Definition: Value Analysis is a combination of creative and analytical techniques, especially for cost minimization and prevention in an innovative way. Moreover, it aims to find the best method to improve the product’s value, service or process without sacrificing its worth and functions.
 It is a problem-solving method which identifies and eliminates unnecessary costs. These costs don’t add value to products. Instead, they make them expensive.
It is a problem-solving method which identifies and eliminates unnecessary costs. These costs don’t add value to products. Instead, they make them expensive.
It is vital in all the branches of an enterprise like:
- Engineering
- Manufacturing
- Procurement
- Marketing
- Management
Analysts try to find unique solutions for critical problems. By doing so, they can fulfil the customer’s requirements at reduced prices.
It combines techniques to discover alternative ways to accomplish the desired goals.
Functions play a significant role in value analysis. Analysts focus on functions to improve the current ability towards expected. Therefore, companies apply some recognized techniques to identify product functions.
Organizations conduct this analysis to create and keep creating value for their customers. To reduce overall cost company conducts a systematic review of Production, Purchase and Design components.
Therefore, they appoint a separate team of knowledgeable personnel for the same. This team uses a combination of several techniques to minimize the cost.
Content: Value Analysis
- Objectives
- Example
- What is Value?
- What is Function?
- When to do Value Analysis?
- Steps
- Value Analysis vs Value Engineering
- Final Words
Objectives of value analysis
The main objective of the value analysis is to cut costs without sacrificing quality. Also, it seeks improvement in the overall functionality of a product as a whole.
The other objectives behind conducting a value analysis are as follows:
- It is conducted when companies want to simplify their products and processes.
- It helps in resolving critical problems, increases efficiency and promotes innovation.
- It contributes to the value-addition process by constantly focusing on design and service.
- Provides a structure with cost-saving initiatives, risk reduction and continuous improvements.
This strategy, when applied to products, facilitates the systematic application of:
- Enhanced Methods
- Alternative Materials
- Newer Processes
- Competences of Suppliers
In the case of services, it is concerned with optimizing service delivery.
Value Analysis Example
Suppose, a car manufacturer observes a reduced sale of a particular modal. It can be a consequence of the following:
- Increased Competition
- New Launch in the same segment
- Hike in price of the raw materials, etc.
Therefore, they will carry out a value analysis of the product. The in-depth review will help them in finding optimized solutions for the problems. Post analysis, the company reduced the car’s cost without hampering the product’s quality.
This way, the manufacturer can sell the same car at reduced prices. Thereby, eliminating competition and boosting sales.
What is Value?
It is simply the utility and worth that the product offers to the customers. However, different customers interpret it in different ways. We can understand it as follows:
- Worth of Things
- Degree of Importance
- Product’s or Service’s Usefulness
- Products Functionality and Efficiency
Companies can identify the product’s value by analyzing its performance and cost. Moreover, they can increase their product value by improving performance and decreasing costs.
In general, four types of economic values exist:
- Cost value
- Exchange value
- Usage value
- Esteem value
We can express it as the ratio of Function and Cost or Utility and Cost.
Value = Function/Cost or Utility/Cost
What is Function?
A function is basically the usefulness of the product desired by the customer. In addition, it is the intent or purpose behind creating a specific product. And it is the thing for which the customer actually pays.
Functional Analysis is part of the value analysis that critically analyses a product’s functionality.
The function is further classified into two categories:
- Necessary Functions
- Unnecessary Functions
Out of the above two, companies can’t change necessary functions. In contrast, they can make alterations to the necessary functions. Companies can minimize costs by enhancing, modifying or eliminating unnecessary functions.
When to do Value Analysis?
Companies conduct value analysis in the following circumstances:
- A particular product or product line registers a decline in sales.
- The cost of the product is higher than that of its rivals.
- The rise in raw materials price is not proportionate with the production.
- Introduction of new and better designs in the market.
- The cost of manufacturing is disproportionate to manufacturing cost.
- The negative trend of rate of return.
- Companies in the ability to meet delivery commitments.
Steps
The systematic work plan of value analysis is divided into Six Steps as follows:
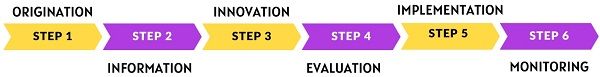
- Origination/Preparation
- Information
- Innovation and Creativity
- Evaluation
- Implementation
- Monitoring
Step: 1 Origination
It starts with the appointment of the value analysis team. The team must be sufficiently skilled and clear about the goal of conducting the analysis. Further, the team examines the product, service or process in detail.
Step: 2 Information
Post, project and team finalization, one needs to conduct a functional analysis. Here, the team determines the product’s functions, uses, features and components. In addition, they figure out the cost relevant to each function.
Step: 3 Innovation and Creativity
This is the stage where innovation and creativity peep in. Here, possible creative alternatives are created to replace the existing ones. This is done to optimize the functionalities. The basic idea is to find an alternative way to improve the value.
Step: 4 Evaluation
After exploring several alternatives, the analysts must evaluate each one thoroughly. Post evaluation, the most prominent ones are taken to the next step.
Step: 5 Implementation
The next step in the foregoing process is to choose and implement the most appropriate alternative. The analysts select the most appropriate method and put it into action.
Step: 6 Monitoring
The last step is to monitor the implemented alternative constantly. It helps in ensuring that the desired objectives are achieved or not.
Value Analysis vs Value Engineering
These terms are synonymous to each other and often used interchangeably. But, the difference lies in the time and the stage at which it is applied.
| Basis | Value Analysis | Value Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A disciplined approach that ensures cost minimization without hampering the quality | A systematic approach focused towards improving the value of the product |
| Application | Existing products | New products |
| Focus | Major focus is on problem-solving | Finding innovative ways to improve the product |
| Type of process | Remedial Process | Preventive process |
| Results | Improves performance | Increase value |
| Conducted by | Workers, Engineers and Sub-contractors | Product Design Team |
| Scope | Reduces overall cost | Reduces cost of production |
Final Words
It is a collection of methods, skills, and abilities to improve products by reducing wasteful expenses. Also, it enhances the features while preserving its performance.
Value Analysis has become an aptly used method for cost minimization. Its functional analysis part makes it different from other cost-reduction methods.
Leave a Reply