Definition: Departmentation implies an organizing process involving the horizontal division of activities and personnel into homogeneous workable units known as Departments/Divisions.
It involves the organization of a large enterprise into smaller administrative units at all levels. It is performed to facilitate smooth functioning within the organization.
Moreover, the departments are further divided to form sub-division to achieve specialization. The basis of differentiation is the similarity, speciality or contiguous nature of activities.
It is one of the essential tasks while structuring the organization. This is because, it directly impacts the three significant elements such as:
- Efficiency
- Economy
- Profitability
When organizations grow, they become complex and large in size. Simultaneously, the number of subordinates under one superior also increases. Thus, it becomes difficult to manage, which restricts their growth.
Post-departmentation, superiors need to manage the optimum number of employees and related tasks. As a result, the productivity of the department and the entire organization increases.
Basically, it enables enterprises to group a manageable number of tasks and employees in a single unit. So that, each unit will work to the best of its capability and produce better results.
The divisionalization takes place in three stages:
- Primary Departmentation – Core function into basic activities
- Intermediate Departmentation – Departments at the middle level
- Ultimate Departmentation – Departments at lower levels
A skilled expert heads each department, called a Departmental Head or Manager. He is liable for the performance and contribution of his department.
Content: Departmentation
- Need and Significance
- Basis or Types
- Importance of Departmentation
- Factors
- Advantages
- Disadvantages/Problems
- Process of Departmentation
- Example
- Bottom Line
Need and Significance
As the organizations grow, it expands horizontally and vertically. Along with the organization, there is equal growth in the number of Processes, Functions and Employees. Therefore, the organizational structure becomes complex and hard to manage.
Moreover, any superior can only manage a definite number of employees under their span. Hence, it triggers the need for departmentalization while designing the organizational structure.
Furthermore, the points given below explain the need for departmentation in brief:
- Long-term Goals: To achieve long-term goals, a systemized working of the enterprise is essential. For this, thoughtful departmentation is necessary, which can contribute to achieving organizational objectives.
- Effective Management: Management is an essential part of the organization. Organizations can attain effective management by grouping tasks and deciding spans.
- Autonomy: Employees get clarity about their responsibilities by dividing activities and tasks. Also, they get the required authority and autonomy to perform as expected.
- Review and Rewards: Reviewing and analyzing employee performance becomes easy through departmentation. Thus, recognizing the best performers and rewarding them becomes easy.
Choosing Basis or Types for Departmentation
Organizations differ in Nature, Type and Size. Deciding the basis of departmentation is a difficult task. So, they can review some pre-defined types of departmentation and choose the most suitable one.
The most commonly used types of departmentation are as follows:
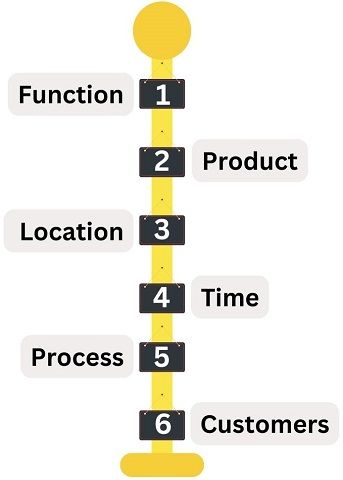
- Functional Departmentation: Here, the categorization takes place based on different management functions. For Example, Marketing, Finance, HR and Sales.
- Product Departmentation: In this type of departmentation, closely related products are grouped. For Example, Separate departments for Footwear, Clothing and Sports.
- Geographic Location Departmentation: The organization with dispersed activities can group their activities at the place of origin. For Example, the company’s Customer Care departments are often located in different cities.
- Time Departmentation: When the work is carried out in shifts, time departmentation is helpful. For Example, Working in shifts is quite common in MNCs. In general, there are Morning, Evening and Night shifts.
- Process Departmentation: In this form of departmentalization, the division occurs based on the manufacturing process. For Example, Developing various parts in different departments and then assembling them.
- Customers Departmentation: Here, the organizations create divisions based on the types of target customers. For Example, The Wholesale, Retail or Export Divisions in the garment manufacturing industry.
Importance of Departmentation
Divisionalisation is vital for organizations in the following ways:

- Identifying Bottlenecks: Grouping gives a crystal-clear picture of the organization’s health. In addition, it helps identify the bottlenecks (if any) in the structure or processes.
- Specialization: It gives an advantage of managerial specialization. The appointed department manager or head is a specialist in his respective field. His expertise and experience aid in the enhanced performance of his department.
- Coordination: By creating divisions, the managers can eliminate unnecessary confusion and latency of work. For this reason, it brings effectiveness in organization-wide communication, control and coordination.
- Workable Units: The segregation of similar types of tasks enables organizations to form workable units. These units are easy to manage in respect of – Cost, Expenses, Operations and Productivity.
- Accountability: During the process of departmentation, the roles and responsibilities are well-defined. It makes personnel accountable for assigned work and responsibilities.
- Expansion: The enterprises that have expansion plans get benefitted from Divisionalisation. As, it helps them in creating a uniform structure and standardization of processes.
Factors
Enterprises must consider the following factors during and before the process of departmentation:
- Costing
- Functions
- Degree of Control
- Interdependence
- Personnel Factors
- Expertise
- Nature & Type of Work
Advantages
The advantages of departmentalization in the enterprise are as follows:
- Clear division of activities, which enables specialization of work.
- The autonomy of work to employees enables them to be more productive and efficient.
- The department heads, or managers skills get improved through departmentation.
- Managers can keenly evaluate the performance of each employee working in their department.
- The Top-level can get department-wise data for 360-degree performance analysis.
- Enterprises can maintain a skilled workforce. Also, they can identify non-performers and lay them off.
Disadvantages/Problems
Following are the disadvantages or problems that can occur during the departmentation process:
- Division of work into independent departments impacts the coordination between them.
- Firms face problems in organizing combined training and development programs.
- Each department ends up creating its own work culture. Consequently, firms can’t develop organization-wide uniform work culture.
- It is unsuitable for small enterprises as there are a manageable number of employees.
- The entire departmentation process is a cost for the company. In addition, setting up a new department involves many other expenses too.
- Delay in decisions due to an enlarged communication channel.
Process of Departmentation
Departmentation process may differ among organizations. But, the basic steps that one can follow are furnished below:
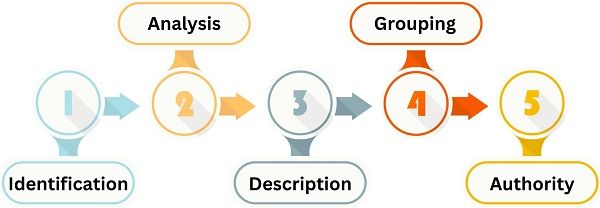
Step 1: Identification
The first step in the process is to identify the potential and relevant tasks and duties.
Step 2: Analysis
After that, conduct a thorough analysis of each identified task.
Step 3: Description
Post-analysis, the functions associated with the identified task are to be listed and described in detail.
Step 4: Grouping
Further, the grouping of the homogeneous functions takes place. Also, a head or departmental manager is appointed for each group.
Step 5: Authority & Responsibility
The last step is deciding the scope of authority and responsibility to the personnel working in respective departments.
Example
Today divisions or departments can be seen in every company, big or small. Here, we have taken examples of the two most common organizations, i.e. Banks and Colleges.
Banking Organization

The structure of a banking organization is very complex. This is because, it offers a wide variety of products and services. Generally, it uses Geographical Departmentation, and the branches are located in urban and rural areas. Further, divisions are created on a functional basis as follows:
- Accounting/Finance
- Administrative/Clerical
- Credit/Lending
- Customer Service
- Enterprise Services/Facilities Management
- Human Resources
- Information Technology
- Investment Banking & Markets
- Legal
- Marketing
- Operations
- Personal Banking
- Project Management/Analysis
- Relationship Management
- Risk/Compliance/Audit
- Sales
College
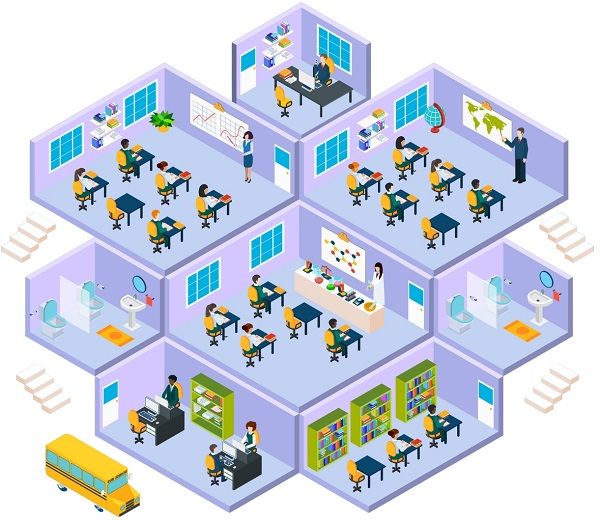

Another organization huge in the structure are Colleges. There is a large number of employees and students in a College. Thus, various departments are created for the smooth functioning of the organization, such as:
- Admin Department
- Accounts Department
- HR Department
- Placement Department
- Subjective Departments (Commerce, IT, Science, etc.)
- Housekeeping Department
- Cultural Activities Department
- Sports Department
- Counselling & Orientation Department
Bottom Line
It refers to the organizing process of determining the structure of how operations are carried out. The undertaking’s operations must be split into several parts to ensure smooth working and achieving long-term goals. But, it must be done in a planned manner to ensure inter-departmental co-ordination.
Leave a Reply