The strategy’s effectiveness and success will depend on how well it is executed. In organizations, top management ensures its implementation by exercising Strategic Control.
It is a specialized version of management control that handles issues and uncertainties. Managers give warning signals and determine the future course of action post-evaluation.
Managers evaluate and ensure the progress of the chosen strategy in the right direction. It tracks ongoing processes, measures results, detects deviations, and takes corrective actions. Moreover, they try to identify and fix the potential or existing loopholes in the strategic plan.
Managers ensure the effective alignment of inputs to generate desired output. They become progressive and move forward towards the achievement of strategic goals.
Strategic Control is like a report card that compares the standards with present performance. As a result, managers learn whether they are working on the right track or not. Moreover, they ensure the achievement of strategic objectives.
Strategic control helps detect potential deviations and the possible reasons behind them. After that, take necessary actions to rectify these deviations and keep the plan on track.
We can easily understand its purpose by answering two questions as follows:
Is the implementation of the strategy as planned?
Whether there is a need to change or alter the strategy?
It measures the overall performance of the organizations. Also, it studies the positive or negative impact of the internal and external factors affecting strategy.
Content: Strategic Control
- Level of Control
- Techniques or Types of Strategic Control
- Strategic Control Process
- Importance/Benefits of Strategic Control
- Challenges or Problems
- Strategic Control vs. Operational Control
- Final Words
Level of Control
Managers at different levels practice strategic control, but the degree of control differs across levels. In general, they measure performance at four basic levels:
- Corporate Level Managers (Chief Officers, Board of Directors, President, Vice President, etc.)
- Divisional Level Managers (Marketing Manager, Finance Manager, Sales Manager, etc.)
- Functional Level Managers (Production Manager, Operations Manager, Accounts Manager, etc.)
- First Level Managers (Floor Manager, Supervisor, Store Manager, etc.)
Techniques or Types of Strategic Control
Below are the basic types of strategic control or techniques that managers use to practice strategic control. These techniques help managers to put things on the right track. In addition, it allows organizations to sail through uncertainties and complex environments.
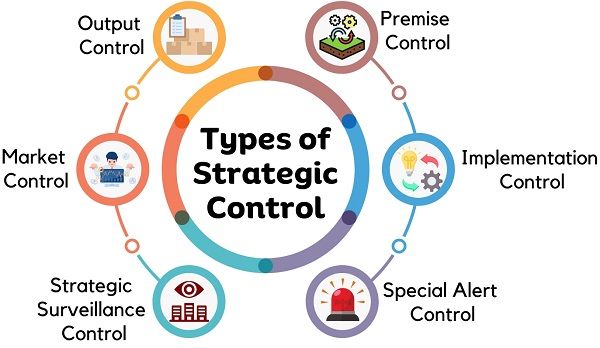
Premise Control
Premises are the assumptions about the internal and external environment during strategic planning. Over a while, these premises may become invalid. This is because, changes can happen to these factors that may affect the strategy.
Premise control is a tool that checks the validity of the premises during controlling. If any premise is invalid, then managers make necessary changes in the strategy. Moreover, they can even make changes to the premise itself.
It monitors two types of factors:
- Environment Factors (Social, Economic, Technological and Political Factors)
- Industry Factors (Competition, Suppliers and Substitutes)
Implementation Control
Implementation of strategies takes place by disintegrating them into incremental sequential steps. Incremental control tracks the progress of these steps.
Managers try to identify the issues arising during the implementation of these steps. Moreover, they make necessary alterations in the overall strategy if required.
The two primary forms of implementation control are as follows:
- Monitoring Strategic Thrusts
- Milestone Review
Special Alert Control
Sometimes, managers need to reconsider the strategy quickly due to some unanticipated incident. It may be triggered by an event raised due to sudden changes in:
- Government Policies
- Industrial Disaster
- Natural Disaster
- Product Recall
- Competitor Acquisition
In such cases, managers need to review and alter the current strategies. Thus, it is a reactive process that creates a contingency strategy. Besides, there may even arise the need to create a separate crisis management team.
Strategic Surveillance Control
It is pretty evident from its name that the managers use this type of control for general monitoring. Managers monitor all those events that might impact the strategy. Consequently, managers can identify some unexpected information that can significantly affect the strategy.
General monitoring involves sourcing information from the following sources to get unanticipated information:
- Reading Newspaper
- Business Magazines
- Attending Meeting
- Trade Conferences, etc.
Market Control
It focuses mainly on the market performance of the organization. It involves comparing the organization with others based on the factors like ROI and Stock Prices.
Conducting this type of strategic control helps assess the organization’s financial aspect.
Output Control
It evaluates the expected and achieved output to measure the strategy’s progress. Managers assess whether the organization can achieve the desired outcome or not. If it differs from the strategy, find possible reasons and rectify them.
Strategic Control Process
The managers exercise strategic control by following four steps given below:
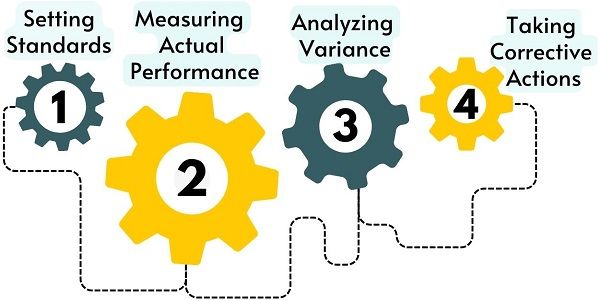
Step 1: Setting Performance Standards
The process begins with planning and setting realistic standards that are to be achieved. For this purpose, the managers must have clarity about the desired output. Besides, the standards should be flexible and must range between maximum and minimum.
Step 2: Measuring Actual Performance
The next step is measuring the work completed from the preset control standards. It helps managers to comprehend the existing situation. Consequently, managers can estimate the amount of work completed and still in progress.
Step 3: Analyzing Variance
The third step in the process is to compare the actual performance with standards. Majorly, it stresses two essential things, i.e., finding the variation and potential reasons behind it. However, the control process is terminated if no variations are found during the analysis.
Step 4: Taking Corrective Actions
Lastly, the managers take the necessary actions to clear deviations and keep the plan on track. In addition, they reset the unrealistic standards that are hard to achieve. Also, they revise the nonworkable objectives and strategies.
Importance/Benefits of Strategic Control
The following points explain the importance of strategic control. These are also the benefits of exercising control in the organization.
- It helps in the successful implementation of the strategy.
- Depicts the realistic picture of the actual progress of the strategy.
- Creates a base for new strategies and error-proofing the existing ones.
- It helps in verifying the validity of the strategic choice.
- It plays a vital role in creating and maintaining the quality of products and processes.
- It improves the effectiveness of the strategy and helps achieve strategic goals.
Challenges or Problems
Managers may face the challenges while implementing strategic control:
- Managers might land in conflicts while deciding on criteria for evaluation.
- The presented control reports may need to be corrected.
- The employees might be non-cooperative during the control process.
- Managers may possess a short-term view towards the strategy while it has been designed for the long term.
Strategic Control vs. Operational Control
| Basis | Strategic Control | Operational Control |
|---|---|---|
| Aim | Concerned about the progress and direction of the strategy | Efficient use of organizational resources |
| Focus | It only focuses on the correct and effective implementation of the chosen strategy | The major focus is on the routines and operations necessary to achieve organizational goals |
| Performed by | Managers belonging to the top-level exercise strategic control | Managers at the functional level perform it |
| Environment | It especially focuses on the external environment | Managers use it to control the internal environment only |
| Duration | Long-term | Short-term |
Final Words
Strategic control is a mechanism top-level managers use to track and control the execution of strategies. They make comparisons, check progress and highlight areas that need attention.
It is crucial for the corporate strategies to succeed. It also helps in taking actions such as continuation or discontinuation of strategy.
Leave a Reply