Definition: The wheel of retailing refers to a hypothesis, which depicts the life cycle of a retail organization. It starts as a discount retail business to attract price-sensitive consumers and then gradually converts into a luxury brand store or departmental store to cater to high-end consumers.
Prof. Malcolm Perrine McNair proposed this theory in the year 1931. He emphasized on the evolution of retailing, where a retail organization starts up by providing low price, basic product features and minimal services at a little profit margin. Then it slowly becomes a brand which offers a wide range of products, high price, better services and multiple other facilities at a considerable profit margin.
Content: Wheel of Retailing
Wheel of Retailing Theory
The wheel of retailing theory explains the life cycle of a retail organization and the different levels through which it passes. The life of a business is divided into four quadrilaterals, each of which are discussed in detail below:
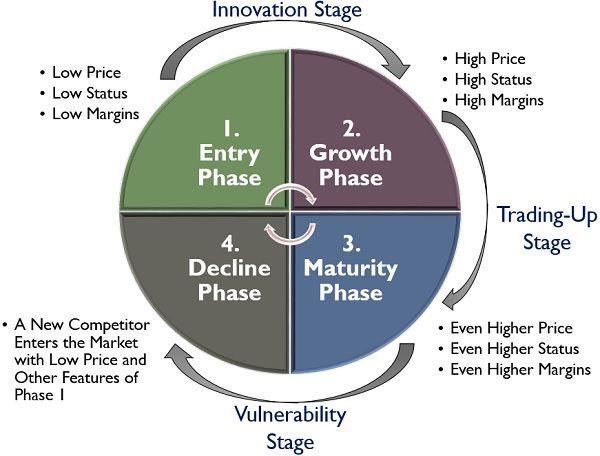
Quad 1: Entry
The initial phase of the wheel of retailing is when the organization enters the market with limited products at a very reasonable price, keeping a low margin.
Since the business entity still needs to build its reputation at this stage, and the consumers are not very much aware of the organization.
Moreover, the organization provides minimal services and the infrastructure used is usually low cost and temporary. Thus, at this level, the company tries to penetrate the market with a low price strategy.
Quad 2: Growth
With the low price strategy, the organization can build its reputation in the market. At this level, the retailer can adopt growth strategies like slightly hiking the price of the products, widening the product category, upgrading the store and providing additional services.
This is the phase where the organization can keep a better margin since more and more consumers prefer to buy the products. Now, the retailer concentrates on the other aspects of competitiveness, rather than price.
Quad 3: Maturity
At this phase, the organization has gained a high reputation and established itself as a well-known business entity. Now, the business is unable to acquire more new consumers, also the customer turnover increases.
Therefore, the retailer’s main area of concern at the maturity level is customer loyalty and retention by enhancing their satisfaction level.
Quad 4: Decline
This is the level where the business starts going down. The other firms enter the market with their low-priced competitive products, to drag customer’s attention. In no time, the competitor’s products take over the market, and the organization tend to lose its customers.
Thus, the organization now plans to revive the business through divestment, merger, acquisition and other strategic alliance.
Wheel of Retailing Strategies
The actions of the retailer or the strategies implemented depend upon the business requirements and stages. The various stages and the strategies adopted to improve the business performance of the organization can be classified as follows:
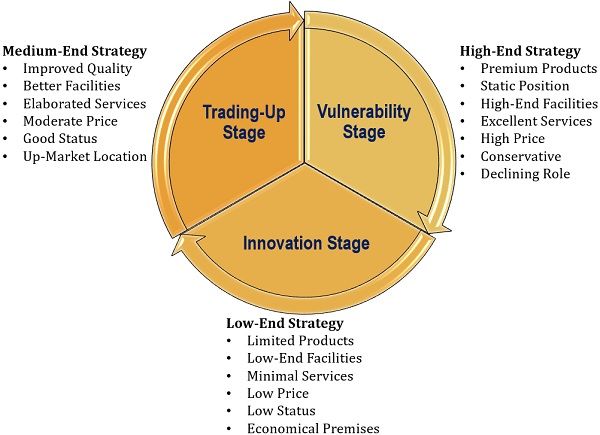
Low-End Strategy at Innovation Stage
The innovation stage is the one where a product is introduced to the customers. At this level, the strategies are also framed for the growth of the business.
It is usually a trial or experimental phase where the retailer adopts low-end strategies to test the products. The organization tries to keep the things simple and attract the consumers through lowest price factor.
Following are the various low-end strategies which lead to the innovation stage:
- Initially, a limited variety of products is introduced in the market.
- Only the essential facilities are provided at the entry stage.
- The services provided are also limited and nothing extraordinary.
- The price of the product is set at the lowest to gain consumer attention.
- The organization’s reputation or status is not very high since the business is at an initial stage.
- The location selected for the store is usually a low-cost premise.
Medium-End Strategy at Trading-Up Stage
The trading-up stage is the next phase where the organization has established its name in the market and develops its business model.
In this phase, the retailer usually pools in more investment into the business. The medium-end strategies which result in this stage are as follows:
- Selling of better and improved range of products.
- The organization also provides various facilities like product exchange, home delivery, online shopping, etc.
- It also provides additional services like customer support, demo, return, etc.
- Even the prices of the initial products are raised moderately, to increase profit margin.
- The organization gains goodwill in the market and builds its reputation.
- The business location is changed to premises located in the prime market place.
High-End Strategy at Vulnerability Stage
At the vulnerability stage, the organization seems to be overburdened by the interest liability on borrowed funds for business growth. Moreover, the return on investment is quite low or starts declining at this phase.
The high-end strategies leading to the vulnerability stage are discussed below:
- The retailer sells only superior products at this stage.
- The organization holds a high position, reputation and status in the market.
- Premium facilities are provided to meet the needs of high-end consumers.
- Special services like five years warranty are also provided.
- The products are priced very high.
- The organization is cautious and triggers attention towards the preservation of its status.
- Gradually, the business starts declining as the new entrants take up the market.
It is a cycle which keeps ongoing since, at vulnerability stage, the organization put in all the efforts to restart with the innovation stage.
Wheel of Retailing Example
Let us take a fictitious case of ABC and Co., an automobile company. The company was established in the year 2001. Given below is the wheel of retailing of the company:
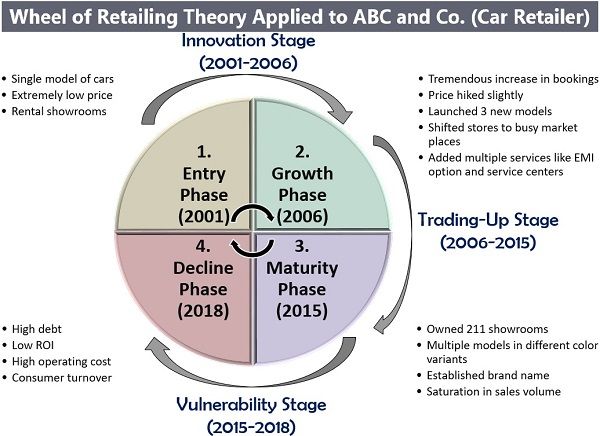
Entry Stage
ABC and Co. entered the market in the year 2001 with a single model of cars which was priced extremely low to target the middle class and the price-sensitive consumer base. It operated from various rental showrooms located in the outskirts of the cities.
Growth Stage
The company was able to gain recognition in the market for affordable cars by the year 2006. The consumers showed interest, and the booking for cars increased tremendously.
The retailer brand now slightly hiked up the price of its initial model and also launched three more models with new features.
Even the stores were shifted to busy market places in various cities for better exposure. Also, activities like credit purchase, service centres, customer relationship management, etc. were introduced.
Maturity Stage
By the year 2015, the company had almost 211 showrooms in the country selling out multiple models of cars in different colour variants. By this time, the company is unable to attract new customers and faces a saturation point in business.
Decline Stage
The company’s sale starts to fall by the year 2018, and the debt on it is quite high. Thus, decreasing the return on investment on the one hand, and increasing the liabilities and operating cost on the other side.
Now, in such a situation, ABC and Co. can either shut down its non-performing showrooms or can come up with an innovative idea which can revive the company’s position.
Limitations
Many scholars criticized the wheel of retailing on the grounds of the following shortcomings:
- Only emphasizes on Price Factor: The biggest drawback of the retailing wheel theory is that it considers the price of a product as the primary factor to enter the market.
- Inapplicable to All Organizations: Moreover, this hypothesis is not applicable in the case of the speciality stores and luxury products launched by new entrants. Their purpose is to target consumers through product features rather than its price.
The wheel of retailing is considered to be of great significance in retail management. However, it overlooks the other aspects of the business like product quality, market conditions, business environment, etc.
Also, the consumers today are brand conscious, more aware and knowledgeable; thus, the application of the wheel of retailing becomes quite vague in the present scenario.
mpc course says
Great article. It is very useful and informative. I got some good ideas about this topic. Thanks for sharing this post.