Definition: Endorsement comes under the Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881. It is a process of affirming the negotiable instrument signed by the drawer (the endorser) for the reason of negotiation, and the receiver of the instrument is known as a drawer (endorsee).
The instrument must be signed by the drawer either in front or backside, and if there is no remaining space in front or back of the document a single piece of paper called allonge can be attached for recording the Endorsement. In general term, endorsement is signing and giving the paper to another person for the purpose of nominating interest to them.
Content: Endorsement
- Endorsement in Insurance Policy
- Types of Endorsement
- Legal Provisions concerning Endorsement
- Conclusion
Endorsement in Insurance Policy
If anyone wants to make any change, amendment, modification, or addition in the existing insurance policy, and an insurer and insured both are mutually ready for these changes, then in that policy insurer can make changes according to the insured. This process is known as “Endorsement in an insurance policy”. If the ownership or Registration number of the vehicle gets transferred or registration number gets changes, or we need to add or delete the name of the bank in our insurance policy or make any other changes that are said to be as endorsement. The endorsement can be done from the issuing office from where the policy has been issued. Some endorsements are done free by the insurance companies whereas some get charged as endorsement fees.
In case of change of Ownership, endorsement fees need to be paid, and in this case, if the previous owner has used or utilized NCV then the NCV should also be submitted for getting endorsement. For getting endorsement supporting document needs to be submitted to the insurance company. If any vehicle’s ownership or registration certificate has been transferred earlier, in that case, the new registration certificate must be produced to the insurance company. The insurance company will make the endorsement in the insurance policy according to the new registration certificate. If one got any change in the registration certificate and didn’t get an endorsement in the insurance policy then in case of any claim, the claim may get rejected.
Types of Endorsement
The following are some types of endorsement:
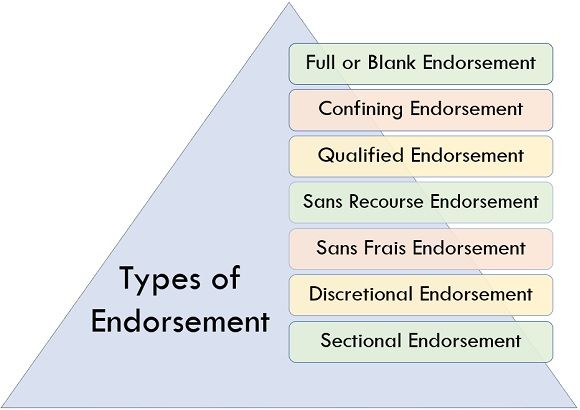
1. Full or Blank Endorsement
If the endorser mentions the guidelines to pay the amount in the instrument and also specify the name of the endorser in the instrument, in that case, such Endorsement is said to be “Full Endorsement”. And if the endorsee only acknowledges his name in the instrument, it is known as “Blank Endorsement”.
2. Confining Endorsement
Confining endorsement suggests restriction of endorsing the document to the other parties, i.e., the endorsee cannot approve it again to any third party. An example of restrictive endorsement is an account payee cheque that cannot be transferred to any other person except the name mentioned in it. In general, the word “only” gets combined with the name of the endorsee, which means the fund can only get issued to a specified person, and he cannot re-endorse such Cheque to others.
3. Qualified Endorsement
Qualified endorsement constitutes the liability on the endorser or forgetting the payment the endorsee has to bear a few supplementary liabilities or conditions which he has to fulfill. The endorser will only get paid after fulfillment of such condition. For Example, if it is mentioned in the instrument that the endorsee will get paid after completion of the project, the endorsee is bound to complete the project first to get the payment.
4. Sans Recourse Endorsement
This endorsement restrains the endorsee’s liabilities up to a specific holder and makes him free from further liabilities of subsequent Endorsement of the instrument to any other party.
5. Sans Frais Endorsement
Sans frais endorsement states that the endorser doesn’t want to bear any further expenses other than the liability of the instrument.
6. Discretional Endorsement
By including some relevant words, this endorsement facilitates the remission of some rights.
For Example, pay to Mr. X or order notice of dishonour forgo – Mr. Y
In the given Example endorser forgo some rights on the instrument, in general, all the previous holders of the bill become liable for the dishonour of the bill, but in discretional endorsement, Mr. Y will directly point out for becoming responsible for the dishonour of the bill.
7. Sectional Endorsement
Sectional endorsement by its name only suggests that it is an endorsement for the particular segment or portion of the document. However, these endorsements are not valid as per law in general.
Legal Provisions concerning Endorsement
The following are some of the provisions with respect to endorsement:
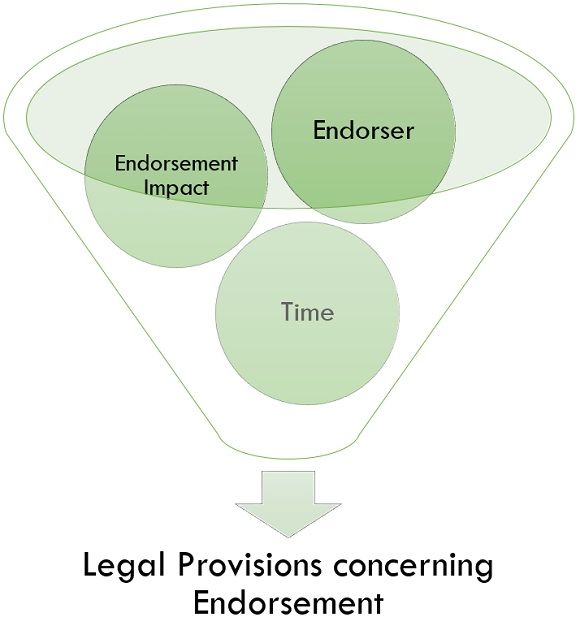
1. Endorsement Impact
According to the Negotiable Instrument Act (Section 50), the endorsee gets the right of further negotiation of the instrument if delivery transfers follow the instrument, i.e., endorsee becomes the holder of the instrument with a right of negotiating it to a third party if required except in case of confining endorsement. In accordance with the Act, the endorsee may act as an agent of the endorser to endorse the instrument to another person or to get sum on behalf of the endorser. As in such circumstances, the property gets transferred to the endorsee, and he becomes its holder.
2. Endorser
According to the Negotiable Instrument Act (Section 50), every drawer of the instrument should endorse and negotiate the instrument; no one can represent another. Therefore, if the instrument is held jointly by several persons, it is essential to get endorsement by all of them individually. However, a drawer must have a law possession over an instrument.
3. Time
According to the Negotiable Instrument Act (Section 50), an endorsement is valid until the time the drawer has made the payment at its maturity or after its maturity date.
Conclusion
An endorsement is done to make negotiation amidst two parties called “Endorser” and “Endorsee”. The one who draws and signs the instrument is known as a drawer, and the one who receives the instrument is known as a drawee.
Leave a Reply