Definition: Outsourcing implies getting work done from the outside bodies. The companies generally use this process to deploy the non-core but relevant sector of their business. For this, two companies draft a legal agreement for the exchange of payments and services.
For an action to be called ‘outsourced’ it should be:
- A recurring action.
- An action that the firm presently furnishes for itself or is commonly scheduled to implement for itself.
Let us understand outsourcing with an example:
Company A is having expertise in manufacturing the medicine but does not have any experience of manufacturing the packaging bottles without which medicines cannot be sold in the market. However, another company B has expertise in manufacturing the bottles. Thus, company A can outsource their non-core work of manufacturing the packaging bottles to company B, whose core area of service is manufacturing the bottles. This will reduce the unnecessary cost of Company A and increases the profit of both companies.
Content: Outsourcing
Types of Outsourcing
Following are the types of outsourcing:
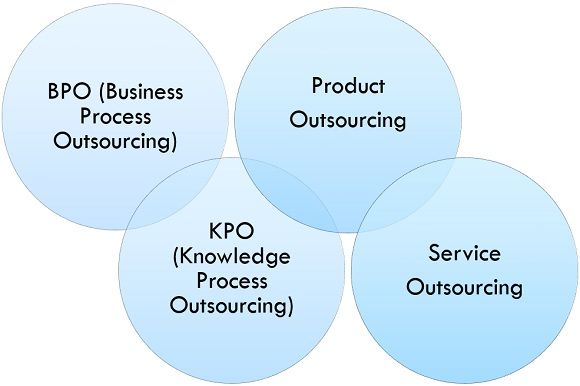
- BPO (Business Process Outsourcing)
It is a form of outsourcing which is involved with the distribution of certain business measure to other company, i.e., Service provider through a legal contract. If Business Process Outsourcing is done outside the country, it is termed as offshore outsourcing and if the country involves in the outsourcing process is a neighbour country than it is called as nearshore outsourcing. Though Business process outsourcing is firmly connected with information technology, it is also known as ‘Information Technology Enabled Services (ITES)’.
- KPO (Knowledge Process Outsourcing)
Knowledge Process Outsourcing is associated with the outsourcing of high-end intelligence work. This consist of professional research containing computer alleviated simulation, analytics, engineering designs, research on finance and equity, work on a cerebral property, patent registration, legal counselling, market exploration, data mining. Evaluating information from a collection of data present across different working units of the company and helping it to determine compelling business strategies.
- Product Outsourcing
The product is the result of an act or an operation by requisite furnishing inputs. It is an output of action, and in separate areas, the product can be characterized in distinctive ways. Alike in operation and production management products are purchased in the form of raw material from the market and sold in the form of finished goods. Similarly, in the marketing management product, everything can be provided to the market to fascinate a demand. When a company needs a product which they cannot manufacture, or it costs high for them to manufacture they outsource such products from the other company who manufacture that product as a core product. This type of outsourcing is known as product outsourcing.
Products can be categorized into two types:

- Tangible Products: Any substantial product which can be touched or felt, such as a computer, bag, etc. are known as tangible products.
- Intangible Products: The products which cannot be touched physically, such as goodwill are known as intangible products.
- Service Outsourcing
Service is a kind of economic movement that is intangible and cannot be stored, and no ownership gets transferred. It is one of the two fundamental segments of economics, and the other essential sector is goods. It comprises postal services, expert services such as service provided by the doctor, consultancy services, accounting banking, insurance, education, etc. When such services are provided by one company to another, it is known as service outsourcing.
Services are discriminated according to the following characteristics:
- Intangible: They are of intangible nature such as repairing of equipment.
- Non- perishable: Services do not have an intensity of endurance above the time of purchase; they perish as they are delivered.
- Inseparable: Service and the service provider cannot be separated, as a service provided is an effort of the service provider.
- Unstandardized: The services offered or delivered each time cannot be of the same quality; it differs every time it provided.
20 Outsourcing Companies
| Outsourcing Companies |
|---|
| Accenture |
| IBM |
| Infosys technologies |
| Sodexo |
| Capgemini |
| Tata consultancy services |
| Wipro technologies |
| Hewlett technologies |
| Genpact |
| Tech Mahindra |
| HCL technologies |
| Hexaware technologies |
| Cognizant technology solutions |
| Zensar technologies |
| Convergys |
| Neusoft group |
| EMCOR group |
| Cambridge solutions |
| ITC infotech |
| Colliers international |
Reasons behind Outsourcing
Following are some of the reasons behind Outsourcing:
- To manage the factor of cost.
- To focus on its core activity sector.
- To approach the creative property.
- To expedite innovations.
- To reduce the risk.
- To serve tax benefits.
- To govern capacity.
Benefits of Outsourcing
Following are the benefits of outsourcing:
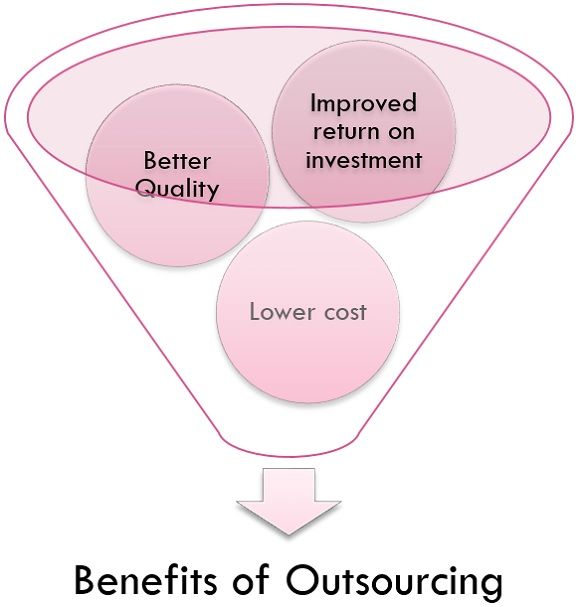
- Better Quality: Sometimes, another firm is just superior at delivering a service or building products than your firm. Thus, it is the best option to outsource that service to another firm for getting the best possible results from that service or product.
- Improved return on investment: A pillar of outsourcing is its ability to shorten the investment in equipment and plants required for the production of the products. If you can maintain the volume of the profits for the product and not waste too much on supplier margins than the return on investment of the firm will increase.
- Lower cost: Some suppliers have a business in their support; outsourcing to low-cost labour can minimize the labour cost of the firm. For example: In India labour cost is much cheaper than the USA; thus, various companies from the USA outsource their low skill works to the low-cost companies in India.
Limitations of Outsourcing
Following points shows the importance of outsourcing:
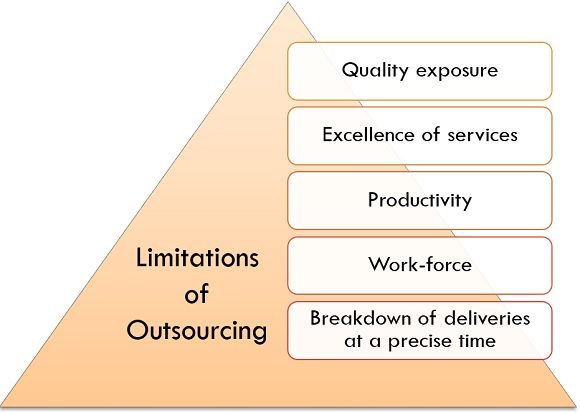
- Quality exposure: There is a possibility of quality exposure of a service or product to be inadequate, due to manufacturing or industrial consequences. It can be due to distinct elements such as information inequality, immense supplier-switching cost, feeble buyer-supplier communication, and scarcity of supplier capabilities.
- Excellence of services: Service legal agreement is a measure of nature of service in the outsourcing obligations. If an obligation is not clearly determined, then there is no measure of quality or service legal agreement established.
- Productivity: Occasionally, offshore outsourcing is used to reduce the extra cost, but it can have an adverse impression on the capacity of the company. In such circumstances, it is better to spend on technology rather in outsourcing, as it will eventually improve productivity.
- Work-force: Variations is often higher under an outsourcer, in such a situation, proficiency of the main firm may be vanished, which is out of the control of the firm. Breakdown of deliveries at a precise time: The target pledged by the outsourcing suppliers usually fails. It occurs because merchants overestimate their capabilities.
Conclusion
Outsourcing means a contract with an outside organization regarding business functions. The simple making and buying decisions regarding a product, whether it should be produced by a firm or outsourced by another firm who is best in providing such products is the basis of the outsourcing process.
Leave a Reply