Definition: International Pricing refers to the strategic marketing activity determining the monetary exchange value of the product sold across countries.
It is the flexible element of the marketing mix which can be altered easily. However, price competition in the market is a significant issue.
Also, it is an essential factor in determining the following:
- International Pricing Policy
- International Sales
- Profitability
Domestic and International pricing is different from one another. This is due to the economic variation across countries. Thus, making it more complex in comparison to domestic pricing.
Some reasons behind these differences are as under:
- The difference in the legal and economic environment.
- Relationship between different markets.
- Less knowledge about the foreign market.
Mostly, the new entrants go global with the same price and strategy as domestic markets. Later on, they change their pricing strategy as per the market conditions.
Conducting in-depth market research is essential for entering and surviving in global markets. The company will suffer losses if the prices are charged too high. On the contrary, profit margins get adversely affected if the prices are extremely low.
For international pricing, it is mandatory to have a consistent supply of knowledge of the following:
- Export Products
- Foreign Markets
- Relevant Market Information
Content: International Pricing
Example
A doting example of international pricing is Apple. It is a famous brand in the telecommunication industry.
Apple offers a premium range of mobile phones, i.e. iPhones. It is a U.S. -based company operating in many parts of the world.
The variation in the price of the iPhone can be seen in different countries. Have a look at the figures below:
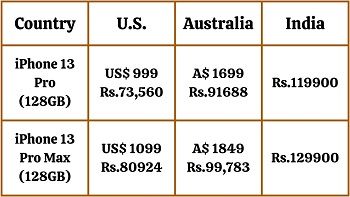
It is quite evident that it is cheaper in its home country. At the same time, there is a hike in prices in other countries. The reason could be many political and economic factors in other countries.
International Pricing Strategies
It comprises critically analyzing the factors and then tactically determining the price. Strategies are similar to that of the domestic market.
But, due to more exposure at the international level, the factors worth consideration increases in number.
One can adopt the following international pricing strategies:
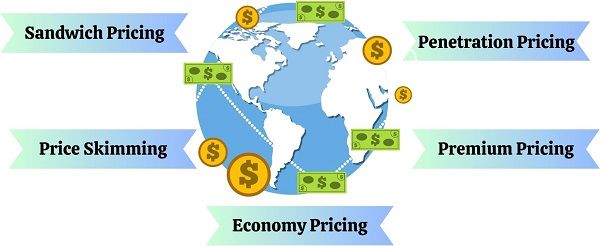
- Penetration Pricing: It is the most commonly practised marketing strategy. In this strategy, the marketers intentionally charge the lower price on products. This strategy is adopted when the product is new to the market.
- Premium Pricing: Marketers use this strategy to position their products in the premium range. This strategy is quite common in the telecommunication industry.
- Economy Pricing: This strategy is suitable for products whose production cost is low. Consequently, the marketer can lower prices in the global markets.
- Price Skimming: It refers to charging a high price for unique or exclusive products. However, companies can only implement this strategy for a short time. This is because, competitors grab the opportunity and launch similar products at a lower cost.
- Sandwich Pricing: It includes launching two or three determinants of the same product. These determinants vary in features and prices, i.e. High, Medium and Low. The basic idea is to trigger the customers to buy the mid-priced product.
International Pricing Policy
It is the set of rules or a course of action stated clearly. In this context, companies’ policies show price fluctuations when exposed to factors other than cost.
Good Pricing Policy
A Good pricing policy enables the company to achieve its short-term objectives. In addition, the prices change along the demand curve without causing a negative shift in the curve.
Poor Pricing Policy
A bad pricing strategy incentivizes customers, salespeople, and competitors, which may affect future sales. Moreover, it allows price change in a way that adversely affects customers’ willingness to pay.
There are three possible international pricing policies given below:
- Extension: It involves keeping the same price as competitors.
- Adaptation: In this policy, the companies charge different prices in different countries.
- Innovation: It combines the policies mentioned above and forms a unique policy.
Objectives
Besides cost, product price at the international level considers the firm’s marketing strategy. Following are some of the objectives of international pricing:
- Market Penetration: Firms need price fixation when they enter the global market. Generally, the prices are kept low to make their place in the new marketplace.
- Expected Returns: Pricing helps generate the expected rate of return for the company.
- Market Skimming: The firms with exclusive products charge high customer prices. Moreover, they keep practising the same until competitors step in.
- Expanding Market Share: Another objective is to achieve a greater market share. This objective can be achieved by reducing the product’s price.
- Beat Competition: It is a great tool to face and win market competition. Very often, companies reduce their product’s price to eliminate competition.
- Profit Maximization: Profit is something for which the entire organization operates. The primary motive behind going global is earning more significant profits.
Factors Affecting
So far, we have learnt that some factors influence pricing in global markets. Some factors affecting international pricing are given below:
- Cost: It is the most influential factor affecting prices in domestic and international markets. Cost is made up of fixed and variable cost, which varies in the short and long run.
- Demand: Price and demand are inversely related and sensitive towards it. Here, companies consider the demand of the countries they are operating in.
- Exchange Rate: It plays a vital role in price fixation. The product’s price increases or decreases as per the prevailing exchange rate.
- Political Environment: It consists of the rules and regulations of the host or foreign county’s government. Companies need to consider these during the price determination process.
- Brand Awareness: A known brand has the backing of an established customer base. For this reason, they can take advantage and charge higher prices. On the other hand, unpopular ones need to keep the prices affordable.
Process
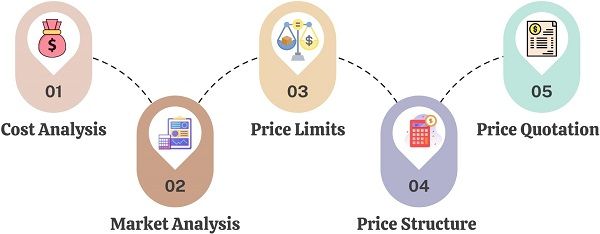
Step:1 Cost Analysis
The price determination process begins with an in-depth analysis of cost. It includes determining the cost of product, distribution and market support.
Step:2 Market Analysis
The next step in the process is analyzing the market of the exporting country. The analysis includes variables like:
- Market Size
- Market Segment
- Price Level
- Competition
Step:3 Price Limits
In this step, companies determine their upper and lower price limits. The upper limits imply the maximum price that could be charged. On the contrary, lower limits refer to the minimum cost of the product.
Step:4 Price Structure
Forth step in the forgoing process is fixing the price structure. For this purpose, companies can use the best-suited pricing strategy for the product. In addition, they may also design Discounts and offers regarding the product.
Step:5 Price Quotation and Term of Sale
Quotation gives details about the concerned product, such as:
- Quantity
- Size
- Weight
- Volume
- Price, etc
Besides details, the company must mention all the terms of sale and the attached risk.
Methods of International Pricing
The following methods can be used for setting-up pricing in Global Markets:
- Cost-based Methods
- Marginal Cost Pricing
- Differential Pricing
- Probe Pricing
- Competitive Pricing
- Transfer Pricing
Parting Words
All in all, the product’s price must be such that the customer is ready to pay. Moreover, companies must try to achieve good pricing management. It must have the capacity to maximize profit, liquidity and shareholder value.
Leave a Reply