Definition: E-commerce or electronic commerce is an intangible business platform which enables the individuals, business entities and companies to sell their products or services and carry out various commercial activities, through an electronic network.
E-commerce has gained immense popularity among the customers who find it convenient to browse the products and services online instead of visiting a physical store.
Identifying this shift in customer’s buying behaviour, most of the sellers, including sole proprietors, corporates and other organizations are inclining towards e-commerce.
Content: E-commerce
E-commerce Business Models
E-commerce business models are designed by keeping in mind the major two parties involved in it. One is the service provider or seller, and the other is the consumer or the customer.
Let us now go through the different types of e-commerce business models:
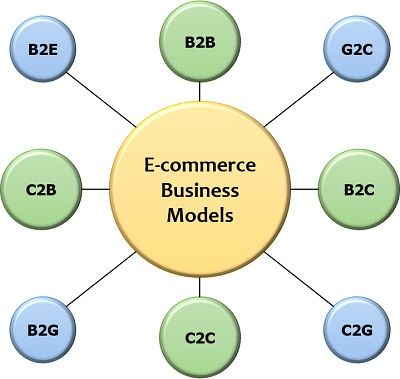
Business to Business (B2B)
In B2B e-commerce, the companies sell their products or services online to other business entities. Even the sharing of information among the organizations take place through Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
E.g. Wholesalers can contact prospective buyer firms to sell bulk goods on the website Indiamart.com.
Business to Customer (B2C)
The most common of all the e-commerce models is the B2C. It refers to the sale of goods or services by the business entities to the customers (individuals) over the internet.
E.g. Apparel companies sell their products to the consumers on Jabong.com.
Customer to Customer (C2C)
When a customer (any person) sells a product or service to another person or customer through an online medium, it is known as C2C e-commerce model.
E.g. A person sells his used car to another person on cardekho.com.
Customer to Business (C2B)
It is that e-business model where the customer or an individual serves the needs of business organizations and also determines the price of the product or service over the internet.
E.g. Content writers freelancing for large content writing firms or websites on freelancer.com.
Government to Citizen (G2C)
When the government releases any information or official notification or any other official communication for the individuals (i.e., the citizens of that particular country) through an online medium, it is termed as G2C model.
E.g. usajobs.gov discloses the latest job openings for the citizens of the USA.
Citizen to Government (C2G)
The online communication or exchange of information by the citizens with the government is called a C2G e-commerce model.
E.g. filling of income tax return on incometaxindia.gov.in
Business to Government (B2G)
The business organizations electronically provide services, goods or information to the government at some cost; this type of e-commerce is known as B2G.
E.g. Government openly invites business entities to fill tenders for multiple government projects at etenders.gov.in.
Business to Employees (B2E)
In a B2E e-commerce model, companies render services and even products to their employees using intranet technology.
E.g. Providing online credit services to the employees.
Types of E-commerce Business
There are multiple ways in which an e-commerce business operates, each of which has a distinct feature.
To know about each type of e-commerce business in detail, let us read below:

Online Store Front: A company can set up its retail website where it can exclusively showcase and sell its products.
E.g. Pepperfry.com is one of the biggest furniture retail stores in India which also have physically located stores in multiple cities.
Dropshipping: In the dropshipping form of e-commerce, the company does not maintain any stock. Instead, it alliances with a third party who manufactures and ships the product directly to the customer whenever the dropshipping merchant receives the order.
E.g. AliDropship.com which is a free dropshipping site of AliExpress.
Affiliate E-commerce: In affiliate e-commerce, marketers invest their efforts, time and resources in marketing the merchant’s products or services on an online platform.
E.g. The Wirecutter is an affiliate platform which reviews consumer durables and electronic gadgets.
Membership/Subscription: Membership promotes the re-purchasing of the products or services again and again by the customers through periodic (weekly, monthly, etc.) subscription options at a discounted price.
E.g. Amazon.com has a subscription option.
E-Marketplace: An e-marketplace is very similar to any other physically located departmental store; the only difference is that it operates online.
E.g. Walmart is a renowned marketplace selling a variety of products at high discounts.
E-services: E-commerce is not just limited to products, e-services such as online education, counselling, entertainment, electronic payments, training, travel bookings, etc. have also gained a lot of popularity.
E.g. Paytm is widely used to make online payments whenever required.
Categories of E-commerce Companies
Based on the existence and location of a business organization, the companies are classified under the following two categories:
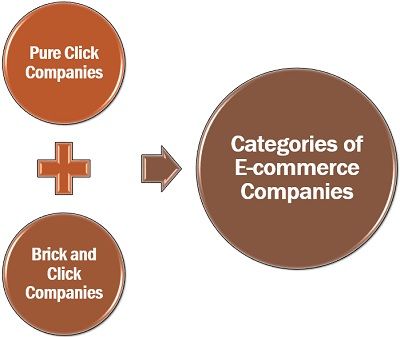
Pure Click Companies: The companies which have an online presence rather than any physical location functional through websites are termed as legitimate click companies.
E.g. magicbricks.com
Brick and Click Companies: The business entities which have a physical presence along with an online existence are known as brick and click companies.
It includes not only those companies which sell products online but also those firms which have an online portal or website to give information about the entity.
E.g. bigbazaar.com
Benefits of E-commerce
Today everything is digitalized, and so is trade and commerce. We cannot imagine a world without the internet in the present scenario.
E-commerce has simplified commercial activities to a great extent by providing global exposure to business organizations.
Following are the various advantages of e-commerce to the business entities:
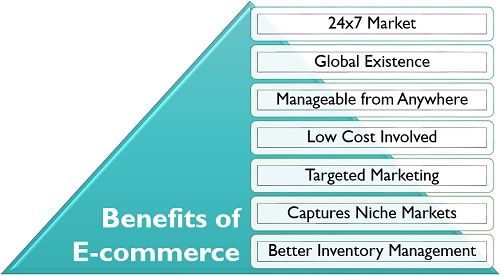
- 24×7 Market: An online market is always open to conveniently shop and explore, for the customers who have access to the internet.
- Global Existence: The companies can reach out to the consumers spread across the globe at one stretch because of e-commerce.
- Manageable from Anywhere: A person can choose to operate the e-commerce business from anywhere in the world. It is possible with the help of a laptop and proper internet connectivity.
- Low Cost Involved: The cost of operating an online store is far less than that of managing a physical outlet, saving the expenses on labour and maintenance of the store.
- Targeted Marketing: The online market provides scope for focussing the prospective customers and developing an interpersonal relationship with them to provide a better service.
- Captures Niche Markets: Niche markets refer to catering a particular section of the society or focusing on an exclusive product feature to outstand the standard products and companies. Developing this type of market requires a mass customer base which is possible only through e-commerce.
- Better Inventory Management: The excessive use of electronic media to carry out business activities, facilitate a better and organized inventory management with the help of software like SAP and other advanced inventory management tools.
Challenges Faced in E-commerce
E-commerce looks quite promising and compact form of business, but it is not that easy.
The company may face the following difficulties while setting up an online market for its products or services:

- Intangibility: The online marketplace is intangible, and the products cannot be touched or examined before purchasing.
- Massive Competition: More and more companies are entering the e-commerce market to sell their products globally, thus increasing the level of competition.
- Technical Issues: Technology is the base of e-commerce, and lack of technical knowledge is the primary reason for failure. Thus, it involves a considerable cost to outsource such activities.
- 24X7 Internet Access: It is necessary to have uninterrupted internet connectivity for the seller to process the orders, which is challenging to have in remote areas.
- Requires Patience: The companies selling products or services online need to keep patience and wait for the desired response since it takes time to gain attention and visibility from customers in e-commerce.
- Lack of Trust: Due to the intangible existence of e-commerce business, there is a lack of trust in shopping and making online payments among the customers.
E-commerce is a fruitful opportunity for small business organizations and individual merchants who lack sufficient resources but plan to expand their business at a minimal cost.
However, it requires basic technical and internet operating knowledge to carry out online commercial activities.
Nowadays, cybercrime is a significant concern in e-commerce, creating issues like identity theft, e-mail bomb, payment frauds, credit card theft, etc. due to which some people are hesitant towards online shopping.
Akhil says
Wow, that was an amazing article about e-commerces