Definition: Balanced Scorecard method was developed by Kaplan and Norton in 1996. They state that it is a fundamental performance management model used by the companies for enhancing the focus on their strategies and outcomes of the business, considering all the priority factors. In simple words, it is a performance matrix used to provide feedback on the company’s internal and external business functions and an overall view of the company’s organizational structure.
It also plays the role of a communication key between the personnel and the management of the company. However, it needs to be updated regularly. It has achieved popularity to such a range that it now governs the field of performance management, i.e., Kennerly and Bourne 2003. Nationally, B.P. Ford and Tesco are among the firms that use versions of the balanced scorecard approach to assure that, when executing performance, the elements that are urgently crucial to the business’s success are considered, which are originally specified as a strategic management system for broadcasting a company’s views and strategy. The balanced scorecard model has rapidly grown from a performance measurement structure into a performance management system. As a strategic management system. The balanced scorecard determines an integrated and systematic approach to management performance, associating vision and strategy with the association and personal objective in all areas of the company’s activities.
The balanced scorecard novelty and power as a performance management system is that it takes into consideration several different angles of the company’s performance, not just a positive financial perspective. The conventional view of financial performance is the primary measure of company performance that had adverse results for various companies. As it led them to rush short-term financial success that could be determined and overlook other aspects of “company’s health”. That mandatory to assure long-term growth, like customer expectations, personnel skills, and effective business processes. The use of a balanced scorecard brings an essential alteration to how companies view performance by concentrating on how managers build value. This alteration is based on creating balance in governing performance.
Content: Balanced Scorecard
Perspectives of Balance Scorecard
Kaplan and Norton 1996 brought in three perspectives to governing performance along with the conventional financial perspective. Thus, there are four perspectives of the balanced scorecard; they are as follows:
- Financial Perspective – Financial growth and prosperity.
- Customer perspective -The customer value proposition.
- Operational perspective – Internal processes and systems.
- Innovation and learning perspective -The human offering by way of knowledge and skills.
With the vision and strategy at the centre, this stimulates the balanced scorecard as a strategic and performance management system, broadcasting a company’s targets into specific goals within each perspective as shown in the figure below:
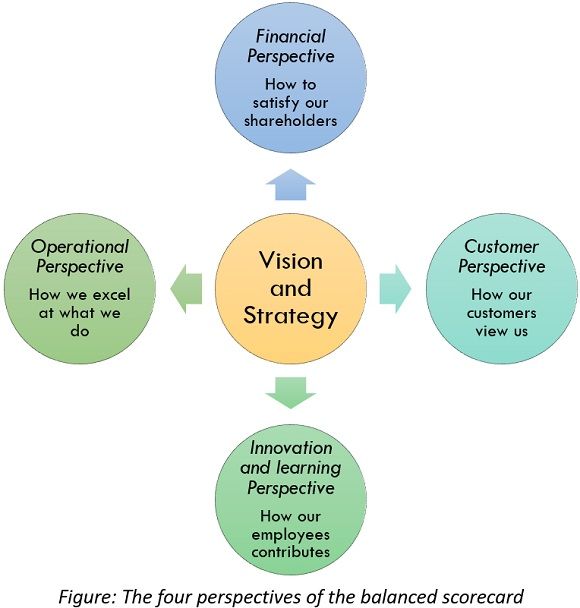
Aims are described as strategic targets at the top level of a company, which are then interpreted into appropriate objectives at the lower levels. The balanced scorecard works in conduct by either designating responsibility to a suitable functional area of the company (e.g., production or sales) or designating responsibility for achieving specific targets to a team. Cascading targets generally means that department or team targets are further interpreted into convenient objectives for humans, which then gives the basis for the performance review. Thus, as a performance management system, the balanced scorecard gives a framework that connects companies targets with individual objectives, and the performance appraisal gives the procedure for reviewing its own performance and progress. Inside larger companies, it is hard to find many balanced scorecards in operation at distinct levels, where aims and objectives have been fallen in a rush and combined with adjusting employee efforts and resources with the comprehensive corporate goals.
Creating the Balanced Scorecard Model
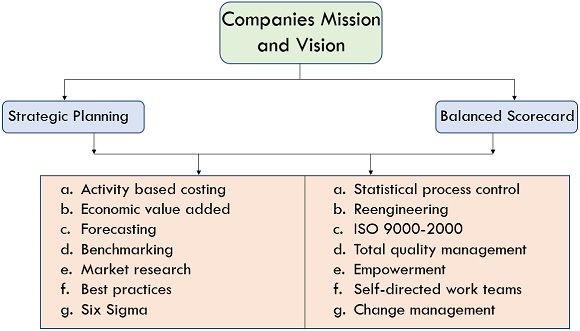
The first segment of the procedure is building a model for the scorecard. First, analyze and clarify strategies; this generally obligates a few arguments and discussions to manage immense disagreements. The next step is to agree on what competence is required within the company to chase the strategy. The final step of developing a model for the balanced scorecard is creating the actual model. This is where an understandable diagram that indicates how the business works- a simple example:
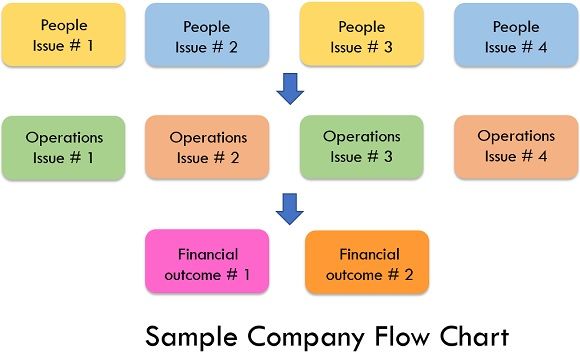
A balanced scorecard process aids the company by measuring performance for repeatedly developing processes and redefining actions to create a big picture, as illustrated below:
A balanced scorecard standard process for management to evaluate business conducts have severe restraints. Companies should not be determined merely using financial data; they must be determined according to whether or not they keep going and performing according to strategy. One modern methodology is the balanced scorecard, which works with financial data, operational measures, consumer satisfaction, internal procedures and the company’s innovation and enhancement actions. Consumer attention tends to fall into four categories:
- Time
- Performance and service
- Quality
- Cost
Internal measures must come from business processes that have a great impact on the consumer satisfaction cycle, time, quality, and personnel skills and productivity. The company must also identify critical core capabilities and try to promise market leadership. Innovation can be determined by an adjustment in value (shareholder value, percentage and value of sales from products less than “y” years old, employee value). Regardless of the modern method of performance appraisal occupied by a company performance feedback can be made more efficient by:
- Feedback of those being assessed must be unknown and combine into a collection.
- Rates must only figure-out personnel behaviour that they become aware of, which they have accomplished at the beginning.
- Rates must draw orientation and training to do the assessments.
- Receiver must receive navigation on how to clarify the feedback.
Conclusion
A balanced scorecard is a well-known strategic management approach developed in the early 1990s by Dr Robert Kaplan and David Norton. It is a measurement and management system that facilitates companies to simplify their vision and strategy and change them into actions. Its aim is to join business performance to companies’ strategy by calculating results in four areas, i.e., financial performance, internal business processes, customer knowledge and learning and growth.
Leave a Reply