Definition: Value investing is a trading strategy that entails identifying the potential yet undervalued stocks and purchasing them at a reduced price after doing a thorough fundamental study to generate good returns over the long run.
In simple terms, purchasing stocks of an underestimated company on sale or at a sensible price.
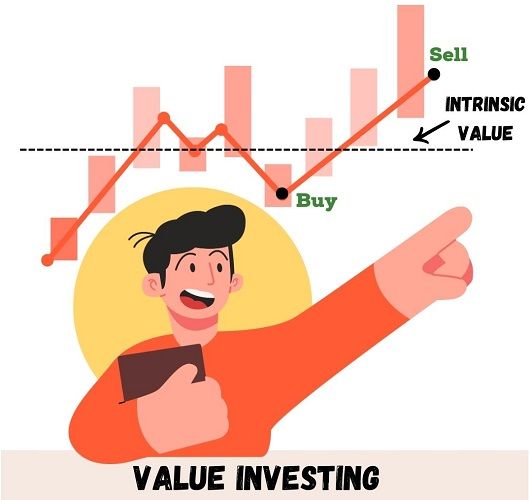
This concept was introduced by Benjamin Graham, also known as the ‘Father of Value Investing‘.
In this strategy, the investors focus on stocks that are undervalued for some reason. Value investors buy such stocks and save a considerable amount on the market price.
The whole concept revolves around two terms, i.e. Value and Price. Value is something that you get out of a specific stock. On the other hand, Price is the amount that you pay to buy a particular stock.
Thus, a significant difference exists between the stock’s value and price. Investors can generate handsome returns by strategically analysing this difference and investing in valuable stocks.
Investors don’t take decisions instinctively. Besides, they conduct an in-depth study called Fundamental Analysis. The analysis is based on the stock’s Fair Value and Intrinsic Value. In addition, it considers the future cash inflow from the company to owners and vice-versa.
Value investing emphasises much on the overvaluation and undervaluation of stocks. This helps them in finding valuable companies and taking the correct investment decision.
Content: Value Investing
- Who is a Value Investor?
- Famous Value Investors
- How does Value Investing work?
- Value Investing vs Growth Investing
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Example
- Final Words
Who is a Value Investor?
They are the one who is interested in investing in undervalued stocks having the potential to generate good returns. They make judgements based on the value of the company or assets.
The value investors stress more on the asset’s intrinsic value and future profits. They try to pay the price less than the intrinsic value.
They keep stalking companies facing temporary downfall in the market price. The reason behind the downward trend can be the biases in the market.
Different types of Value Investors are as follows:
- Passive Screeners: Such investors study characteristics to identify undervalued stocks.
- Contrarian Investors: They are the ones who invest in the stocks that other investors already gave up for various reasons.
- Activist Value Investors: This type of investor focuses on companies with poor management. But, they still have the potential to grow.
Famous Value Investors
Given below are some famous investors who made huge profits with value investing strategy:
- Warren Buffet
- Peter Linton
- Charlie Munger
- Michal Burry
- David Dodd
- Christopher Browne
- Michael Lee-Chin
- David Abrams
- Mohnish Pabrai
- Tom Gayner
How does Value Investing work?
Sometimes the market overreacts to the good or bad news. As a result, some companies become prey to the rat race and fall below their intrinsic value.
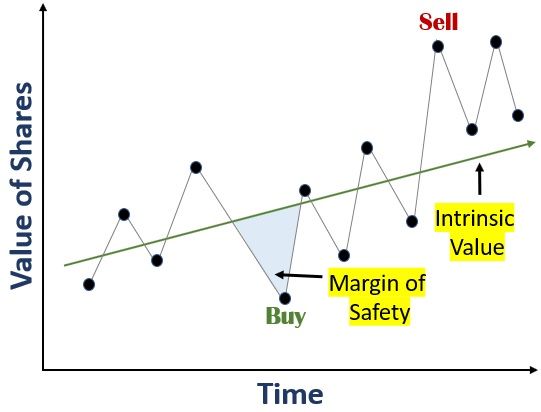
Value investors grab this opportunity and invest in such stocks. They evaluate the company’s value by studying intrinsic value and margin of safety.
The margin of safety is the total discounted price or gap between the stock’s market price and intrinsic value.
Thus, investors buy the stocks on sale with a broad margin of safety. After that, they sell these shares to reach their intrinsic value or rise above it.
Important Tip
- Investors must go for stocks when the share trades below the book value.
- Select the stocks which trade at a low multiple of the equity earnings.
- Buy the share that yields a high dividend.
Value Investing vs Growth Investing
The chart below outlines the differences between Value Investing and Growth Investing.
| Basis | Value Investing | Growth Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Buying low-priced stocks trading at a discount | Buying growing stocks & holding them for the long term |
| Risk factor | It involves low risk | It involves high risk |
| Strategy | Buy on sale and sell stocks when high | Buy stocks with increasing trend and hold |
| Price | Low price | Higher Price |
| Type of Stock | Investing is in the average-performing stock | Investing in the fastest-growing stocks |
| Type of Company | Established valuable companies but currently underestimated | New companies having huge potential to grow |
Value Investing Strategies
There are some strategies available that assist in finding the undervalued stocks as follows:
- Deep Value Investing
- Dividend Investing
- Growth at a reasonable price Investing
- Contrarian investing
1. Deep Value Investing
It involves investing the stocks that have a broad margin of safety. In other words, the stocks with deep discounts on the intrinsic value. The potential reasons can be the unfavourable market or industry conditions.
The investor must conduct a detailed fundamental analysis and be patient.
2. Dividend Investing
In this strategy, the investors focus on those shares that pay good dividends. It is best suited for investors with regular income seeking stable returns.
3. Growth at a reasonable price Investing
It is a mix of value and growth strategy. Here, the investors find stocks that are undervalued but have growth potential. Such stock has a competitive advantage and can sustain the market for a long.
4. Contrarian investing
As its name suggests, the investors trust their analysis and invest in stocks rejected by other investors. Such investors grab opportunities which others might not see.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The following are the advantages of using a value investing strategy:
- Risk minimisation: It involves less risk because the investor is already buying at a low market price.
- Substantial Returns: It yields good returns in comparison to other stocks. As the amount is invested in the undervalued stock, it will appreciate over time.
- Lower Investment: The investor needs to invest less money as compared to a growth stock.
It suffers through following disadvantages:
- Long-term Option: It does not give returns in the short term. The investor needs a lot of patience to enjoy the returns.
- Time-consuming process: It is not a one-day process. Investors have to find such stocks and wait for them to arrive at their intrinsic value.
Example
During co-vid, the share market showed a downward trend. Due to this reason, many investors were selling their shares. The value investors grabbed the opportunity and bought shares at much lower prices. After a year, they generated high returns due to market corrections.
Final Words
All in all, it involves picking the stocks that appear to be trading below their intrinsic value. To be profitable, they need to keep a lot of patience and remain disciplined.
It is an effective strategy used by many successful investors like Warren Buffet. But, one must spend sufficient time identifying such stock and avoid getting into a Value Trap.
Leave a Reply