Definition: Scientific management concept was developed by F.W. Taylor who implemented the scientific techniques such as observation, logic, analysis and combination to study the working conditions and management at the floor level in the factories and production units.
The concept of scientific management was given to improve the productivity, efficiency and effectiveness in the organization through the application of the proposed scientific principles and techniques.
Content: Scientific Management
Frederick Taylor and Scientific Management
Frederick Winslow Taylor (1856-1915) was an American mechanical engineer and a consultant who proposed the concept of scientific management under the name ‘The Principles of Scientific Management’ in the year 1911. He was also known as the ‘Father of Scientific Management’.
Taylor made observations regarding the inexcusable work methods in the companies like Bethlehem Steel, Simonds Rolling Machine and Midvale Steel.
In that era, there was a scarcity of skilled labour in the industries. Taylor found that the organizations and the managers failed to utilize the available human resources effectively, and also, no contribution was made in the direction of enhancing the labour’s efficiency.
During his observation, Taylor identified the various factors leading to low productivity and inefficiency in the organization. Some of these are as follows:
- The labour brought their poorly designed personal tools to be used in the workplace.
- Unorganized job training was provided to the workers, and they tend to decide the speed of the work and machine by themselves.
- Instead of the individual’s skills set, the workers were hired according to the ‘first-come, first-hired’ basis.
- The managers used to work along with labours leaving aside the essential planning and organizing activities. Thus, these crucial management functions were performed by untrained employees.
Based on his findings, Taylor criticized the ineffective ways of the managers to handle the work situations and also for providing liberty to the employees for deciding their work methods and speed by themselves.
Principles of Scientific Management
Taylor suggested four important tenets based on his findings and research of the production areas of some renowned companies. These are as follows: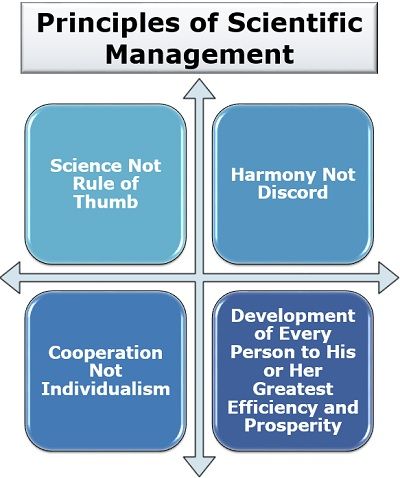
Science Not Rule of Thumb
The concept of the rule of thumb was based on the trial and error method. However, Taylor believed that to perform any task efficiently; there is only one best possible method which is developed after an in-depth analysis of that job.
Thus, it becomes the standard way of carrying out that particular task each time, throughout the organization.
When science is applied instead of the rule of thumb, to any job, it standardizes that work. Moreover, the workers get a specialized way of performing the task and wastage of a lot of time, cost and resources can be avoided.
Harmony Not Discord
Taylor emphasized on maintaining peace and harmony in the workplace, and there should be no conflict among the managers and the workers. Conflicts only result in negatively, i.e., a decline in the productivity of the organization.
There can be a significant improvement and growth in productivity if there exists a friendly relationship between the managers and the labours where both value the efforts of each other,
Thus, there should be a mental revolution in the organization to change how both groups see each other.
Cooperation Not Individualism
An organization is made up of different individuals (i.e., personnel), and each one of them is equally important. Business is all about teamwork and cooperation, in the absence of which the organization may fail to attain the desired results.
Therefore, the employees in an organization must work together, keeping aside their objectives and ego to achieve the common goals set by the management. There should not be any competition among the workers; instead, they should cooperate at work.
The workers should not oppose the management by putting up irrelevant demands and then going on strikes for their fulfilment. The administration should also encourage the workers to give suggestions and create an open communication system in the organization.
Development of Every Person to His or Her Greatest Efficiency and Prosperity
Taylor believed that employees should be given proper training of the task they perform because no human being is perfect, and there is always a scope of improvement.
Moreover, training and development improve the competency, skills and learning of the workforce. It is beneficial for both the organization and the workers.
Techniques of Scientific Management
Along with the scientific management principles, Taylor also introduced some methods to improve the productivity of the workers and ensure smooth functioning of the organization.
These methods were majorly developed for the manufacturing and production industry and were based on his analysis of such units.
Let us now discuss each of these techniques in detail below: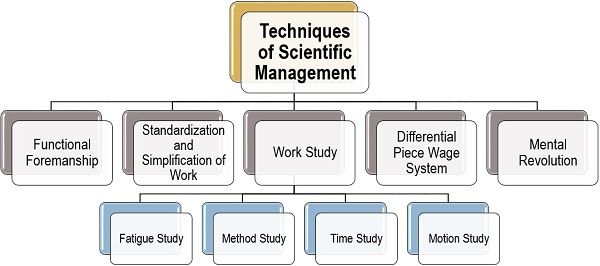
Functional Foremanship
Taylor suggested that to improve efficiency and effectiveness of the operational activities the managers must possess specific skills like leadership, intelligence, tactical skills, knowledge, judgement, education, experience, honesty, good health and energy.
He realized that no single person could have all of these qualities. Therefore, he came up with the idea that the managerial activities should be divided into two parts, i.e., planning and production.
Also, there should be two individual in charges appointed under the factory manager for carrying out both of these activities holding the position of planning incharge and production incharge, respectively.
Moreover, there should be four different clerks under each of the incharge, i.e., the planning incharge and production incharge. They hold expertise in their respective areas and supervise the performance of each worker.
Let us now see the hierarchy under the functional foremanship as suggested by F.W. Taylor: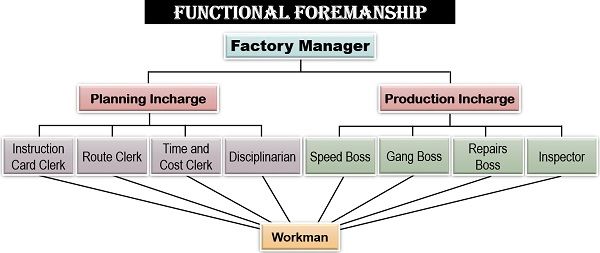
Factory Manager
A factory manager is a person who holds the highest managerial position in the unit and is responsible for the proper functioning of the organization.
Planning Incharge: A planning incharge is responsible for the formulation of policies, strategies and procedures of the operational activities. To simplify the work, following four clerks are appointed under the planning incharge:
- Instruction Card Clerk: The instruction card clerk will determine and direct how the work has to be performed.
- Route Clerk: A route clerk will decide what all is to be done and the steps which are to be taken to perform a particular task.
- Time and Cost Clerk: The person who determines the time limit in which the work is to be completed and the cost involved in carrying out each task is known as a time and cost clerk.
- Disciplinarian: A disciplinarian is a clerk who ensures discipline, following rules and regulations and code of conduct in the organization.
Production Incharge: A production incharge needs to take care of all the operational and production activities. The four clerks assigned under a production incharge are as follows:
- Speed Boss: The speed boss is responsible for getting the work done on time.
- Gang Boss: The person who looks after the availability of all the equipment, tools and accessories is a gang boss.
- Repairs Boss: The repairs boss has to take care of the repairs, maintenance and overhauling of the tools and machinery used for production.
- Inspector: The inspector is responsible for ensuring that all activities are being carried out in a planned manner. He/she also checks whether the quality of the products are as per the standards or not.
Workman
A workman is a labour or the worker at the operational level of the organization which is responsible for actually performing the given task. Each worker is supervised and monitored by the eight different clerks, as mentioned above.
Therefore, we can also interpret that the functional foremanship is the only scientific management technique, which is ‘contrary to the principle of unity of command’.
Standardization and Simplification of Work
Taylor suggested that there should be a fixed standard for everything, i.e., the product, raw material, process, machinery and working conditions. This is to save the time and cost and bring in specialization in the organization.
Also, the task and the product line should be simplified enough to save the extended cost of tools, machine and labour by eliminating the unproductive tasks and narrowing the product line.
Work-Study
Taylor emphasized on examining and analyzing the working at the operational level of the organization. It develops a systematic course of action and resolves the problems faced by the labours and workers who are responsible for accomplishing the given task and duties.
Under the technique of work-study, there are following four significant concerns of the organization:
Fatigue Study
According to Taylor, the task can be accomplished effectively and efficiently only if the worker is allowed to take the required amount of rest during the working hours.
Under the fatigue study, the organization needs to plan for the following:
- The number of rest intervals: The organization needs to decide the number of times, for which rest is allowed to the labours in a day.
- Frequency of rest intervals: The time interval after which the employee’s rest time is scheduled is termed as the frequency of the rest intervals.
- Duration of each rest interval: The organization also determine the period of each rest interval. Such that the worker neither remains exhausted nor moves into a state of laziness.
Method Study
The managers come across numerous ways of performing a particular task or carrying out the production of goods or services.
Out of all these possible methods, selection of the most appropriate way, which is cost-effective and also increases the production is considered a method study.
Time Study
Analyzing the time consumed for carrying out the given task in a specified manner is Taylor’s another scientific management technique which is called a time study.
If an activity takes more time than the defined standard, it may lead to delay and decline in productivity. And if a task is accomplished much before the given time, it may lack efficiency.
Motion Study
The examining of every movement of the workers during the working hours to find out the unproductive task and activities comes under motion study.
The actions and movements which do not generate any output should be eliminated to simplify the work.
Differential Piece Wage System
The wages paid to the workers should be based on their production capability, i.e., the number of pieces labour can manufacture in a given period, instead of a fixed rate of remuneration.
A standard number of units of production should be determined, and the wages should be decided accordingly. If a worker is unable to produce the usual quantity, then some amount will be deducted from the decided remuneration. However, if a worker produces more than the standard number of units, he or she will be liable for additional compensation.
In simple terms, Taylor suggested the ideas of performance-based remuneration and incentive-based motivation.
Mental Revolution
Taylor gave a powerful concept on changing the perception of both the employees and the management. Here, both of them work in collaboration and consider themselves as members of a family.
He said, to achieve the organizational goals efficiently, there must be proper coordination and understanding among the workers and the management. A friendly and cordial work environment leads to the growth of the organization as well as the individuals.
The employees should not consider themselves as just the workers of the organization, but believe themselves to be the members of a family. Even the management must understand that the workers are also human beings and an essential part of the organization. Both of them must value the efforts of each other and work together, creating a positive environment to achieve common organizational goals and objectives.
Criticism of Scientific Management
Scientific management has been criticized by many scholars due to its following shortcomings for the workers as well as the employers:
Criticism from the Worker’s Point of View
Scientific management leads to monotony for the workers since they need to use standardized ways and cannot implement their innovation and creativity to their work.
Workers felt that the management is upgrading with technology by employing new machines to deplete job opportunities.
Due to scientific management, a standardized system is developed in the organization. Here, the wage rate, compensation, working duration, rest intervals are fixed, thus leaving no scope for the trade unions to work for the labour welfare.
The workers claim that scientific management results in their exploitation. Since they believe that a hike in the wage rate is not proportionate to the increase in production, i.e., it is usually less.
This concept emphasizes on completion of work within the given standard time of output, therefore, leading to the acceleration of work which has negative consequences on workers’ health.
Criticism from the Employer’s Point of View
The employer considers scientific management as a time-consuming process since it takes very long to bring mental revolution and implement standardization and specialization in the organization.
The implementation of scientific management is an expensive affair. A lot of costs is incurred on the planning and training of the workers and the administration.
This concept focuses on increasing productivity of the organization; however, it may lead to over-production, which further results in recession.
Alpha says
The expression of word for every topic is so much excellent. It clear all fundamentals.I am really appreciate your work.
Thank you so much and I also request to you that Please bring the notes of Commerce(From +2 to +3).😊
ramesh says
Very good analysis
Firoza says
great
Manshura says
Just amazing,, great job