Definition: A dividend policy can be defined as the dividend distribution guidelines provided by the board of directors of a company. It sets the parameter for delivering returns to the equity shareholders, on the capital invested by them in the business.
While taking such decisions, the company has to maintain a proper balance between its debt and equity composition.
Content: Dividend Policy
What is a Dividend?
A dividend is nothing but the return declared to the equity shareholders through the distribution of a portion of profits earned by the organization.
Factors Affecting Dividend Policy
Many a time we wonder, how a company frames its dividend policy?
These dividend decisions of an organization are dependent upon the following determinants:
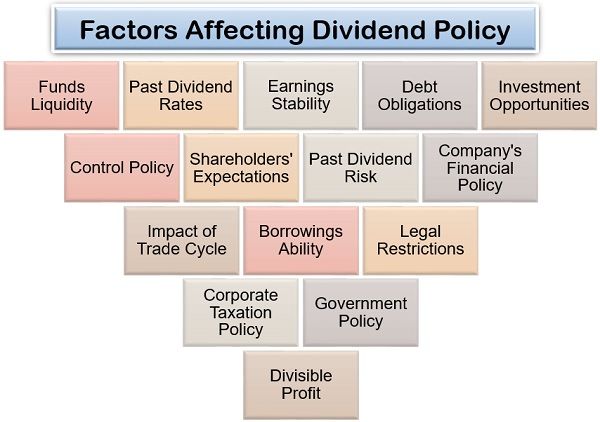
Funds Liquidity: It should be framed in consideration of retaining adequate working capital and surplus funds for the uninterrupted business functioning.
Past Dividend Rates: There should be a steady rate of return on dividends to maintain stability; therefore previous year’s allowed return is given due consideration.
Earnings Stability: When the earnings of the company are stable and show profitability, the company should provide dividends accordingly.
Debt Obligations: The organization which has leveraged funds through debts need to pay interest on borrowed funds. Therefore, such companies cannot pay a fair dividend to its shareholders.
Investment Opportunities: One of the significant factors of dividend policy decision making is determining the future investment needs and maintaining sufficient surplus funds for any further project.
Control Policy: When the company does not want to increase the shareholders’ control over the organization, it tries to portray the investment to be unattractive, by giving out fewer dividends.
Shareholders’ Expectations: The investment objectives and intentions of the shareholders determine their dividend expectations. Some shareholders consider dividends as a regular income, while the others seek for capital gain or value appraisal.
Nature and Size of Organization: Huge entities have a high capital requirement for expansion, diversification or other projects. Also, some business may require enormous funds for working capital and other entities require the same for fixed assets. All this impacts the dividend policy of the company.
Company’s Financial Policy: If the company’s financial policy is to raise funds through equity, it will pay higher dividends. On the contrary, if it functions more on leveraged funds, the dividend payouts will always be minimal.
Impact of Trade Cycle: During inflation or when the organization lacks adequate funds for business expansion, the company is unable to provide handsome dividends.
Borrowings Ability: The company’s with high goodwill has excellent credibility in the capital as well as financial markets. With a better borrowing capability, the organization can give decent dividends to the shareholders.
Legal Restrictions: In India, the Companies Act 1956 legally abide the organizations to pay dividends to the shareholders; thus, resulting in higher goodwill.
Corporate Taxation Policy: If the organization has to pay substantial corporate tax or dividend tax, it would be left with little profit to pay out as dividends.
Government Policy: If the government intervenes a particular industry and restricts the issue of shares or debentures, the company’s growth and dividend policy also gets affected.
Divisible Profit: The last but a crucial factor is the company’s profitability itself. If the organization fails to generate enough profit, it won’t be able to give out decent dividends to the shareholders.
Types of Dividend Policy
What patterns do the companies follow while paying out dividends?
The following categories of dividend policies provide the answer to the above question:
Stable Dividend Policy
In this policy, the company decides a fixed amount of dividend for the shareholders, which is paid periodically. There is no change in the dividend allowed even if the company incurs loss or generates high profit.
Regular Dividend Policy
Here, a certain percentage of the company’s profit is allowed as dividends to the shareholders. When the gain is high, the shareholders’ earnings will also hike and vice-versa. It is one of the most appropriate policy to be adopted for creating goodwill.
Irregular Dividend Policy
Under this changeable policy, the company may or may not pay dividends to the shareholders. The top management i.e., the board of directors solely take all dividend decisions, as per their priorities.
No Dividend Policy
Here, the company always retain the profits to fund further projects. Moreover, it has no intention of declaring any dividends to its shareholders. This strategy may seem to be beneficial for business growth but usually discourages the investors aiming for sustainable income.
Essentials of a Sound Dividend Policy
A company’s dividend decisions and policy signify its future and financial well-being. Therefore, it needs to be systematically framed and implemented.
Let us see the three essential steps to take flawless dividend decisions:
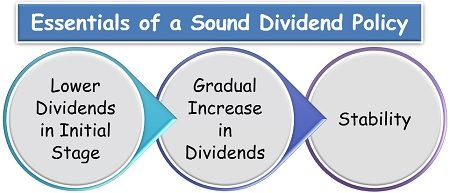
- Lower Dividends in Initial Stage: When the company is at the beginning stage and earns little profit, it should still provide dividends to the shareholders, though less.
- Gradual Increase in Dividends: As the company prosper and grow, the dividend should be kept on increasing proportionately, to build shareholders’ confidence.
- Stability: It is one of the crucial features of a superior dividend policy. When the company can survive in the market, it should ensure a stable rate of return in the form of dividends to its shareholders. This leads to retention of shareholders and gains investors interest, all resulting in the enhancement of shares market value.
Importance of Dividend Policy
Dividend policy provides as a base for all capital budgeting activities and in designing a company’s capital structure.
Following are some of the reasons for which dividend policy is essential in every business organization:
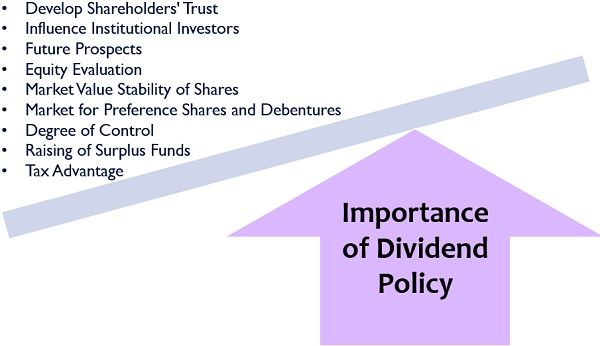
- Develop Shareholders’ Trust: When the company has a constant net earnings percentage, it secures a stable market value and pays suitable dividends. The shareholders also feel confident about their investment decision, in such an organization.
- Influence Institutional Investors: A fair policy means a strong reputation in the financial market. Thus, the company’s strong market position attracts organizational investors who tend to leverage a higher sum to the company.
- Future Prospects: The fund adequacy for next project undertaking and investment opportunities is planned, decides its dividend policy such that to avoid illiquidity.
- Equity Evaluation: The value of stocks is usually determined through its dividend policy since it signifies the organizational growth and efficiency.
- Market Value Stability of Shares: A suitable dividend policy means satisfied investors, who would always prefer to hold the shares for the long term. This leads to stability and a positive impact on the stocks’ market value.
- Market for Preference Shares and Debentures: A company with the proficient dividend policy may also borrow funds by issuing preference shares and debentures in the market, along with equity shares.
- Degree of Control: It helps the organization to exercise proper control over business finance. Since, the company may land up with a shortage of funds for future opportunities, if the company distributes maximum profit as dividends.
- Raising of Surplus Funds: It also creates organizational goodwill and image in the market because of which the company becomes capable of raising additional capital.
- Tax Advantage: The tax rates are less on the qualified dividends, which are received as a capital gain when compared to the percentage of income tax charged.
Example
A well known Indian company, ‘Tata Chemicals Ltd.’, listed on Bombay Stock Exchange, have a dividend policy to pay an annual return to its shareholders in the form of dividends.
The company also shares its intention of paying out special dividends on earning extraordinary profits or other events.
It has also listed all the factors which it considers while dividend decision-making process. These include past dividend payouts, investment opportunities, debt obligations, earnings, maintaining reserves for adverse situations, government policy, etc.
Cyrus says
Easy to understand