Definition: The Consumer Decision Making Process is the sequential interrelated steps explaining the approach of the consumers in making buying decisions. Also, it involves an in-depth analysis of the consumers’ purchase behaviour. We can also refer to it as the Buyer Decision-Making Process.
It is the traditional model depicting the process of Consumer Decision-Making. However, it is still a widely used model to understand how the consumer makes the buying decision.
The process starts long before actually buying the product. And it continues until the consumer finds a desirable product/service satisfying his need.
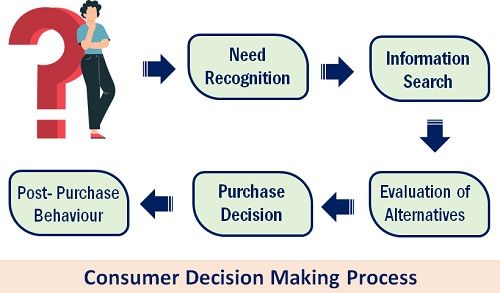
The framework of the Buyer Decision-Making Process contains five stages as follows:
- Identification and Recognition of the need.
- Gathering necessary information to find the available options.
- Evaluation of various alternatives.
- Making the final purchase Decision.
- The consumers’ post-purchase behaviour.
A deep understanding of the consumer’s decision-making process is crucial for marketers. They must analyze all the aspects and sources that influence the decision-making process.
By this, marketers can ease the targeting process. They can make more focused and effective marketing campaigns.
Content: Consumer Decision-Making Process
Steps in Consumer Decision-Making Process
As discussed above, the entire consumer’s decision-making process is divided into five stages. The consumer evaluates and makes the buying decision by passing through these stages.
The steps in Consumer Decision Making process studied universally are as follows:
It is not necessary that every consumer compulsorily passes through all the stages. Because the consumers’ decision depends on the nature and type of the product that he wishes to buy.
They can skip some stages and directly make the purchase decision in some cases. In contrast, they can even reverse back to the previous stages for a detailed evaluation. Besides, some stages may repeatedly occur throughout the process.
Let’s understand the steps in the buyer decision-making process in length.
Need Recognition
The decision-making process triggers as soon as he identifies the Need or a Problem. The problem or need arises when:
- There is a variance between consumers’ current and desired conditions.
- When he faces any difficulty in a specific situation.
- When he identifies his unsatisfied need and so on.

It is a crucial part of the process as no purchase process will ever initiate without the need. For Example, Mr Bob realises that he is tired and needs some water to drink.
Consumer problems can be Simple or Complex. On the other hand, their needs can be Original or Derived. In addition, it can be generated instantaneously or get influenced by external stimuli.
In individuals, Internal or External stimulus senses the need for any product or service.
- Internal Stimuli: In this, the need generation occurs due to internal drives like Thrust, Hunger, etc.
- External Stimuli: Need that generates in response to any Advertisement, Radio Jingle, Pamphlets, etc.
Information Search
After identifying the need, the consumers start collecting valuable information about how they can meet their needs. For research, the consumer uses both Internal and External sources.

Through research, he will be able to identify the desired product to solve his problem.
The information search broadly involves research about:
- The types of products available.
- The number of brands available for the same.
- The location from where it can be acquired.
The information varies with the Products and Buyers’ characteristics.
Following are the sources from which a consumer can gather relevant information:
- Personal Sources
- Family
- Friends
- Neighbour
- Acquittances
- Commercial Sources
- Advertisements
- Dealers
- Retailers
- Salesperson
- Window Displaying, etc
- Public Sources
- Mass media and News Paper
- Radio and Television
- Consumer Rating Organizations
- Experiences Sources
- Demo
- Test Drives, etc
- Internet
The information collected greatly influences the decision of the consumer. Among these personal sources are the most influential ones.
If the consumer acquires enough information, then he may make a purchase decision immediately. However, if he fails to gather sufficient information, he may wait or suppress the need. Or repeat the procedure until he finds the valuable information.
Evaluation of Alternatives
The next step in the forgoing process is the evaluation of the alternatives. Here, the consumer has to choose between the researched Brands, Products and Services.

Consumers compare several Attributes, Parameters and Criteria while evaluating different alternatives. They assign weights to the factors or combination thereof to filter the alternatives.
Mostly, they use heuristics and make rational judgement during product selection.
It is to be noted that the evaluation process varies across consumers. It also differs in one consumer for different products.
Purchase Decision
After a detailed evaluation of the alternatives, the consumer makes the purchase decision. He will choose and buy the most suitable option that perfectly satisfies his need.

Here, he actually purchases the product from the platforms where it is available. Say, from Stores, E-commerce Platforms, Dealers, etc.
It is assumed that the consumer is convinced by the salesperson’s pitch and ready to bear the risk associated with the product. But, two factors may influence the buyer’s purchase decision that is:
- The unforeseen situational factors like – an economic breakdown, sudden price rise, etc.
- Other’s attitudes about the purchase decision. It can be in the form of positive or negative feedback.
Post Purchase Behaviour
It is the last but most essential stage of the process. In this, the post-purchase behaviour of the consumer is analyzed. It gives feedback to the marketer about the Success and Failure of the product.

Briefly, after consumption, whether the consumer is Satisfied or Dissatisfied. This stage broadly covers three major things:
- Customers Feedback
- Products Usage
- Products Disposal
Example
Lets us understand the complete process by taking a hypothetical example.
Step: 1 Need Recognition
Steve met with an accident while returning home from work and broke his Cell Phone. Consequently, he lost connectivity with his family and social circle. Hence, he decided to buy a new one.
Step: 2 Information Search
He searched the E-commerce Apps, Websites and visited the nearby Retail Outlets. His friends also recommended some brands and models.
Step: 3 Evaluation of Alternatives
After detailed research, Steve figured out that he wanted a 50mgpx Camera and 5g enabled phone. In addition, he was looking out for the vendors providing mobile covers for free.
Steve filtered three brands offering the above features in his budget. Two of them were selling the phone without any offer. In contrast, the third vendor offered two free mobile covers with the phone.
Step: 4 Purchase Decision
Steve purchased the phone from a third vendor satisfying all his needs.
Step: 5 Post Purchase Behaviour
He was satisfied with the phone and recommended the same to all his friends.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the consumer decision-making process is a problem-solving process. It starts with an unsatisfied need and ends with purchasing a suitable product.
It is essential from the marketing point of view. Because it enlightens them in manufacturing and delivering valuable products.
Comfort says
Great
Chidera says
I found it easy to understand and very helpful