.
The marketers should convey instructions on the packaging about product disposal. - Quality Products: The companies should produce quality products and disclose complete details. They should contain important information like ingredients, uses and precautions.
Also, the packaging must mention all the areas of concern related to the product.
Final Words
While market planning, product-related decisions are vital decisions the marketer makes. It includes all the critical decisions for existing and new products, from development to launch.
The marketers must decide the compelling product mix, packaging, branding, labelling and positioning. It enables organizations to remain competitive and thrive in the long run.
Jahnavi says
Super simply informative more to me.
Manveer says
Such a beautiful information thnks alot……..carry on this work