Definition: Differential pricing, also known as dual pricing is a two-price system or segmented price system in which the seller charges different prices for the same product for different buyers. With respect to demand and supply in the market, this system sets us a free market system.
The basic concept of this system is that it is a fluctuating price system, i.e., some part of the output is sold at regular prices, whereas some part of the output is allowed to be sold at fluctuating prices according to the consumer’s buying capability and by any other market forces such as purchase timing, etc.
Content: Differential Pricing
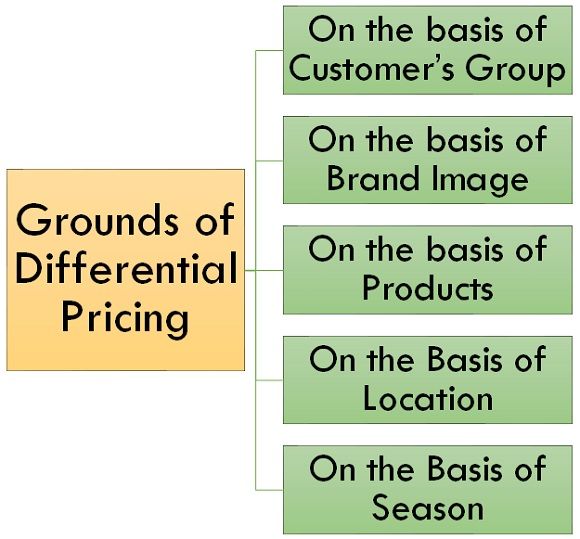
Grounds of Differential Pricing
Following are some grounds on which the differential pricing is based on:
-
On the basis of Customer’s Group
Market has many customer’s groups with different demands or requirements for which they are ready to pay. Thus, differential pricing system creates it as a group of deciding the required product price by every different sector of the group. It may vary for each customer group based on the purchasing power of the groups.
For example, many companies provide discount coupons to their loyal or regular customers. By applying such coupons, the customer’s get the product at a discounted rate, whereas all other customers will get the same product at a regular rate.
-
On the basis of Brand Image
The image of a brand in every different region may differ according to the choice and taste of the regional consumers. There is a huge possibility that the brand having a wonderful image in the eyes of the customers of one state or country might not have that much good image in the eyes of the customers of the other state or country.
The company has to differentiate the prices of the same product according to the demand and image of the product. The country or state where it has a good image can provide relatively much higher prices than other countries.
-
On the basis of Products
Various products in the market have various variants, and every variant of a single product has a different price.
For example, A mobile manufacturing company manufactures various variants of the products with various different features and prices. A customer can buy an affordable variant according to their budget and requirement. However, in few variants, some premium variants are also available for which the companies charge some specific amount other than normal product prices.
-
On the Basis of Location
The companies operating in rural areas might charge more than the companies operating in urban areas for similar manufactured products as the price includes all the other expenses related to the product until it reaches the final consumer, such as transportation cost. The farther the distance will be from the consumer’s location, the higher the price will be. Thus, the price of the same product may vary according to the multiple selling locations, especially in the case of international selling differential pricing plays a vital role.
-
On the Basis of Season
Let us understand it with an example of a raincoat. The prices of the raincoats will be high in the rainy season because of the high demand and need for a product, whereas if you buy a raincoat in any other season, there might be high chances that you get it at a discounted rate.
Advantages of Differential Pricing
Following are some of the advantages of differential pricing:
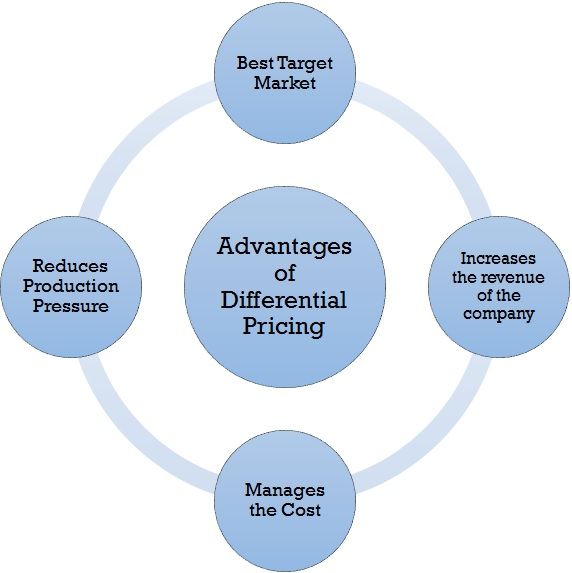
1. Best Target Market: The most important and crucial aspect of marketing strategies is the marketing mix which includes 4 p’s, and one amongst them is pricing. When a company opts for differential pricing, the wider section of the audience gets covered under it. As the price for every sector is different, the consumers of different economic classes can try out the products. Thus, differential pricing benefits in increasing the consumer base of different segments.
2. Increases the revenue of the company: Differential pricing helps increase the companies’ revenue by increasing the sale of the product as much as possible, as differential pricing offers the products to the customers according to their paying capacity.
3. Manages the Cost: Differential pricing helps the companies to manage the costs incurred by them in the production and transportation of the products. As already discussed earlier, every customer has a different buying capacity. Differential pricing helps the company cover a large group of consumers to sell their product and cover the cost incurred by them.
4. Reduces Production Pressure: To make the production more effective, it is essential that buying and selling cycle goes hand in hand. As if goods are produced and not sold, they would either lose their life or be discarded. To avoid such loss differential pricing system becomes beneficial to ensure that most of the produced goods get sold at high or low prices.
Objectives of Differential Pricing
Following are some basic objectives of differential pricing:
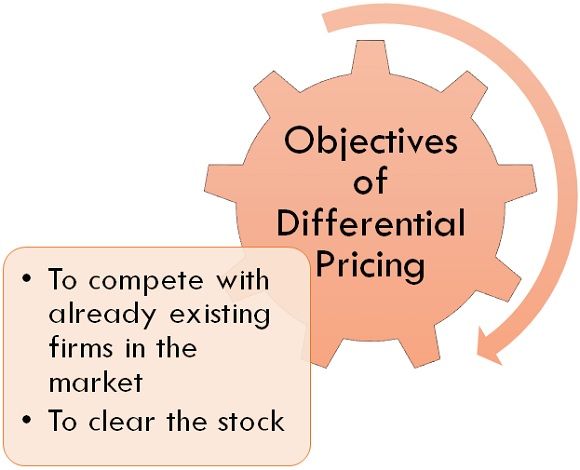
- To compete with already existing firms in the market: Some new companies adopt differential pricing system to attract the customers of existing firms in the market by selling the same quality product in relatively lower prices than other competitive firms.
- To clear the stock: When the company has already manufactured the products, and they are not yet sold and lying in the stock for a longer period of time, the company adopts a differential pricing system to clear the stock by reducing the prices of the products for a specific period of time and try to sell out the relying stock as much as possible.
Conclusion
Differential pricing is a segmented form of marketing mix strategy as in this system, the price of one product may differ from customer to customer. The prices of the product may rise or fall according to the demand for the product. For Example, In seasonal products, product prices increase in the season of demand whereas falls in the off-season.
Leave a Reply